![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the use of a CT? |
1. Good to visualize a fracture 2. Limited soft tissue information |
|
|
What is usually the exam of choice for spinal cord imaging? |
1. MRI--- good bone and soft tissue visualization |
|
|
What is the urgency of spinal cord compression? |
1. Surgical emergency--- 6mm or less |
|
|
What are the ssx of spinal cord compression? |
1. Progressive radiculopathy 2. Back pain 3. Shuffling gait 4. Visible atrophy |
|
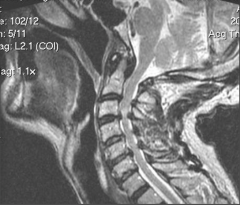
|
1. Spinal cord compression 2. Reduced A/P diameter |
|
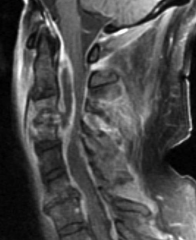
|
1. Epidural abscess |
|
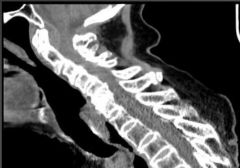
|
1. Epidural hematoma |
|
|
What is cauda equina syndrome? |
1. Compression of cauda equina nerve roots 2. Ssx can be similar to spinal cord compression 3. No specific measurement warrants surgery |
|
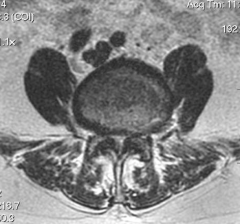
|
1. Cauda equina syndrome |
|
|
What is the urgency of cauda equina syndrome? |
1. MRI emergency |
|
|
What are the ssx of cauda equina syndrome? |
1. Urinary incontinence/retention 2. Fecal incontinence 3. Saddle anesthesia 4. Lower extremity paralysis |
|
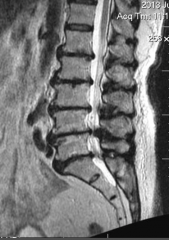
|
1. Cauda equina syndrome |
|
|
What causes neurogenic claudication? |
1. Central canal spinal stenosis 2. As central canal caliber decreases, intrathecal pressure at that site increases 3. High pressure collapses veins supplying nerve roots--- ischemia, pain, etc. |
|
|
How do you separate neurogenic claudication from regula claudication? |
1. Neurogenic patient gets to symptomatic relief from ambulation 2. Must sit or lie down to get relief |
|
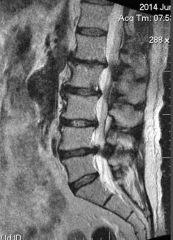
|
1. Neurogenic claudication |
|
|
What are the MCC of brachial plexus injury? What are the risks? |
1. Contact sports--- stingers 2. Risk--- nerve rootlet avulsion, nerve root sheath can tear, muscle can denervate and atrophy |
|
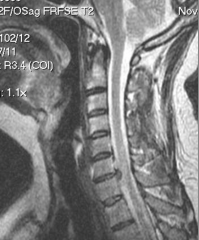
|
1. Cervical nerve impingement---- |
|
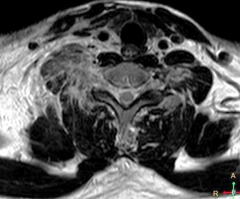
|
1. Nerve rootlet avulsion |
|
|
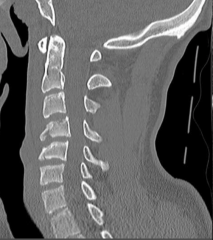
What is a flexion tear drop fracture? |
1. Fractures of the anterior/inferior portion of the vetrebra 2. Compresses the anterior of the vertebra and adjacent disc |
|
|
1. Flexion tear drop fracture |
|
|
What is an intramedullary mass? |
1. Something within the spinal cord |
|
|
What is an intradural extramedullary mass? |
1. Inside the dura, outside the spinal cord |
|
|
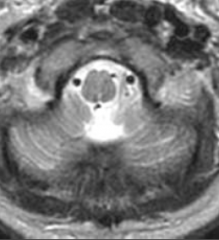
What is a syrinx? |
1. Intramedullary mass--- hydromyelia, syringomyelia 2. Most are congenital |
|
|
With what malformation is a syrinx associated? |
1. Chiari I |
|
|
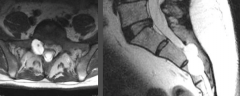
What is a Tarlov cyst? |
1. Extradural 2. Contain nerve--- associated with dorsal nerve root 3. Most in sacral area |
|
|
What are the ssx of a Tarlov cyst? |
1. Pain 2. Radiculopathy |
|
|
What is a myelomeningocele? |
1. Nerve tissue and meninges exiting bony defect |
|
|
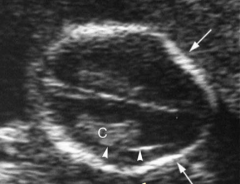
How do you detect spina bifida? |
1. Lemon sign on OB ultrasound 2. Banana sign " |
|
|
1. Syrinx |
|
|
1. Tarlov cyst |
|
|
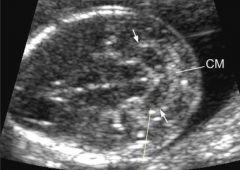
1. Lemon sign--- spina bifida 2. Flattened or concave contour of right and left frontal areas of skull |
|
|
1. Banana sign--- spina bifida 2. Anterior curving or flattening of the cerebellum with loss of cisterna magna |
|
|
What is acute transverse myelitis? |
1. Post-infectious complication--- viral 2. Affects white and gray matter 3. Ssx=pain, paresthesia, loss/dysfunction in motor, autonomic, and sensory |
|
|
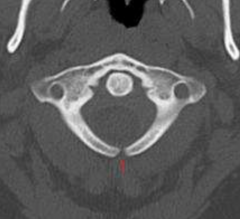
1. Spina bifida occulta |
|
|
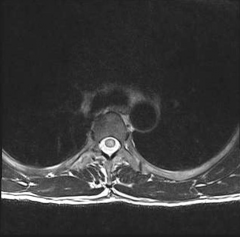
1. Transverse myelitis |
|
|
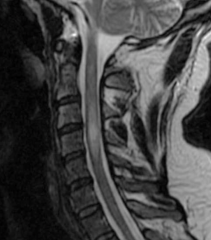
How is MS best visualized? |
1. MRI--- T2 intense plaques in white matter |
|
|
1. MS--- plaques |

