![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
most specific finding for alveolar process?
|
air bronchograms
|
|
|
|
What is the most specific finding for interstitial lung process
|
Kerley B lines - thickened interlobular septae
--seen in the costophrenic region |
|
|
|
General DDx for interstitial lung processes (five)
|
Fluid - edema
Blood - hemorrhage Pus - infection Tumor - lymphangitic spread Fibrosis |
|
|
|
Infections with calcifications; other conditions
|
TB, histo/cocci/blasto
-->sarcoid, silicosis |
|
|
|
Infections with adenopathy
|
TB, fungal, anthrax, tularemia, plague
|
|
|
|
DDx for white-out of an entire lung; how to differentiate
|
Total lung collapse - mediastinum shifts to ipsilateral side
Large Pleural Effusion - mediastinum shifts to opposite side |
|
|
|
Non-infectious causes of alveolar pattern on CXR
|
Tumors (lymphoma, bronchoalveolar cell carcinoma); Inflammation (sarcoid, alveolar proteinosis)
|
|
|
|
Peripheral alveolar pattern suggests what?
|
More specific finding: eosinophilic infections
|
|
|
|
Bibasilar alveolar pattern?
|
aspiration pneumonia
|
|
|
|
Hampton's humps
|
geometric wedges of opacity fanning out to the periphery; signifies large PE and infarct
|
|
|
|
Displacement of fissures outlined by pneumonia is indicative of what?
|
volume loss; suspicious for post-obstructive pneumonia, should follow up with bronchoscopy
|
|
|
|
Multilobar alveolar pneumonia?
|
NOT pneumococcus - legionella, gram negatives, aspiration, aspergillus
|
|
|
|
How do you differentiate between sets of ribs and diaphragms on lateral CXR?
|
the right ribs are larger and more posterior; the R diaphragm will travel all the way back to meet them, and is also visible all the way to the front of the chest
|
|
|
|
Infectious causes of interstitial pattern
|
Viral pneumonia - influenza, parainfluenza, adenovirus
Mycoplasma In immunocompromised: PCP, CMV |
|
|
|
air crescent - specific for what?
|
invasive aspergillus - retreating infarct
|
|
|
|
Why does someone get a lung abscess?
|
1. aspiration pneumonia
2. poor compliance/treatment 3. obstruction 4. TE fistula --do a CT to evaluate any time you have an abscess |
|
|
|
What is the Gohn complex radiologically?
|
Calcification! In the granuloma and in the hilar lymph nodes; remember this is primary TB
-->remember that when TB heals it calcifies, as all granulomas do -->for some reason miliary TB does not calcify! |
|
|
|
diffuse punctate calcifications all over the lung;
|
varicella pneumonia after it has healed! When active, it is a necrotizing bronchiolitis. Remember, miliary TB Does not calcify
|
|
|
|
Scarring in the lung apex with strange position of the hilum?
|
volume loss from retraction of TB
|
|
|
|
a pleural effusion that has septations or that is not in dependent portions of the lung?
|
empyema!
|
|
|
|
What is a pleural rind? What is the ddx?
|
Thickening of the pleura, not in a dependent position
--TB --empyema --pleural hemorrhage --mesothelioma --pleural mets --pleural fibrosis |
|
|
|
Describe three "types" of atelectasis and what they look like
|
1. discoid, focal, sub-segmental: focal alveolar collapse
--small focal linear densities 2. Atelectasis and/or infiltrate --slightly larger, patchy infiltrate 3. Lobar atelectasis/lobar collapse --dense lobar consolidations --surroundings respond to volume loss (mediastinum shifts toward, hemidiaphragm lifts) |
|
|
|
Differentiate between large pleural effusion and lung collapse
|
Mediastinum:
shifts toward a collapse, away from an effusion if at all |
|
|
|
Medical treatment that may hasten reabsorption of simple pneumothorax?
