![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
101 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Disk |
On one side a disk has a sliding write protect window that allows the disk to be written to or protected from any writing or changing of data that is occurring |
|
|
|
Read/write heads |
floppy drives have two read/write heads that are responsible for placing the data, the 1s and 0s onto the disk. |
|
|
|
# hard drive subsystem parts |
1)the hard drive, 2) a cable that attaches to an adapter or the motherboard, 3)control circuits located on an adapter or the motherboard |
|
|
|
RPM (revolutions per second) |
The hard drive platters spin at different rotational rated called RPMs. Common ones are 5400,7200,10000, 15000 rpm. The faster the rpm, the faster the transfer rate and generally, increase cost |
|
|
|
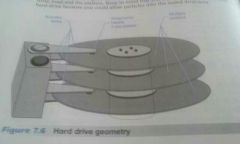
Head crash/ HDI (head to disk interference) |
If a read/write head touches the platter,a head crash occurs. This is sometimes called a HDI and it can damage the platters or the read/write head, causing data to corrupt |
|
|
|
Sectors |
Each track is separated into sectors, with the circle devided into smaller pieces. Normally each sector stores 512 bytes |

|
|
|
IDE (intergrated drive electronics) (hard drive) interface 1/2 |
Rules that make up a standard called an interface that governs communication with the hard drive.
Rules specify the number of heads on drive, what commands the drive responds to, the cables used with the drive, number of devices supported, the number of data bits transfered at one time. |
Aka ATA (ATX attachment)or EIDE(enhanced IDE) |
|
|
SCSI (small computer system interface) (Hard drive) interface 2/2 |
IDE is common &found in home and office computers. Commonly found in network servers. |
|
|
|
PATA (parallel ATA) |
Multiple devices can attach to the same bus with both types of devices. With parallel IDE or PATA, it was only 2 devices and with SCSI it was more. But the concept is the same. |
|
|
|
# |
When multiple devices share the same bus, they have to wait their turn to access the bus and there are configuration issues with which to contend |

|
|
|
SATA (serial ATA) |
The ATA serial device is known as SATA. A serial architecture is a point to point bus where each device has a single connection back to the controller. |

|
|
|
SAS (serial attached SCSI) |
The SCSI serial device is the SAS. A serial architecture is a point to point bus where each device has a single connection back to the controller. SAS drives come in two flavors-3 and 6Gbps. Normally hard drives but SAS could be used for other devices such as tape drives |

|
|
|
PATA (serial ATA) |
PATA is the older IDE/EIDE type which uses a 40 pin cable that connects the hard drive to an adapter or the motherboard and transfers 16 bits of data at a time. Each cable usually has three or two connectors. |

|
|
|
ATA/ATAPI (AT attachment packet interface) |
ATAPI increased support of devices such as CD/DVD and tape drives |
|
|
|
# |
A motherboard that has two IDE connectors connectors can have up to four PATA devices, two per motherboard connection. |
|
|
|
# if a PATA cable has two connectors and two devices are needed, buy another cable |
One 40 pin motherboard PATA connector can support up to two PATA devices. Some cables have two connectors-one that connects to the motherboard and one that attaches to the PATA device. If a second Is added, purchase a new cable |
|
|
|
# crosswalk |
Signals from one wire can interfere with the signals on an adjacent wire; this is called crosswalk |
|
|
|
SATA 1 |
The original specification transfers data at 1.5Gbps (1.5Gb/s) |
|
|
|
SATA 2 / II The 3Gbps version |
SATA 3 / III Runs at a max of 6Gbps which is the latest release III Runs at a max of 6Gbps which is the latest release Runs at a max of 6Gbps which is the latest release |
|
|
|
# SATA is a point to point interface which means |
1)each drive connects to the host through a dedicated link 2)each device has the entire interface bandwidth. SATA uses a smaller 7 pin cable that is more like a network cable than the traditional IDE ribbon cable |
|
|
|
# |
An internal SATA device uses a 15 pin SATA power connector rather than a molex that the older hard drives used. |

|
|
|
7 pin internal SATA device cables |

|
|
|
|
eSATA (External SATA) |
Provides external device connectivity using the SATA standard. Allows shielded cable lengths(6.56) with faster connections than USB 2.0 or most IEEE 1394 types |

