![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
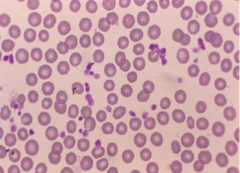
|
Dog Large Central pallor |
|
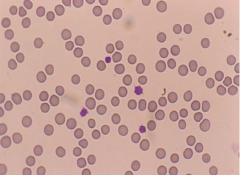
|
Smaller No central pallor |
|
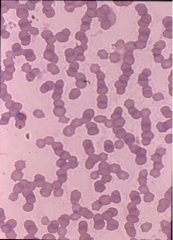
|
Horse and Cat Rouleaux in normal spp |
|
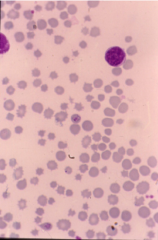
|
Poikilocytosis |
|
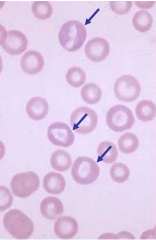
|
Macrocytic Hypochromic (regeneration) |
|
|
Microcytic Hypochromic (iron deficiency) |
|
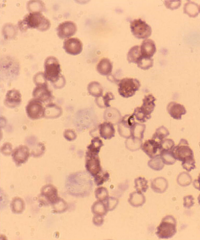
|
Echinocytosis - numerous regular pin point projections |
|
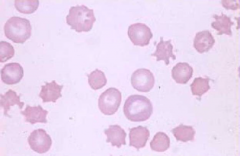
|
Acanthocytes |
|
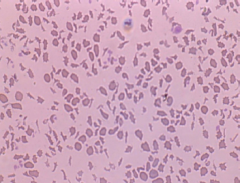
|
Schistocytes |
|
|
What causes poikilocytosis |
Turbulence Abnormal microvasculature DIC Haemangiosarcoma |
|
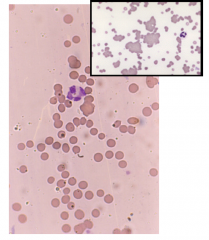
|
Spherocytes |
|
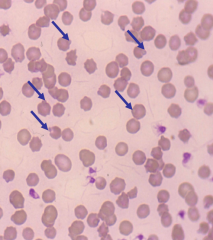
|
Heinz bodies |
|
|
What are heinz bodies a feature of |
oxidative damage |
|
|
What are features of haemolytic anaemia |
Spherocytes |
|
|
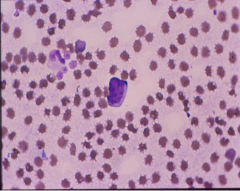
Signs of regeneration |
Normoblasts Reticulocytes, Howell-jolly bodies
|
|
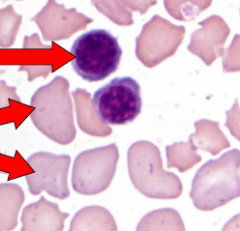
|
Normoblast (Top) Reticulocytes (Middle and bottom)
|
|
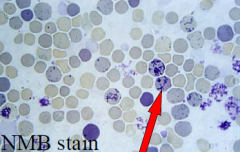
|
Reticulocytes |
|
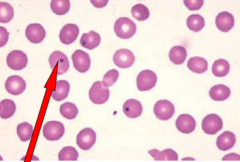
|
Howell jolly bodies |
|
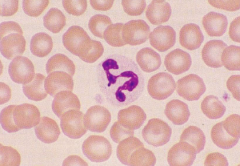
|
Mature neutrophil canine |
|
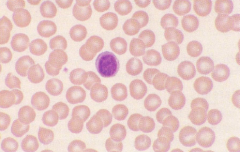
|
canine lymphocyte |
|
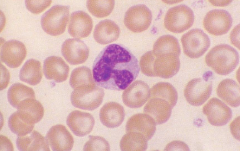
|
Canince monocyte |
|
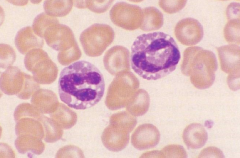
|
Canine eosinophil |
|
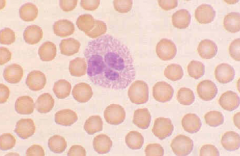
|
Feline eosinophil |
|
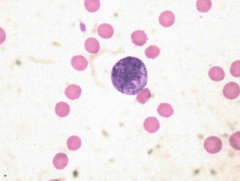
|
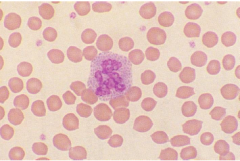
Canine basophil |
|
|
Feline basophil |
|
|
What does inflammation cause? |
Shift to the left |
|
|
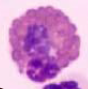
Equine eosinophil |
|
|
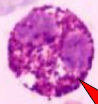
Equine basophil |
|
|
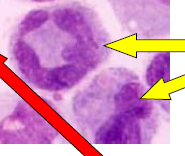
Equine monocytes |
|
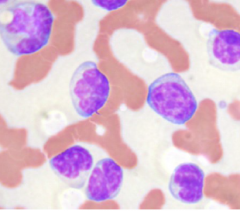
|
Equine lymphocytes |
|
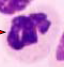
|
Equine neutrophil |
|
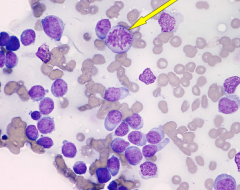
|
Lymphoid leukemia |
|
|
Advantages of a practice lab |
Useful for emergeny care - rapid results Add interest to job Impressive for clients Lower cost per test |
|
|
Disadvantages of a practice lab |
Unreliable if quality control is poor Some technical skill required Interpretation required Takes time and monmey Artefacts may be misinterpreted leading to a false diagnosis Safety issues must be observed |
