![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cnidaria |
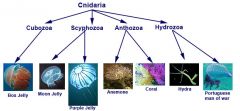
Phylum including corals, sea anemones, and jellyfish |
|
|
Mesoglea |
The jelly stuff between the epidermis and gastrodermis |
|
|
Gastroderm |
Layer of cells lining the gastrovascular cavity that secrete enzymes ti break up food particles |
|
|
Gastrovascular Cavity |
Central cavity that takes in food and expels waste |
|
|
Basal Disc |
The point at which a polyp forms its sessile connection to a hard surface like a rock |
|
|
Epidermis |
The outer most layer of cells that help capture food and secrete mucus |
|
|
Polyp |

Cnidarians that form sessile attachments and have tentacles and mouth that face up EX: sea anemone |
|
|
Medusa |

Cnidarian that has a mouth and tentacles that face downwards. They are able to swim by pulsing through the water EX: jellyfish |
|
|
Radial Symmetry |

Symmetry in a circular fashion. Allows the organism to capture food in 360 degrees |
|
|
Cnidocytes |
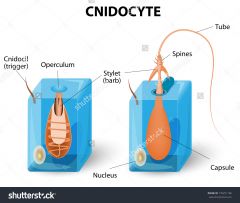
Stinging cells along the tentacles |
|
|
Nematocyst |
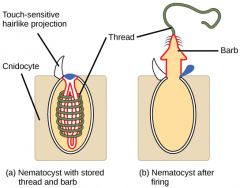
Long, coiled, tubular harpoon thing that is inverted inside the cnidocytes that fires when it comes into contact with prey then releases venom into the animals bloodstream |
|
|
Cnidocil |
The trigger on the cnidocyte that senses prey and tells thbe nematocyst to fire |
|
|
Plankton |

An organism that cannot swim against the current |
|
|
Nerve Net |
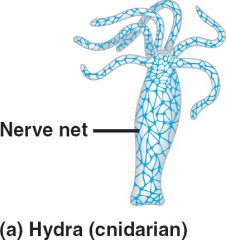
Thin fibers running along throughout the cnidarian forming a network that responds to mechanical and chemical stimulus |
|
|
Mechanoreception |
The ability for cnidarians to respond to the stimulus of touch or pressure. |
|
|
Chemoreception |
The ability of cnidarians to respond to chemical stimuli |
|
|
Photoreception |
The cnidarians ability to react to changes in lighting |
|
|
Sexual Reproduction |
When the sperm meets the eggs of the female cnidarian. Some cnidarians are able to produce both themselves. |
|
|
Fertilization |
When the sperm and egg successfully join and a new organism starts growing |
|
|
Larva |
New baby cnidarians |
|
|
Cilia |
small hairlike structures that move in a beating pattern that move the larva along |
|
|
Asexual Reproduction |
Reproduction without involving eggs or sperm |
|
|
Budding |

Growing a new identical organism of an already existing one |
|
|
Regenration |
The ability for a cnidarian to grow back damaged or missing cells. They can even regrow into an entirely new organism |
|
|
Hydrozoa |

Ex: Hydra, Obelia, Portuguese Man of War |
|
|
Scyphozoa |

Ex: Moon jellies |
|
|
Anthozoa |

Ex: Coral, Sea Anemone |