|
|
|
SSD (solid state drive) |
are storage devices that are nonvolatile flash memory technologies instead of hard drive technologies. SSDs connect to the computer through several types of interfaces: SATA,SAS,PCIE,USB,PATA,SCSI |
|
|
|
SSD (solid state drive) |
SSDs eliminate the number one cause of of hard drive failure:moving parts. They're usually flash memory. Quit and fast |

|
|
|
# SSDs are used in the following industries. |
#Medical-CTR-MRI image storage # IT video surveillance # industrial robotic systems # automotive-diagnosis, store safety info, store travel statistics. |
|
|
|
Write amplification |
The minimum amount of memory storage space effected by a write request. Writing takes longer than reaflding. |
|
|
|
Wear levering |
A technique used to erase and write data using all of the memory blocks instead of the same memory blocks repeatedly. SSD manufacturers use various technologies. 1) software to track usage and direct write operations 2)a certain amount of reserved memory blocks to use when a memory block does fail. 3) a combination of the two techniques |
|
|
|
SLCc (single level memory cells) Tech used with SSD |
Store 1 bit in each memory cell and last longer than MLCs, but they are more expensive. |
|
|
|
MLC (multi level memory cells) Tech used with SSD |
Store more than 1 bit in each memory cell and are cheaper to manufacture. But they have slower transfer speeds |
|
|
|
SCSI 2 |
can control many different types of the vices such as scanners, tape drives, hard drives, optical drives, printers, and array subsystems The parallel SCSI standard allows a connection of multiple internal and external devices to the same adapter. |

|
|
|
MTBF (mean time between failures) |
The average number of hours before a drive or sodtware/hardware is likely to fail Measurement of how reliable a hard drive product or component is. |
|
|
|
Master or slave |
Each channel(connector) can have master or slave to distinguish between the devices. The 2 settings are simply used to distinguish between the two devices because only one of the two can transmit data when connected to the same IDE channel(cable) if two hard drives are installed on the primary channel one is primary master or primary slave |
|
|
|
Single IDE |
The single IDE setting is used when only one device connects to the cable. |
|
|
|
# Master or slave |
The master IDE setting is used in conjunction with the slave setting and both are used when two IDE devices vonnect to the same cable |
|
|
|
Cable select |
The cable select IDE option replaces the master/slave setting. The device automatically configures itself to either the master or slave setting depending on the specific cable connector to which the device attaches. |
|
|
|
# to use the cable select option |
A special 80-conductor,40-pin cable is needed. This cable has pin 28 disabled. All 80-conductor (40-pin) cable that meet the ATA specifications automatically support cable select, and the connectors are color coded |

|
|
|
# SATA physical installation |
SATA drives don't have master slave cable select, termination jumpers or settings. A serial 7-pin data connector attaches from the SATA controller to the internal SATA drive. A 15-pin cable connects power to the drive. Not berg or molex connector. It has its own connector. |

|
|
|
SCSI ID (drive select ID) |
Allows each device to share the same SCSI bus, and it assigns a priority for each device. The SCSI interface Allows a device to communicate directly with another SCSI device connected on the same SCSI chain. |
|
|
|
# |
Standard SCSI devices (8-bit) recognize SCSI IDs 0-7. Wide SCSI (16-bit)recognize SCSI IDs 0-15. The SCSI priority values follow from highest to lowest value |

