![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Common concerns
|
Headache Facial pain, paresis, paralysis Visual changes Hearing changes Vertigo/dizziness Epitaxis Pharyngitis Laryngitis Lyphadenopathy Goiter Lumps/bumps Pt Concerns |
|
|
Head and neck: inspection
|
Head: Size, shape/symmetry, skin condition, hair, scalp, unusual movements Neck: Symmetry, mobility, range of motion, neck vessels |
|
|
Some things which may be observed
|
2. Acanthosis nigricans, Skin tags = INSULIN RESISTANCE |
|
|
Cranial Nerve V examination
|
TRIGEMINAL 1. Corneal reflex - cotton wool, blink tests (V = sensory test, VII = blink test) 2. Facial sensation - sterile sharp item on forehead, cheek, jaw VS dull. If abnormal, temp and light touch. 3. Motor: pt opens mouth, clenches teeth (pterygoid) - palpate temporal, masseters 4. Jaw jerk - if INCREASED closure, UMNL |
|
|
CN VII
|
2. Fascial expression: Look up and wrinkle forehead. Shut eyes tightly. Grins. (frown, show teeth, puff cheeks, whistle - optional) 3. Corneal blink (w/CN5 testing) |
|
|
Bell's palsy: signs
|
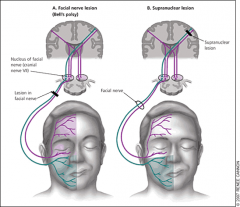
2. Wrinkling only on one half = supranuclearlesion . 3. Bell's usually resolves itself |
|
|
Other CN VII defects
|
2. Acromegally?? |
|
|
How to palpate head/neck
|
2. Neck: anterior midline structures, thyroid gland, carotid artery pulses, lymph nodes, muscle strength, cervical vertebrae |
|
|
Head and neck: auscultation
|
Neck: carotid arteries, thyroid gland for BRUITS (using bell) |
|
|
Neck exam summary
|
2. Palpate neck for tenderness, deformity, masses while swallowing water. 3. Assess cranial nerve XI: shoulder resistance to force. Note asymmetry too. Shoulder shrug and turn head with resisting force from PA. 4. Auscultate, palpate each carotid. |
|
|
CN XI defect signs
|
2. Weakened shoulder elevation (SCM doesn't work) 3. Usually due to surgery, blunt trauma, traction injury, penetrating injury. |
|
|
Head and neck exam - PAIN
|
Palpate to elicit pain See if pain is referred (spreads out from frontal sinus, maxillary sinus, ethnoid sinus, posterior suboccipital region) Use pain scale |
|
|
TMJ exam (*2 parts) + common causes
|
2. Place fingers behind tragus, anterior to external canal meatus. Repeat. 3. Arthritis, degenerative process, bruxism/clenching, trauma |
|
|
Lymph node, gland exam
|
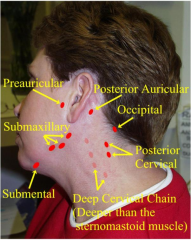
1. Palpate with pad of index/middle fingers in small circular motions: a) Preauricular b) Postauricular c) Occipital d) Tonsillar e) Submandibular f) Submental g) Superficial (anterior) cervical h) Supraclavicular I) have pt turn towards side, palpate for deep cervical |
|
|
Lymph node defects (3)
|
2. Congenital: Branchial cleft cyst. Need to remove - potential to be cancerous 3. Congential: Thyroglossal duct cyst - rises out when pt sticks out tongue. Refer to ENT. |
|
|
Thyroid exam
|
2. Move behind pt, ID cricoid cartilage with both hands 3. Move down 2-3 tracheal rings while palpating isthmus 4. Move laterally, note size and symmetry of lobes, presence of nodules 5. Have pt trip head to left, displace thyroid and trachea, feel right lobe. Repeat on other side. |
|
|
Throid defects to look for
|
|
|
|
Anatomy of outer ear
|

|
|
|
External ear inspection/palpation
|
Palpate: Auricle, Tragus, Mastoid |
|
|
Otoscope examination |
2. Grasp auricle, pull back 3. Angle speculum anteriorly to see TM 4. Hold otoscope STEM UP or angled, brace hand on pt's head 5. Stay on anterior 1/3 - hair line - cartilaginous area! OPT: Use insuffalator bulb to see if eardrum will move. If it does, that means no fluid (good). |
|
|
Defects of external and internal ear
|
2. Uric acid deposits (GOUT) 3. Congenital defects 4. Basal cell carcinoma 5. Too much cerumen (If can't see 1/2 TM, clean) 6. Foreign body (ear plug, bug) 7. Collapsing canal 8. Exostosis - bony growth - benign, assoc. w/cold water 9. Candidiasis 10. Aspergillus Niger 11. Lichenification - itching with key - abraded, thick skin 12. Tympanosclerosis (scarring - due to infection, perforation, surgery) 13. Acute otitis media w/effusion (AOME): pink, retracted --> red, bulging, potential for perforation. Most common in pars tensa. 14. Otitis media w. effusion 15. Tympanic membrane perforation NOTE: Red reflex IS NORMAL |
|
|
Label parts of tympanic membrane **
|
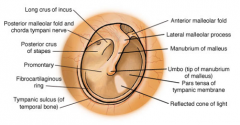
|
|
|
Tympanic membrane perforation **
|
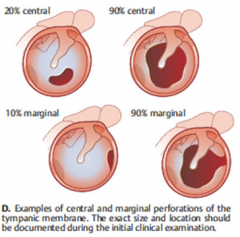
If margin is part of it, harder to heal. Central heal on their own
|
|
|
Hearing screening tests
|
1. Whispered voice test - repeat if wrong. Need 3/6 to pass. One ear at a time. |
|
|
Nasal/sinus examination
|
2. Inspect w/ otoscope: Septum, mucous membranes, inferior turbinates, middle turbinates. 3. Test CN1 if indicated. |
|
|
Nose defects
|
2. Septum deviation 3. Polyps (on turbinates) |
|
|
Oral cavity examination
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oropharyngeal exam
|
*Test by asking pt to say "ahh", "kahh" (CN 9/10) |
|
|
Oropharyngeal exam steps
|
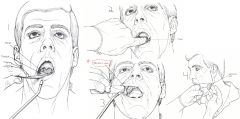
|
|
|
Oral defects
|
2. Leukoplakia 3. Squamous cell carcinoma 4. Tonsillar hypertrophy (ALWAYS abnormal*) 5. Kissing tonsils 6. Supperative tonsils 7. Peritonsillar abscess |
|
|
How to test CN via oral exam
|
2. CN X (Vagus) - assymetrical palate elevation, vocal change - hoarseness, aphonia 3. XII (Hypoglossal) - Upper motor neuron = contralateral deviation of tongue. Lower motor neuron = ipsilateral deviation of tongue. |
|
|
Rinne's test
|
IF failed whispered voice test
2. When pt can't hear it anymore, bring it out in front 3. Ask if pt can still hear |
|
|
Weber's test
|
PT should hear sound everywhere - not just one ear = sensory neural hearing loss. Refer to audiologist for hearing test |
|
|
Dix-Hallpike maneuver
|
Tilt head, slowly lower - observe 30 seconds. Raise back up - observe 30 seconds Note any nystagmus (positive) Repeat with head tilted to other side. |
|
|
Transillumination
|
2. maxillary sinuses (with mouth open) |

