![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Who was the first to excavate Egpyt and publish?
|
Flynder Petri
|
|
|
Why is southern Egypt called Upper Egypt and northern called Lower Egypt?
|
The Nile flow from the south to the North with fan like tributaries flowing to the Mediterranean. (Egptian Delta)
|
|
|
Define ALLUVIL?
|
Fertile soil, as on the banks of the Nile due to extreme winter flooding, 20 miles wide
|
|
|
How did the egyptian increase the fertile land wideth?
|
irrigation from as early as 4000 BCE
|
|
|
Why was Egyptian culture more stable than Mesopotamian?
|
Tremendous local natural resources, (gold) and predictible weather (flooding of Nile every winter), therefore they remained isolated bc they didn't need to trade.
Exception: traded w Lebanon for timbre which they didin't have |
|
|
Describe Neolithic Egypt?
|
5000-4000 BCE
cliff caves by Nile burials with gifts |
|
|
Pre-Dynastic/Chalcolithic Egypt?
Amratian Culture/Naqadal I?4000-3500 Gerzean Culture/Naquada II?3500-3200 |
Amration Culture- moved down to Nile banks and cleared swamps, hut, gold jewelery, Ivory(hippos, elephants) inlllllayed w bituman(trade w Meso),
stone work(palete for kohl Black top redware w incised animals, nile life religion- female with raised arms Gerzean Culture-pottery- reversed tech- now decoration painted on white ground- more figuration and narrative, boats w god statues, smiting symbols, have textiles preserve due to dry climate |
|
|
how do we know most of Egyptian culture?
|
elaborate burial tombs, afterlife more NB than earthly life(villages not built to endure time)
|
|
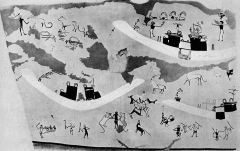
|
Wall painting on plaster, Tomb 100 @ hierakonpolis, Egypt, Pre-Dynastic, 3500-3200BCE 16'3" w
riverboats w cabin perhaps festival, narrative depicts several independant grouping of activities w beginning of iconographic elements- boats, battle, master of animals, smiting enemies, corraled animals. Comosite perpective-frontal, profile, birds eye |
|
|
Egypt was divide into_______ during the pre-dynastic period?
|
NOMES
|
|
|
Proto dynastic period? NB event
|
3000-2920 BCE
King Narmer unified the nomes, thereafter refered to as dynasty |
|

|
Palette of King Naarmer,(3000-2920BCE) from Heirkanpolis, Egypt, pre-dynastic, slate, 2'1" h
NB comparble to the Rosetta Stone in dechering Egytian culture. oldes historic antiquity Depict the unificatioon of Egypt. Begining of iconographic egyptian elements Front- depicts(1 costume) King Narmer in twisted perspective, wearing the height crown of Upper Egypt,(2) smiting his ememies. (3)Hawk- Horace god, protector of Pharoh, smites ememy(papyrus flower- lowere egypt), (4)begining of inscription in cartoouche, heiroglyphics Back- after battle, decapitatd ememies,feet bw legs, Narmer wear low, white crown of lower egypt enigmatic serpantine necked beasts creat hole for grinding kohl |
|
|
Define MASTABA?
|
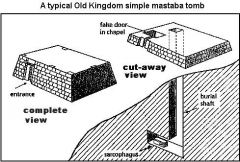
bench-like
Name of Egyptian Tombs I(BEGINING of seperate burials for royalty) flat top buildings, air shaft in roof, first ones were brick later stone |
|
|
By the III dynasty --------- becomes more pwerful?
|
Pharoh
|
|
|
First political capital of Egypt?
|
Memphis
|
|
|
What type of cities formed on the East bank of the Nile?
West Bank? |
east- rinsing sun- land of the living
west- setting sun, lan of the dead, tombs, payramids |
|

