![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Public IP Address |
An IP address is considered public if the IP number is valid and falls outside any of the IP address ranges reserved for private uses by Internet standards |
|
|
Private IP Address |
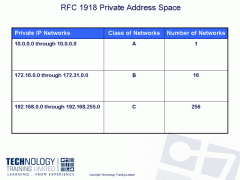
|
|
|
NAT |
Network Address Translation
NAT allows an enterprise to use private IP addresses for each host, plus a small number of public addresses. |
|
|
PAT |
Port Address Translation
Port address translation (PAT) is a function that allows multiple users within a private network to make use of a minimal number of IP addresses. Its basic function is to share a single IP public address between multiple clients who need to use the Internet publicly. It is an extension of network address translation (NAT). |
|
|
AS Sequence |
AS Seq
This is the order in which the AS chooses its path. |
|
|
PA |
Path Attribute
Define information about a path or route through a network. |
|
|
AS Path |
Autonomous System Path
This has many subcomponents such as AS Seq |
|
|
Public ASN |
Public Autonomous System Number
Assigned by IANA similar to IP addresses. Public ASN are 1 - 64495 |
|
|
Default Route |
A specific route set on the router to reach a destination. |
|
|
Single Homed |
Single ISP with a Single Link |
|
|
Dual Homed |
Two (or more) links to the internet, but with all links connecting to a single ISP |
|
|
Single multihomed |
Single link per ISP |
|
|
Dual multihomed |
Two or more links each to two or more different ISPs |
|
|
ASN |
Autonomous System Number
An ASN is a globally unique number used to identify an Autonomous System.
NOTE: Those numbers are 1 through 65535
|
|
|
eBGP Multihop |
This is the 5th configuration step for using loopback IP addresses with eBGP peers
NOTE: The default time to live (TTL) is one and a mulltihop requires more there for the packet is dropped unless discarded. |
|
|
Update Source (BGP) |
The BGP update source on one router must match the IP address configured on the other router's neighbor command, and vice versa. |
|
|
BGP Table |
List of paths |
|
|
Requirements for forming eBGP neighbors. |
|
|
|
BGP Open Message |
This generally performs the same functions as the EIGRP or OSPF hello messages. |
|
|
Idle |
The BGP process is either administratively down or awaiting the next retry attemp |
|
|
Connect
|
The BGP process is waiting for the TCP connection to be completed
|
|
|
Active |
The TCP connection has been completed, but no BGP messages have been sent to the peer yet |
|
|
Opensent |
The TCP connection exists, and a BGP open message has been sent to the peer, but the matching Open message has not yet been received from the other router |
|
|
Openconfirm |
An open message has been both sent to and received from the other router. It is waiting for a BGP keepalive message to determine if a neighbor is matched |
|
|
Established |
All neighbor parameters match, the neighbor relationship works, and the peers can now exchange update messages |
|
|
Open |
Used to establish a neighbor relationship and exchange basic parameters, including ASN and MD5 authentication values |
|
|
Keepalive |
Sent on a periodic basis to maintain neighbor relationship.
NOTE: If it does not receive a resopnce within the hold timer the neighbor is brought to a down state |
|
|
Update |
Used to exchange PAs and the associated prefix/length (NLRI) that use those attributes |
|
|
NLRI |
Network Layer Reachability Information
is the same thing as
prefix and length |
|
|
Notification |
Used to signal a BGP error: Typically results in a reset to the neighbor relationship |
|
|
null0 |
This is a discard route
NOTE: This is not meant to be advertised, it's only purpose is to enable the operation of the network command |
|
|
What Command
List possible default routes |
show ip bgp |
|
|
What Command
List possible routes per prefix |
show ip bgp prefix[subnet-mask] |
|
|
What Command
List routes learned from one neighbor, before any inbound filtering is applied |
show ip bgp neighbors ip-address received routes |
|
|
What Command
List routes learned from a specific neighbor that passed any inbound filters |
show ip bgp neighbors ip-address routes |
|
|
What Command
List routes advertised to a neighbor after applying outbound filtering |
show ip bgp neighbors ip-address advertised-routes |
|
|
What Command
List the number of prefixes per learned neighbor |
show ip bgp summary |

