![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Fill in the missing areas in the aerobic cellular respiration equation.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> XXXXX + XXXXXX + XXXXXX |
6CO2 + 6 H20 + Energy
|
|
|
Cellular respiration in the presense of O2 is called XXXXXXXX XXXXXXX.
|
Aerobic Respiration
|
|
|
Glycolysis is the decomposition of glucose to XXXXXXXX.
|
Pyruvate
|
|
|
In Glycolysis what molecules are added and what molecules are gained? (4)
|
1. 2 ATP invested
2. 2 NADH Produced 3. 4 ATP are produced 4. 2 Pyruvate are formed |
|
|
Before Krebs cycle, pyruvate combines with XXXXX to form XXXXXXX.
What is also produced in that reaction |
Ezyme CoA, Acetyl CoA, 1 NADH, 1CO2 per pyruvate
|
|
|
What happens in the Krebs cycle and what are its products
|
Pyruvate binds Oxaloacetate (OAA) to form Citrate which then forms 7 intermediate products:
Forms: 3NADH 1FADH2 1ATP 2CO2 |
|
|
XXXXXXXXX XXXXXX is the process of extracting ATP from NADH and FADH2. Also what is this step called?
|
Oxidative Phosphorylation occurs at electron transport chain.
|
|
|
Cellular respiration pathways graph |
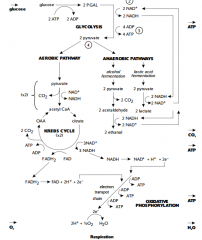
|
|
|
What are the carrier proteins generally referred to in the electron transport chain?
|
Cytochromes
|
|
|
NADH generates XXXXXX ATP while FADH2 generates XXXXXX ATP?
|
Three/Two
|
|
|
What is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain? What does it become?
|
Oxygen, water
|
|
|
How many ATP can be theoretically made from one molecule of glucose? Is this number different from Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes?
|
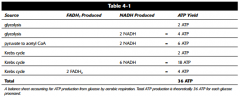
36 eukaryotes/38 prokaryotes/ Yes because eukaryotes have to transfer the NADH created in the cytoplasm to the mitochondria which takes 2 ATP.
|
|
|
What is the actual number of ATP that can be created per molecule of glucose? Why?
|
Around 30/Due to variations in mitochondrial efficiencies and competing biochemical processes.
|
|
|
What are the four areas of the mitochondria?
|
1. Outer Membrane
2. Intermembrane Space 3. Inner Membrane 4. Matrix |
|
|
What two major processes of aerobic respiration occur in the mitochondria?
|
1. Kreb Cycle
2. Oxidative Phosphorylation |
|
|
What layer of the mitochondria do protons accumulate?
|
Intermembrane Space
|
|
|
What layer of the mitochondria does oxidative phosphorylation occur? What structure is present in this layer?
|
Inner Membrane/Cristae
|
|
|
Where does the Kreb cycle occur specifically during aerobic respiration in eukaryotes?
|
The Matrix of the Mitochondria
|
|
|
Chemiosmosis
|
ATP generation method from proton conc gradient
|
|
|
ATP synthase generates XXXXXX?
|
ATP
|
|
|
What are the two types of phosphorylation to produce ATP?
|
1. Substrate level Phosphorylation ( in glycolysis)
2. Oxidative Phosphorylation |
|
|
When there is no oxygen what must a cell do to produce ATP if it is an aerobe?
|
Anaerobic Respiration
|
|
|
What are two common pathways of anaerobic respiration?
|
1. Alcohol fermentation - yeast
2. Lactic Acid Fermentation - muscle |
|
|
What is the objective of fermentation?
|
To release some NAD+ for use in glycolysis
|
|
|
What happens in alcohol fermentation |
Pyruvate loses CO2 to become acetyladehyde which makes NAD+ which can feed back into glycolysis |
|
|
What happens in lactic acid fermentation |
Pyruvate makes lactate while making NAD+ |