|
Stepped Pyramid, tomb of Djoser, @Saqqara, Egypt, dynasty III, 2630-2611BCE, Imhotep(cheif advisor) desinged, Stone(eternity), in Necropolis(city of dead)
|
|
|
NECROPOLIS
|
city of the dead
necro- dead polis- city |
|
|
The stepped pyramid was based on
|
zigurat or stacked Mastaba
|
|
|
Palace of the King at Saqqara?
|
not left, but based on nature- the fluted colums thought to be reeds bound togethr, Wall carved relief hebsed festival(rejeuvination of King), walls glazed tile, SERDAB in each room from this point on
|
|
|
SERDAB
|
portrait statue of King in tomb, thought the KA of pharoh would inhabit when he visited earth, small opening in front of it to allow entrance and exit
|
|
|
Defn KLAFT?
|
egyptian headress worn by pharoh, cloth folded behind ears
|
|

What became standard for representing Phorah from here oon?
|
Kiing seated
phoaroh wears Klaft false beard |
|
|
What are the two out buildings @ The Stepped pyramid od Djoser for?
|
dummy, facades (stone ruble behind)only to represent upper and lower Egypt.
|
|
|
Describe plan of stepped pyramid
|
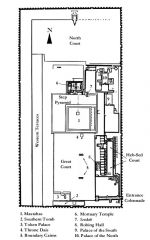
|
|

|
Papyrus engaged colum from North palace of stepped pyramid at Saqqara
Papyrus reps Lower Egypt |
|
|
Describe Facad of entrace to stepped palace
|

recessed an butress design, entrance end of long side
|
|

ID
|
relief in wall of stepped pyramid shows pharoh in rejeuvination festival of hep sed
|
|
|
Where are the first historical evidence of colums?
|
Engage papyrus colums at the stepped pyramid and fluted engaged colums @ same.
|
|
|
Khufu's Pyramid?
|
The Great Pyramid @ Giza
Largest pyramid, placed according to compass, symbols of sun(rays) god kings could use to ascednd to heaven,blocks of limestone w polished limestone exterior, built with ramps, 16 Y, kings tom in center, queens tomb smaller and under kings, two air shafts out sides, fasle tomb and passages lead undergroound, 3 small pyramids at base for wives, mastabas for family burial |
|
|
Describe Khufu's pyramid
|
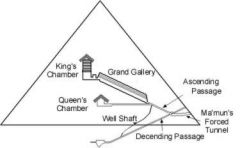
The Great Pyramid @ Giza
Largest pyramid, placed according to compass, symbols of sun(rays) god kings could use to ascednd to heaven,blocks of limestone w polished limestone exterior, built with ramps, 16 Y, kings tom in center, queens tomb smaller and under kings, two air shafts out sides, fasle tomb and passages lead undergroound, 3 small pyramids at base for wives, mastabas for family burial |
|
|
Describe Khufu complex
|
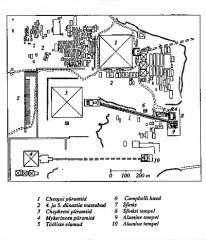
Valley temple- by nile, received body after parade down Nile
Mortuary temple- causeway connected from valley temple, enbalming of body |
|
|
What was used to embalm body?
|
NATRON - found in Nile Valley salt
|
|
|
How does Khaf-re 's temple differs from his father's ?
|
Smaller, pharoh's tomb now below,fewer mastabas(smaller family), Great Sphinx (sandstone)by causeway, prayers on walls of tomb but only sarcophagus left as w Khufu's
causeway left, Valley Temple also(post & lintel) portrait statue of Khaf-re bw posts |
|
|
What was the function of the sphinx?
|
lion symbole of power, king of beasts, Cobra on head also symbol of pharonic power, solid block of stone
steele as per inscription, probably a portrait of Khaf-re, rediscoverd on cleaned 1000 later by Tutmoses III |
|
|
Where was the capital of egypt at time of old kingdom?
|
Memphis
|
|
|
Egyptian aesthetic?
|
massive simple shapes
no embelishment as Mesopotaminan |
|
|
Why is Menkaure's tomb the smallest?
Describe |
Pharoh losing economic power, less money due to building of elaborate Khufu's pyramid
same structure, original casing blocks at base indicate not finished as some are not polished |
|

