![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cnidaria |
A phylum including corals, sea anemones, and jellyfish. |
|
|
Ectoderm/ Epidermis |
The outer layer in cnidarians. These cells help capture food and secrete mucus. |
|
|
Endoderm |
The inner layer of cells in cnidarians. Cells in this layer produce digestive enzymes and break up food particles. |
|
|
Mesoglea |
The jellylike material between the epidermis and endoderm. |
|
|
Gastrovascular cavity |
A central cavity that extends into hollow tentacles. |
|
|
Polyp |

A form with the body shaped like a hollow cylinder or a bag that opens and closes at the top |
|
|
Medusa |

A form with the body shaped like an umbrella with the mouth and tentacles facing down. They are not sessile and swim freely in the open ocean. |
|
|
Radial Symmetry |
The bodies extending out like a cylinder from a central axis. Corals, jellyfish, and sea anemones have this form of symmetry. |
|
|
cnidocytes |
stinging cells, each containing a nematocyst |
|
|
nematocyst |
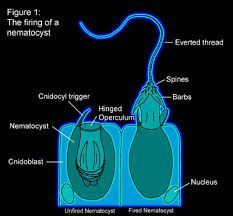
A coiled, tubular, harpoon like structure that allows cnidocytes to sting. They inject venom into the prey. |
|
|
Hydrostatic skeleton |
the water pressure that supports soft tissues |
|
|
Enzymes |
Digestive chemicals that break chunks of food down into tiny particles |
|
|
Plankton |
A classification of organisms that cannot swim against a current. |
|
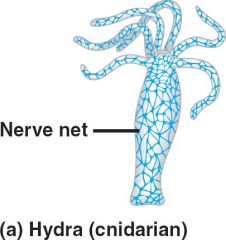
Nerve Net |
A connection or network of cells with long thin fibers that respond to mechanical or chemical stimuli. |
|
|
Mechanoreception |
The ability to respond to a stimulus of touch or pressure. |
|
|
Chemoreception |
The ability to respond to chemical stimuli |
|
|
Photoreception |
The ability to respond to changes in light intensity |
|
|
Sexual reproduction |
females produce eggs in ovaries, males produce sperm in the testes, and they are fertilized. |
|
|
Fertilization |
egg and sperm unite |
|
|
larva |
Young growing organism that is not yet an adult. They can swim, but not against a current. |
|
|
Cilia |
Small hairlike structures that help (larva) with movement by beating back and forth. |
|
|
Asexual reproduction |
Produces identical offspring from one parent. An example for cnidarians is budding. |
|
|
Budding |
A form of asexual reproduction. Cells begin to bulge out from the side or base of the parent, and form a new organism. |
|
|
Regeneration |
regrowing lost or damage parts |
|
Class Hydrozoa |
Contains the form medusa Freshwater polyps regenerative Reproduce sexually and asexually (budding) Eat larval insects and tiny crustaceans Examples: Obelia colonies and Portuguese man of war |
|

Class Scyphozoa |
True jellies Have radial symmetry Eat plankton like mollusks, crustaceans, copepods, and zoo plankton. Medusa and polyp forms Gonads are used to identify moon jellies Contains: Common jelly, moon jelly, or Aurelia. |
|
|
Class Anthozoa |
Sea anemone Subclass Zoantharia contains corals sessile get food from currents |
|

Class Anthozoa Subclass Zoantharia |
Contains corals sessile food from currents stung by tentacles |