|
|
|
SE (single-ended) terminator |
Terminators used by most SCSI devices. It can use passive and active and passive terminators |
|
|
|
Passive terminator |
Terminators used on SCSI-1 devices. They are not good for long cable distances because they are susceptible to noise interference |
|
|
|
FPT (forced perfect termination) |
A special type of active terminator that can be used with SE devices |
|
|
|
HVD (high-voltage differential) |
A technology that was used in a few SCSI-2 devices that allowed a longer SCSI bus length. HVD devices must use HVD terminators (sometimes called differential terminators) |
|
|
|
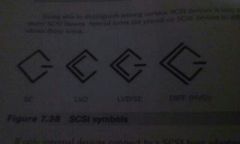
LVD (low-voltage differential) |
A technology that is backwards compatible with SE and required on all devices that adhere to the ultra SCSI standard. LVD bus length can also be up to 39ft (11.88meters) depending on the number of devices. LVD devices use either LVD terminators or LVD/SE |
|
|
|
Pass through terminator |
A terminator used by most internal hard drives. It has an extra connector and allows a device that does not have terminators to be terminated through the connector that attaches the cable |
|
|
|
Daisy chaining |
SCSI allows multiple devices to be connected to one SCSI host adapter and share the same SCSI bus;. Daisy chaining is like Connecting multiple Christmas lights sets together. If multiple internal SCSI devices attach to the SCSI adapter, then use an internal SCSI cable with multiple connectors |
|
|
|
# SAS |
An interesting point about SAS Is is that some SAS connectors can accept SATA 3 devices. However, the reverse is not true- you cannot attach a SAS device to a SATA connector |
|
|
|
AHCI (advanced host controller interface) |
Mode, which won installed, allows SATA drives to be inserted/removed when power is on and use commands that allow the host circuits to communicate with attached devices to implement SATA features |
|
|
|
# SATA drives can be set in different modes of operation: |
(1) legacy mode, which is used in a system that doesn't have SATA drivers natively.(2) AHCI (3) Raid mode. |
|
|
|
Legacy mode |
used in a system that doesn't have SATA drivers natively. |
|
|
|
# hard drive preparation |
(1) portions the hard drive (2) high-level format the hard drive |
|
|
|
Partitioning |
A hard drive allows a drive letter to be assigned to one or more parts of the hard drive. |
|
|
|
High-level formatting |
Prepares the drive for use for a particular file system. This allows the drive to accept data from the operating system. from the operating system. |
|
|
|
# |
For today's computers a drive cannot be used until it has been partitioned and high-level formatted |
|
|
|
Disk management |
Replaced FDISK. A program that is available after the operating system is installed, or by using the diskpart utility from the command line. |
|
|
|
File system |
Defines how data is stored on a drive. The most common windows file systems are: FAT16, FAT32, exFAT, NTFS. |
|
|
|
CDFS (Compact disk file system) (File system) |
A file system for optical media |
|
|
|
FAT/FAT 16 (File system) |
Used with all versions of Windows. 2 GB portion limitation with old operating systems. 4GB partion limitation with all versions of Windows xp or higher. |
|
|
|
FAT32 |
Used with all versions of Windows 9xand higher. Supports drives up to 2TB. Can recognize volumes greater than 32GB, but cannot create them that big |
|
|
|
NTFS |
Used with Windows xp, Vista, and 7. Supports drives up to 16EB(equals 16 billion bytes) but in practice is only 16TB (equals 16 thousand bytes). Supports file compression and file security. NTFS allows faster file acess and uses hard drive space more efficiently. |
|
|
|
NTFS 2 |
Supports individual file compression and has the best file security |
|
|
|
Cluster |
The operating system sets aside one cluster as a minimun for every file. A cluster is the smallest amount of space reserved for one file and is made up of a specific number of sectors |

|
|
|
# how to convert partions |
Use the convert program in Windows to convert a FAT16, FAT32, or exFAT partion to NTFS. Acess a command prompt window, type the following commands. Convert x: /FS:NTFS |
|
|
|
Primary partion |
If there is only one hard drive installed in a system and the entire hard drive is one partion, it is the primary partion. The primary partion on the first detected hard drive is assigned the drive letter c:. |

|
|
|
Extended partion |
If the drive is devided so only part of the drive is the primary partion, the rest of the cylinder can be designated as extended partion. An extended partion allows a drive to be further devided into logical drives |

|
|
|
Logical drives/ volume |
Assigned a drive letter and can include a logical drive as well as a removable media such as a CD, diskette,DVD, BD, or flash drive Assigned drive letters such as D:,E:, or others |