|
Khaf-re, Dyn IV, 2520-2494BCE,from Giza, 5'6"h, Dorite
from Valley Temple Horace hawk embraces Khaf-re, protectiooon god of kings, side of throne papyrus & lotus(unified Egypt) kilt, bare chest , strong idealic body, klaft, no human imperfectioooon like wrinkle or fat, idealized portrait no expresion, notheing ephemeral, timelesss |
|

|
Menkaure & Queen, dyn IV, 2490-2472BCE, Graywacke, 4'6"H fron Valley temple @Giza
less $ material, smaller , high relief, than Khaf-re's statue, group perhaps some age aroound mouth & eyes, NB as pharoh's power decreases his image is not so eternal, feet flat on ground to show permanance, forward leg longer to not have hips shift |
|

|
Seated Scribe Kay? from his Mastba @ Saqqara, dyn V, 2450-2350 BCE,painted limestone,1'9"h
realistic portrait -sagging belly, chest NB scribes of very high status and wealth to hve a mastaba and comissioon serdab, kings powe decresing |
|

|
Ka-Aper, Saqqara, wood, 3'7", gesso covered & painted
local governor,Realistic, round face and belly, inlaid crystal eyes, NB powerful private |
|

|
Ti watching hippo hunt, relief from mastaba of Ti, Saqqara, egypt, Dyn V, 2450-2350BCE, painted limestone, 4'h
NB depict idealic life on the nile,flora & fawna of nile above, bacdgrouond lined stems of papyrus |
|

|
Goats treading see, cattle herding, from the Mastaba of Ti, Saqquara, Egypt, Dyn V2450-2350BCE, relief painted limestone
-sophisticated techn of overlapping shapes to show depth but new , each animal in different position with humanized expressioooon oon face(anxiety of mother as her calf is carried across canal by servant. |
|
|
Where is Pyramid of Pepi I?
NB NB of his statuary? |
@ Saqqara, Dynasty VI
1 st king of VI small muc brick pyramid, due to lack of funds spent on gret pyramids of previoous dynsty -pharaoh depected kneeling, making offerings to gods |
|
|
Dynasty V NB?
|
Nomes gaining in power
scribe very high status, wealthy, build mastabas for themselves |
|
|
What happens in the 1 st Intermediary Period?
|
local nomes assert power, civil unrest
-breakdown of Pharaonic power & palacial schools of art , rsulting in cheaper 2nd class art |
|
|
Who reunites Egypt and begins the Middle Kingdom?
|
Mentu-hotep I or II, Dyn. XI-XII
From Thebes in south(upper Egypt) wears new combo crow of upper and lower E |
|
|
describe traditional symbols of upper & lower Egypt & crowns
|
Upper- tall white crown, lotus flower
Lower- short red crown, papyrus flower |
|
|
Deir el -Bahri
|

Deir el-Bahri , Dyn XI is the site of Menu-hotep II, and later Hatshepsut of the New Kingdom.
1.Menu-hotep combined the elements of the great pyramids at Giza, valley temple, mortuary temple and tomb into one mastaba like complex carve into stone cliffs outside Thebes know as The Valley of the Kings 2. A ramp flanked by trees, led up to the main terrace of rows of colonnades in the center of which once stood a solid core which is not preserve. Fn unkown. 3. behind that more collonnades, and mortuary temple,carve into the cliff chamber for queen and wives, chapels to gods 4. a shaft descend to the kings tomb below groound level |
|
|
what new position was created by Mentu-hotep?XI
|
Vizier- 2 nd in command, organization of Egypt
1. Meket-re 2. Sesostris I-revived pyramid, mud brick |
|
|
Dynasty XII kings NB?
|
expanded kingdom to include Nubia (gold mines) and east to Syani and Jordan (copper)
NB rise in prosperity |
|

|
Fragmentary head of Sesostris III/ SenusretIII?-
Dyn XII,Red quartzite, 6 1/2" h NB pharaoh depicted looks tired, downturned expression, bags undr deep set eyes, furrowed brow represents psychological change in view of king. lost confidence in stbility of pharoah |
|

