![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
ominous cause of L hydrocele
|
RCC involving the L renal vein, to which the L gonadal vein drains
|
|
|
cysts in the kidney
|
The classic appearance of cysts on CT are homogenous non-enhancing water-density masses. The presence of pancreatic and renal cysts in this patient suggests Von Hippel Lindau (VHL) syndrome, though additional studies and family history should be obtained. VHL is a rare autosomal dominant syndrome affecting multiple organ systems. Common manifestations are multiple cysts and tumors of the kidney and pancreas, CNS hemangioblastomas, adrenal pheochromocytomas, retinal angiomatosis, and café au-lait spots. Renal cysts in VHL often progress into renal cell carcinoma, the second most common cause of death in these patients, who are screened annually beginning at age 20. Of note, if this patient had presented with multiple cysts in kidneys alone, differential diagnosis expands to include polycystic kidney disease, Von Hippel Lindau (VHL) syndrome, tuberous sclerosis, acquired renal cysts (e.g. dialysis), and hepatic fibrosis-renal cystic disease.
|
|
|
Chailiditis
|
interposition of the colon between liver and diaphragm
|
|
|
Multiple air fluid levels in the bowel without dilation?
|
Think diarrhea.
|
|
|
What do you think of when you see a dystrophic calcification?
|
TTIII - tumor, trauma, infection, Inflammation, Infarction
OR of course, stones |
|
|
What's the main significance of a porcelain gall bladder?
|
Increased risk of cholangiocarcinoma! Due to chronic dysplastic cholecystitis
|
|
|
ground glass appearance to the abdomen?
|
ascites - bowel loops float up and obstruct your view of everything else
|
|
|
Appendicitis on CT
|
appendix is dilated and NOT filled with contrast (blocked)
--look for fat stranding (fluid) in the surroundings abscess, perforation, phlegmon are complications |
|
|
How do you find the appendix on CT?
|
look for the ileocecal valve, which is surrounded by a ring of fat in the cecum; about 2cm below that
|
|
|
DIfference between air in the portal venous system and air in the biliary tree
|
portal system - periphery of liver; smaller, linear, branching
biliary tract - central, Y-shaped, tubular |
|
|
Cause of air in the portal venous system?
|
bowel ischemia/infarction
|
|
|
CAuse of air in biliary tract
|
improper connection between bowel and biliary tract OR emphysematous infection
|
|
|
Riggler Sign
|
both sides of the bowel wall are outlined by air - white line seen with black on either side - sign of pneumoperitoneum
|
|
|
Football sign
|
visible abdominal ligaments ("Seams") on plain film - falciform (RUQ in the liver, by the spine) and lateral umbilical ligaments
|
|
|
relevance of the phrenicocolic ligament
|
a single white line seen in the LUQ that can be mistaken for haustra of Chalaiditis syndrome; only seen with massive pneumoperitoneum
|
|
|
air-fluid level within the abdomen and outside the bowel wall; common location
|
abscess - common under the R diaphragm, mimicing a stomach - due to R paracolic gutter, along which infection can traverse; the phrenicocolic ligament blocks on the L
|
|
|
What typically causes a sentinel loop of bowel?
|
local inflammation from an "-itis": pancreatitis, appendicitis, etc.
|
|
|
most common cause of functional ileus?
|
post-op!
|
|
|
Progression of bowel ischemia on radiograph
|
1. thumbprinting - focal area of gas with infiltration by soft tissue
2. Rigler's sign from pneumoperitoneum 3. pneumatosis coli |
|
|
What causes thumbprinting?
|
ischemia, anti-coagulation, diverticulitis, trauma, IBD, CMV
|
|
|
cauliflour calfication in the pelvis?
|
chronic prostatitis
|
|
|
"popcorn" calcifications in the pelvis?
|
fibroids
|
|
|
What likes to metastasize to the stomach
|
breast and lung
|
|
|
Hampton's line
|
thin mucosal overhanging flap over and ulcer - indicative of a benign ulcer
|
|
|
If an ulcer projects outside the expected lumen in profile, is it benign or malignant?
|
benign
|
|
|
Carmen Kirklin meniscus complex
|
indicates a malignant stomach ulcer - nodular rolled up edges of the ulcer crater overlap when a paddle is placed over them, forming a meniscoid filling defect
|
|
|
"wild folds" in the stomach?
|
lymphoma
|
|
|
signs of obstruction of ampulla of vater
|
double duct sign - two adjacent dilated ducts (bile and pancreatic)
dilated pancreatic duct in the tail of the pancreas dilated bile ducts in the liver |
|
|
A process in what other organ can involve the splenic flexure of the colon?