|
supplemental oxygen
|
|
|
|
Hydropneumothorax
|
a horizontal air-fluid level! Simple pleural effusion will usually have a meniscus
|
|
|
|
What in apices can mimic pneumothorax?
|
bullous emphysema; concave lines give it away
|
|
|
|
Differentiate between pneumopericardium and pneumomediastinum
|
pneumopericardium will always stay below the mid-ascending aorta
pneumomediastinum will often have many black streaky lines involving the superior mediastinum and deep cervical tissue |
|
|
|
pneumoperitoneum AND Pneumomediastinum?
|
Boerhaave's syndrome
|
|
|
|
R border of the mediastinum, top to bottom
|
brachiocephalic vessels, SVC, ascending aorta, RA
|
|
|
|
L border of the mediastinum, top to bottom
|
brachiocephalic vessels, aortic knob, pulmonary artery, LV
|
|
|
|
What normally lives in the cardiophrenic angles? What can enlarge this area?
|
fat pads
enlarge: steroid therapy (fat) lymph nodes pericardial cysts pleural tumors |
|
|
|
What is the bulge on the bottom of the R paratrachael stripe?
|
azygos arch
|
|
|
|
popcorn calcifications in a lung nodule?
|
hamartoma
|
|
|
|
which two lesions cavitate in the lung?
|
TB, squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
|
Which type of lesions tend to enhance?
|
Malignant - granulomas enhance, however, lowering specificity
|
|
|
|
how to check for pericardial effusion on CXR?
|
tramtrack sign - on lateral CXR - will see a light gray line between two dark gray lines parallel to and abutting the anterior chest wall - this represents the fluid separating the pericardial and epicardial fat pads
|
|
|
|
Some causes of pericarditis
|
Infectious
Viral- Coxsackie, Influenza, Mumps, HSV, Varicella Zoster Virus, Adenovirus Pyogenic- postoperative infection , primary pneumococcal infection, empyema Tuberculous, Mycotic, Syphilitic and Parasitic (rare in developed countries) Noninfectious Acute myocardial infarction and Dressler's syndrome (post MI, pericardiotomy) Uremia- indication for emergency dialysis- usually painless Neoplasia- radiation or metastases- usually from lung, breast, melanoma and lymphoma Myxedema Trauma Sarcoidosis Collagen Vascular Disorders- Rheumatic fever, SLE, RA, Scleroderma, Wegener's Drug-induced- Procainamide, Hydralazine, Isoniazid, Cromolyn, Minoxidil Amyloid |
|
|
|
Causes of calcified pericardium?
|
chronic TB or hemorrhagic pericarditis
|
|
|
|
"water bottle heart"
|
pericarditis with effusion - enlarged heart with sagging apex
|
|
|
|
Characteristics of benign lung nodules on CXR or CT
|
fat - hamartoma
calcifications that are organized or popcorn |
|
|
|
retrosternal pneumonia
|
there should not be opacity between the anterior edge of the heart and the sternum on lateral CXR
|
|
|
|
Who gets bibasilar pneumonia?
|
alcoholics (aspiration)
|
|
|
|
How do you tell the difference between a consolidation and lobar collapse?
|
Look for signs of volume loss - shift of other structures, fissures moving, etc
|
|
|
|
Bullous Emphysema
|
|
|
Vytorin
|
ezetimibe/simvastatin
ez ET i mibe and SIM va stat in |
statin-reduces LDL and tri's--raises HDL
|
|
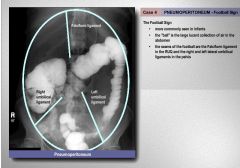
What other abnormality besides air is in this KUB?
|
fluid: hydropneumoperitoneum - notice the large air fluid level - often due to huge small bowel perforation
|
|
|
|
Bowel Ischemia
|
|
|
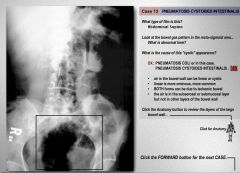
|
hadioasfja;fj
|
|
|
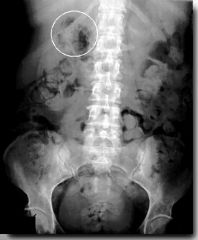
What is this?