|

Beni-hason,(n 100m of thebes) Necropolis on EAST bank of nile,Dyn XII, limestone cliffs, cemetary for governors of nomes
1. two colum stone carves porches entrances 2. interior chambers carved into stolid stone to resemble built architeture, post and lintels, beams 3. walls painted with life scenes of owner, hunting, fishing, victory batles, animal sacrifices 4. tomb ID by carving over door |
|
|
2 nd Intermediary Period?
Capita |
Dynasty 13-17
The Hyksos Period( dyn 13-15) Thebean Dy 17 Hyksos people migrated into Egypt(asiadic) and took over Avaris capital of Hyksos |
|
|
End of Dyn 12?
|
crisis and collapse in succession
dussinigration of pharaonic power |
|
|
Avaris?
|
capital of Hyksos dynasty15-16
modern Tell el Daba fragmentary wall paintings look heavily influence by Minoan culture, Hyksos warrior bodies in pit burial NB show infleunc of mediterean culture, seen as forieng rule |
|

|
hatshepsut as male, temple of Deir el Bahri, Dy 18
red granite, 8'6"h 1sr time woman was Pharoah |
|

|
Senmut & Nefru, Dyn 18,Granite, 3'1/2"h,Thebes, Egypt
tutor, possible lover of Hat. New style- cube statue |
|
|
Tutmosis III?
|
most enegeetic pharoah, expanded to Siani & Syria, now superpower
step son & nephew of hatshepsut |
|
|
Amarna?
|
new capital under Amun-hotepIV/Akhen-aten
|
|
|
Amun-hotep IV/Akhenaten
|
new monetheastic religion of sungod Aten
new sculture-elongated eyes, diagonal cheeks, emppphasis mouth, femininiaztions of his charateristics |
|

|
head of Queen Tiye,(mother of Akhenaten& powerful ruller w her husband), from Gurab, dyn 18, 1353-1335BCE,wood, gold , lapis, serious, stong , frowning expressioon shows ne artistic standards of Amarna style, old age
|
|

|
Tomb of Nebamun, from The Valley of Nobles on the west bank of Thebes, dyn 18,1400-1350,fresco,2'8"h
fowling scene, idealic lif on the Nile theme, painting not relief, incredible skille ex cat, heirarchical persp w Nebamum, fat cone on head of wife 7 stained linen dress |
|

|
Akhenaten,dyn 18, 1353-1335,Temple of Aten, Karnak, sand stone, 13'h
androgenoous charateristics to rep pharoaoh new Amarna style of art; elongated face, ephasis on mouth, heavy lidded almond eyes, effemininate body,belly ,hips, thighs painted eyes, incredible skill depicting body under fabric traditioona symbols of pharonic power the crook and flail |
|

|
Nefertiti,studio of tutmose,Armarna,dyn 18, 1353-1335, painted plaster and limestone,1'8"h
elogated neck but proportional face. accurate likeness, new crown, same new slightly amused expression as akhenaten. |
|

|
Royal family worshiping sun god Aten,
dy 18, 1353-1355, limestone, 1212 1/4"h,Amarna. Show informal intamacy charateristic,belly, elongated skull, of Armana style, aten extending rays to royal family |
|
|
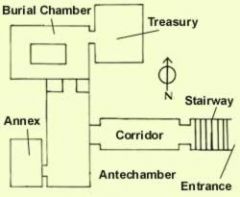
Tomb of Tut-ank-amun, dyn 18, Thebes, only unplundered tomb, show wealth and Armarna stlye,
descedning staircast to corridor to Ante chamber- guilded furniture filled,chariots, provisions, 2 stutue gaurd tomb door, inlaid chest annex-parially plundered, provisions. bed tomb-series of shrines inside each other, stone sarcaughagus with mummy cases inside each other, last one solid gold, gold death mask inlaid w semiprecioous stone, Treasury-anubis statue, boat models guilded shrine info on egyptian life and warfare incomparable |
|

|
painted chest from tomb of Tutankhamen, dyn 18, thebes
depicts young king in scences of conquest, war and hunting |
|

|
deathe maks
|

