![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Inhibit Transpeptidase Cause Lysis (Bacteriocidal) Gram + |
Penicillins/Cephalosporins |
|
|
|
Inactivates Penicillins/Cephalosporins |
b-lactamase |
|
|
|
Oral Gm + NOT resistant b-lactamase |
Amoxicillin / Ampicillin (2nd gen) |
|
|
|
Gm - NOT resistant to b-lactamase
|
Piperacillin (4th gen) (last case scenario) |
Enhanced with Tazobactam |
|
|
IV /Parenteral Gm + or Gm - Pen Allergy rxn |
Imipenem - Cilastatin |
|
|
|
PBP Gm - NO Pen allergy rxn IV / Parenteral |
Aztreonam |
|
|
|
Gm + Endocarditis IV / Parenteral NO Pen Allergy rxn |
Vancomycin |
MRSA |
|
|
Pen Allergy Rxn |
Cephalosporins |
Ok for minor rxns only (like rash) |
|
|
Gm - Gonorrhea Pneumonia Meningitis Changes form in Urine What can use in place of |
Ceftriaxone |
Can use Cefixime in place of (oral) |
|
|
Bactericidal Inhibits bacterial DNA Gyrase |
Quinolones / Fluoroquinolones |
By inhibiting DNA Gyrase, it keeps DNA supercoiled preventing TS/TL |
|
|
Used infrequently in lower UTI for common Gm - organisms (ie e Coli) |
Nalidixic Acid and Cinoxacin (older drug)
(Quinolones)
Limited Usage |
ADR Rash |
|
|
What class is Ciprofloxacin and how is it taken |
Fluoroquinolones - Extends Gm - significantly
PO, IV |
|
|
|
What class is Ofloxacin and how is it taken |
Fluoroquinolones - Extends Gm - significantly
PO, IV |
|
|
|
Dont take Antacids with what drug class |
Fluroquinolones |
Good PO though |
|
|
How are fluoroquinolones excreted
What is the exception? |
Urine unchanged
Exception: Moxifloxacin (biliary) |
|
|
|
*Inhibits CYP-450 drug metabolizing enzymes
Increases half life of other drugs
What drug class is it? |
Ciprofloxacin
(Fluoroquinolone) |
|
|
|
*Broad gram -
What is best against Pseudomonas, what drug?
Good against gonorrhea |
Ciprofloxacin |
|
|
|
Travelers Diarrhea
Neutropenic Patients
UTI in Men |
Ofloxacin |
|
|
|
What drug class are these from:
Levofloxacin Moxifloxacin
What gram type are they effective against |
Fluoroquinolones
Gm +
Especially Streptococcus |
Levofloxacin is L-isomer of Ofloxacin |
|
|
Photosensitivity
Nephrotoxicity
Crystalluria in Alkaline urine
*Cartilage erosion Tendonitis
Contraindicated: pregnancy/nursing/children
What drug type? |
FQ |
Levofloxacin
Moxifloxacin |
|
|
Describe difference in urine ph with FQ's vs Sulfonamides |
FQ's - Crystalluria in Alkaline urine
Sulfonamides - Crystalluria in Acidic urine |
|
|
|
Adjust dosage of FQ based on what? bc of nephrotoxicity |
Creatine Clearance |
|
|
|
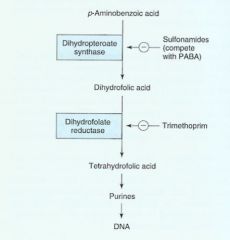
*This drug type inhibits dihydropteronate synthase
What does dihydropteronate synthase do? (on hint)
No Pen Allergy rxn |
Sulfonamide |
Dihydropteronate Synthase catalyzes PABA to folic acid required for DNA synthesis |
|
|
Sulfonamide flow chart mechanism |
|
|
|
|
What is the main indication for systemic Sulfonamide use alone? |
Gm -: E coli
P. Mirababilis for uncomplicated UTI's |
|
|
|
What drug class?
Good PO Metabolized via acetylation in liver
Excretion mainly in urine |
Sulfonamides |
Crystallinuria in Acidic Urine |
|
|
Systemic Use of what drug for UTI's primarily?
What drug class also? |
Sulfisoxazole and Sulfamethoxazole* |
Folic Acid |
|
|
*ADR: Rash. Serious= Stevens Johnson syndrome
*Hemolytic Anemia, especially with G-6-PD deficiency
Contraindicated in pregnancy = Kernicterus (yellow pigment in brain) |
Sulfamethoxazole (sulfonamide) |
|
|
|
Yellow pigment in brain |
Kernicterus |
Sulfamethoxazole (Sulfonamide) |
|
|
*Hemolytic Anemia, especially with G-6-PD deficiency |
Sulfamethoxazole (sulfonamide) |
|
|
|
*Combo of what drugs inhibits sequential steps in folic acid synthesis
*Resistance develops quickly when either drug used alone |
Trimethoprim / Sulfamethoxazole
(Sulfonamide) |
|
|
|
Folic Acid Deficiency Weak Base |
Trimethoprim
NOT SULFAMETHOXAZOLE |
|
|
|
Gm - activity is main indication Excludes Pseudomonas
Indications: UTI |
Trimethoprim / Sulfamethoxazole
(Sulfonamide) |
|
|
|
Increased ADR's in AIDS patients with TMP/SMX: Fever, rash, decreased blood cells, folate deficiency may cause macrocytic anemia |
Trimethoprim
(Sulfonamide) |
|
|
|
Main treatment for UTI
What is exception also? |
PO FQ
NO FQ in pregnancy, no Sulfonamides near term |
|
|
|
Male Prostatitis treatment? |
FQ , Ie Ofloxacin |
|
|
|
Summary Flow Chart |
|
|

