![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell staining for: 1. Histology looks at? 2. Histochemistry looks at? 3. Immunostaining looks at? 4. In situ hybridization looks at? |
1. chemical composition 2. enzymes 3. antigens (using epitopes from antibodies) 4. mRNA (gene transcription) |
|
|
What are the pros and cons of freezing and fixing a specimen? |
Freeze it: preserves function (enzymatic activity) butstructure is distorted Fix it: preserves structure but destroys function |
|
|
For histochemical strategies Ex.) In myosin ATP has to become ADP How can we get the enzyme (ATPase) to function? How would the precipitate (product) = CoS, be identified? |
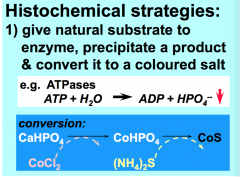
Give it a metabolite that enzyme (ATPase) will hydrolyze It will show a stable dark brown color |
|
|
Immunostaining: What is the direct staining? What is indirect staining? Why might indirect be used? What problem can arise here? |
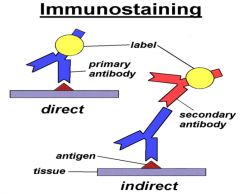
Direct staining: one antibody molecule recognizesspecific epitope and color reaction Indirect: Primary antibody recognizes epitope, then secondantibody molecule binds to the first antibody – much moreprofound color reaction using secondary antibody Albumen blocks all electrical charges |
|
|
For in situ hybridization, mRNA is unstable and must be? What 2 probes can be used for this? What does in situ hybridization tell us? Also used for myosin mRNAs |
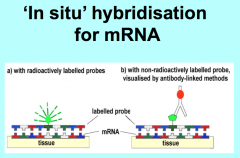
In situ hybridization:mRNA is very unstable: must be fixed quickly Tells what transcripts are being expressed in a gene |
|
|
In summary: cell staining methodsprovide informationabout what 3 things? |
cell structure cell function cell pathology |
|
|
Muscle shortening: What stays constant and what narrows? What muscle types are slow? What are fast? What types are used for normal activity? What types are used for heavy activity? |
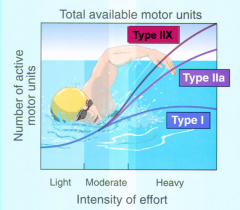
Muscle shortening: A bands were constant width but I bandsnarrowed Type I = slow Type IIA and IIX = fast Normal: type I and IIA Heavy activity: (all of them) but more type IIX -Type IIX is the most powerful fiber type |
|
|
Chewing muscles have specific units If you don’t use muscle, for example Type II gets smaller,this is called? |
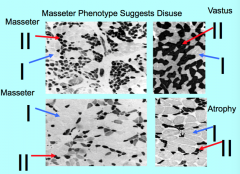
Chewing muscles have specific units Atrophy |
|
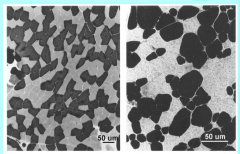
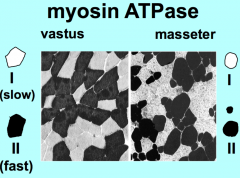
Type I are? Type II are? |
|
|
|
Little to no type II muscles result in? Too much type II muscles result in? |
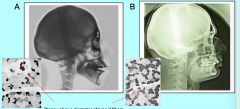
Open bite Deep bite |
|
|
Fast fiber (II) size is variable in? Masseter fast fibers (II) varies by compartment Deep massater has? |
Masticatory muscles Masseter fast fibers (II) varies by compartment Superficial = close to cheek Middle = mixture Deep = close to jaw Has spindle clusters for Jaw posture (opening and closing) |
|
|
In dentofacial deformity patients, what 2 things are prevalent? |
Asymmetry TMD (Temporomandibular Joint Disorder ) |