|
emphysematous pyelonephritis
|
|
|
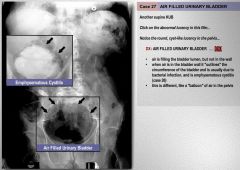
What is causing the air in the bladder?
|
A fistula
|
|
|
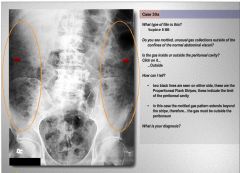
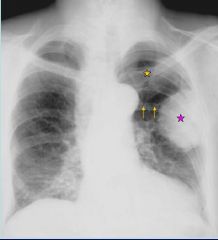
What are the arrows? what is the diagnosis?
|
The arrows are the properitoneal flank stripes; limit of the peritoneum; since the gas goes past those, its subcutaneous emphysema
|
|
|
|
Classic signs of Pancoast Tumor
|
Horner's Syndrome
Shoulder and arm pain in C8, T1, T2 Atrophy and Weakness of hand muscles |
|
|
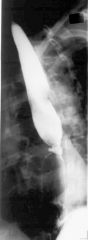
What is the diagnosis?
|
Barrett's Stricture - classic mid esophageal stricture with accompanying ulcer
|
|
|
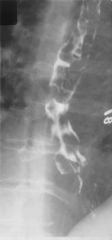
What is the diagnosis?
|
Esophageal varices; only other possibility is carcinosarcoma, which is extremely rare, but has a varicoid appearance on BaSw
|
|
|
|
Most reliable signs of hyperinflation on CXR
|
flattening of the hemidiaphragm, increased size (>2cm) of the retrosternal airspace (between the sternum and chest)
|
|
|
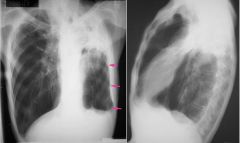
What is the diagnosis for the pink arrows? Differential?
|
fibrothorax - prior TB, prior empyema, asbestos exposure, or prior trauma
|
|
|
|
most common cause of a small heart on CXR (tear drop heart)
|
COPD
|
|
|
|
Chronic steroid use in a pulmonary patient can cause what three bone abnormalities?
|
osteopenia, medullary infarcts, hypertrophic osteoarthropathy
|
|
|
|
Weird way to tell apart ascending and descending thoracic aortic anuerisms?
|
Both will show an apical cap and pleural effusion, but the SIDE matters: R side for ascending, L side for descending
|
|
|
|
Stanford Classification of aortic dissection
|
A - ascending
B - descending |
|
|
|
rachitic rosary
|
string of beads on the ribs - sign of rickets
|
|
|
|
fissural pseudotumor
|
round collection on frontal CXR, elliptical on lateral - actually an effusion stuck in the fissure
|
|
|
|
Which type of lung cancer can look like a pneumonia?
|
bronchoalveolar carcinoma
|
|
|
|
What does a hydatid cyst look like?
|
kind of like an abscess - thin walled cyst but instead of an air fluid level there is a solid sphere on the bottom with a crescentic interface
|
|
|
|
shaggy esophageal mucosa
|
Candida - polypoid filling defects
|
|
|
|
What strange malignancy favors the apices of the lung?
|
Langerhans cell histiocytosis, formerly called Histiocytosis X, is a rare disease wherein histiocytes infiltrate many tissues. The hallmark cell is the Langerhans cell. Isolated bone or chest infiltration may be referred to as eosinophilic granuloma of bone or pulmonary eosinophilic granuloma (PEG), respectively. It is increased in smokers.
|
|
|
|
Which way does the mediastinum shift in mesothelioma?
|
ipsilateral
|
|