|
|
What is precision |
How similar results of repeated assays on the same sample are |
|
|
What is accuracy |
How close assay results are to the true value |
|
|
What are the 3 main methods of quality assessment |
Quality assurance - external program - they send you samples and then tell you how far you are from true value and compare to other practices Quality control - use commercial serum with known samples alongside patient samples Repeat analtsis on the same asmple multiple times/different days |
|
|
What tubes should you use for routine haematology and platelets |
EDTA (purple) |
|
|
What tubes should you use for most biochem |
clotted sample (red) |
|
|
What tubes should you use for coagulation tests |
fluoride oxalate (grey/yellow) |
|
|
What tubes should you use for hormone tests |
heparin (green) |
|
|
What tubes do you use for serology |
Serum only (clotted) |
|
|
What do you use for virus isolation |
heparin (green) |
|
|
how does haemolysis interfere with tests |
altered pH and K Alter analytes or reaction |
|
|
What does icterus interfere with |
Absorbance in biochem |
|
|
What is MCV |
Mean cell volume |
|
|
What does MCV indicate |
Macrocytosis if high or microcytosis if low |
|
|
What does MCHC indicate |
Hypochromia/normochromia Haemaglobin content |
|
|
What are reticulocytes |
Immature RBC with clumps of RNA (reticulin) |
|
|
Causes of non regenerative anaemia |
Iron deficienct Bone marrow aplasia/hypoplasia Anaemia of inflammatory disease Bone marrow neoplasm |
|
|
What would you see on a stress leukogram (SMILED) |
Segmented neutrophils Monocytes increased Lymphocytes and Eosnophils decreased |
|
|
What would you see if there was hypersensetivity |
Eosinophilia and basophilia |
|
|
What would you see if there was extreme neutrophillic leukocytosis |
severe
|
|
|
Enzymes we test for |
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) |
|
|
Serum proteins we test for |
TP, albumin, globulin, acute phase proteins |
|
|
Polyclonal gammopathy |
Increase in multiple
|
|
|
Monoclonal gammopathy |
Increase in a single
|
|
|
Reasons for increased enzymes |
Membrane blebbing |
|
|
Electrolytes and blood gases we measure |
Na, K, Cl, Ca, PO4 |
|
|
metabolites we measure |
Glucose, urea, creatinine, bile acids, bilirubin
|
|
|
Hormones we measure |
Cortisol |
|
|
What non pathological features would change results |
Age - higher AP and phosphate with bone growth Breed - higher pcv and lower T4 sighthounds |