|
the pancreas
|
|
|
What is a pseudocyst
|
complication of acute pancreatitis - looks like an abscess - fluid filled density on CT
|
|
|
What should never be in the bladder?
|
Air or colonic contrast material; sign of a sigmoid or rectovesicular fistula; often diverticulitis, IBD, cancer
|
|
|
Common complications of diverticulae?
|
fistulae; abscess formation near the bowel; peritonitis
|
|
|
Rigler's triad of gallstone ileus?
|
1. dilated loops of small bowel
2. stone in the distal ileum 3. Air in the biliary tract - due to a cholecystoduodenal fistula that allows the stone to pass into the bowel |
|
|
lucency between the heart and the diaphragm?
|
likely a pneumothorax - equivalent to deep sulcus sign
|
|
|
Sign of intussusception on CT scan, barium enema
|
dilated loop of bowel with a fat density crescent inside it - this is the mesenteric fat from the telescoping bowel
--coiled spring of barium |
|
|
Two types of "polyps" in IBD
|
inflammatory psuedopolyps - occur in the acute phase of disease - rounded filling defects
filiform pseudopolyps - linear and roundish polyps |
|
|
creeping mesenteric fat
|
sign of Crohn's - the bowel is really highlighted because of increased mesenteric fat
|
|
|
comb sign
|
sign of Crohn's the vessels in the mesentery are accentuated because of increased fat and inflammation
|
|
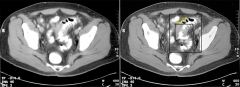
|
Diverticulitis - thickened wall, air levels representing the diverticuli themselves
|
|
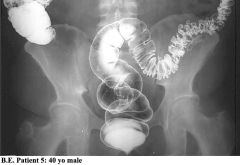
What is this?
|
Diverticulitis - notice the mass effect on the colon and the air collections
|
|
|
Characteristics of TCC as contrasted to RCC
|
TCC tends to involve the calyceal system if it involves the kidney; multifocal tumors are common; strictures and stenosis in the kidney or ureters are common
|
|
|
Differentiate pyelonephritis from kidney infarcts
|
both are wedge shaped filling defects on pyelogram phase of CT; pyelonephritis the wedges will originate at the papilla of the calcyes; infarcts are BETWEEN papillae
|
|
|
what is the classic appearance of chronic pyelonephritis?
|
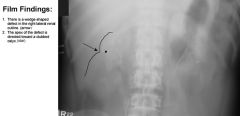
wedge shaped defect pointing toward a clubbed calyx
|
|
|
Bosniak classification
|
Category I Classic simple cysts described above Benign, ignore
Category II a) 1 or 2 internal septae less than 1mm thick b) Small amount of delicate calcification in wall of septum c) Hyperdense cysts that are less than 3cm in diameter, homogenous, sharply marginated, non-enhancing, at least � exophytic Benign, ignore Category IIF Minimally complicated cysts, thought to be benign but somewhat suspicious Follow up 3, 6 and 12 months Category III Primarily cystic but with features such as thickened or enhanced septi, thick irregular calcification, irregular margination, multilocular mass, uniform wall thickening or non-enhancing areas of nodularity 50% malignant, requires surgical treatment Category IV Cystic neoplasms or necrosis of solid tumor, solid and enhancing areas of nodularity Malignant, requires surgical treatment |
|
|
How many septae are you allowed in Bosniak II renal cysts
|
only one or two; not thick
|
|
|
analgesic abuse increases the risk of what cancer
|
TCC
|
|
|
Two broad categories that cause clubbed calcyces?
|
hydronephrosis and papillary necrosis
|
|
|
Differential of papillary necrosis
|
Pyelonephritis
Obstruction *Sickle cell disease Tuberculosis Cirrhosis (alcoholism) *Analgesic nephropathy Renal vein thrombosis *Diabetes mellitus |
|
|
4 presentations of papillary necrosis
|

|
|
|
calcifications in the bladder wall
|
TCC, schistosoma hematobium
|
|
|
psammomatous calcification
|
sand-like: red flag for cystadenocarcinoma - primary in bowel or ovary; see this in the liver as a met
|
|
|
Acute pyelonephritis on US
|
The kidney is enlarged with inhomogenous echotexture and loss of corticomedullary differentiation.
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of angioedema?
|
overactivation of complement factor C1 - lack of an inhibitor
|
|
|
WHere to look for hydronephrosis on US?
|
The dilation will be black and will be found in the central hilar area; the calyceal system is dilating
|
|
|
WHere to look for hydronephrosis on US?
|
The dilation will be black and will be found in the central hilar area; the calyceal system is dilating
|