|
|
|
MBR (master boot record) |
The partion table is part of the MBR that contains a program that reads the partion table, looks for the primary partion marked as active, and goes to that partion to boot the system. |
|
|
|
MBR (master boot record) |
The partion table is part of the MBR that contains a program that reads the partion table, looks for the primary partion marked as active, and goes to that partion to boot the system. |
|
|
|
System partion |
A windows system partion Is the partition on the hard drive that holds the hardware-specific files needed to load the operating system. |
|
|
|
Boot partition |
A windows boot partition is the partition on the hard drive that contains the operating system. The boot partition and the system partion can be on the same partition with windows |
|
|
|
HPA (host protected area) |
A hidden area of the hard drive used to hold a copy of the operating system; sometimes installed applications use the HPA when the operating system becomes so corrupted that re-installation us necessary |
|
|
|
GPT (GUID/globally unique identifier, partion table) |
A partion type that is not shown. Available with 64-bit windows operating systems. Allows up to 128 partions and volumes up to 18EB. |
|
|
|
GPT 2 |
GPT partitioning is accomplished using disk management tool or using the diskpart command-line utility. A GPT disk can also have more than the MBR-based disk limit of four primary partions |
|
|
|
Basic storage (Local disk management terms) |
One of the two types of storage. This is what has traditionally been known as partition. It is the default method because it is used by all operating systems |
|
|
|
Basic disk |
Any drive that has been partitioned and setup for writing files. A basic disk has primary partitions, extended partitions, and logical drives contained within the extended partitions |
|
|
|
Dynamic storage (Local disk management terms) |
The second type of storage; contrast with basic storage. Allows you to create primary partitions, logical drives, and dynamic volumes on removable storage devices. More powerful than basic storage and uses dynamic disk |
|
|
|
Dynamic disk (Local disk management terms) |
A disk made up of volumes. A volume can be the entire hard disk, parts of the hard disk combined into one unit, and other specific types of volumes, such as single,panned,Dr stripped volumes Cannot be on a removable drive |
|
|
|
Simple volume (Local disk management terms) |
Disk space allocated from one hard drive. The space does not have to be contagious |
|
|
|
Spanned volume (Local disk management terms) |
Disk space created from multiple hard drives. Windows writes data to a spanned volume in such a way that the first hard drive is used until the space is filled. Then, the second hard drive space is used for writing. This continues until all hard drives in the spanned vole are utilized |
|
|
|
Stripped volume/stripping/ RAID 0 (Local disk management terms) |
Data is written across 2-32 hard drives. It is different from a spanned volume in that each drive is used alternately. |
|
|
|
System volume (Local disk management terms) |
Holds the files needed to boot the operating system. |
|
|
|
Boot volume (Local disk management terms) |
Holds the remaining operating system files. Can be the same volume as the system volume |
|
|
|
RAW volume (Local disk management terms) |
A volume that has never been high-level formatted random does not contain a file system |
|
|
|
RAID (Redundant Array of independent disks) |
Allows reading from and writing to multiple hard drives for larger storage areas, better performance, and fault tolerance. |
|
|
|
# FAULT TOLERANCE |
Fault tolerance is the ability to continue functioning after a hardware or software failure |
|
|
|
Disk duplexing /Disk mirroring / RAID 1 |
Protects against hard drive failure. Uses two or more hard drives and one disk controller. |
|
|
|
Disk striping/RAID 0 |
Data is alternatively written on two or more hard drives, which increases system performance. These drives are seen by the system as one logical drive. RAID 0 does not protect data when the hard drive fails. This is th e fastest read and write performance |
|
|
|
RAID 5/ Disk striping with parity |
Writes data to three or more hard drives. Included with data is parity information. If the drive fails, the data can be rebuilt from the two other drives' information. This level can read and write data quickly |
|
|
|
Quick format--full format(standard) |
Scans for and marks bad sectors. This prevents the operating system from being installed on a sector thst may cause operating system issues. The quick format simply prepares the drive for data and takes a lot less time than a full format |
|
|
|
FATs(File allocation tables) |
The high-level format creates two FATs: one primary one secondary. The formatting process also creates the root directory that renumbers the sectors |
|
|
|
DBR (DOS boot record) Boot sector |
The area of the disk that contains information about the system files is the DBR. Located on the hard drives cylinder 0 head 1, sector 1. |
|
|
|
Lost clusters |
Clusters disassociated from data files. They occupy disk space |
|
|
|
Disk cleanup |
A program windows has that removes temporary files, offline Internet files, empties the recycle bin, compresses unused files, removes unused programs, (1) start>all programs>accessories>system tools>disk cleanup (2)select drive letter and click OK (3) |
|
|
|
Defragmentation |
The process of placing files in contiguous sectors |

|
|
|
Incremental backup |
Backs up all files that have changed since the last backup. The files selected are the ones that have the archive bits set to on |
|
|
|
Differential backup |
Backs up files that have been changed since the last full backup. (Files that have the archive nit set to on), but the backup software does not reset the archive bit like the incremental backup does |
|
|
|
BitLocker |
A drive encryption to protect and entire disk volume including the operating system, user files, swap files, and hibernation files On vista/7, enterprise & ultimate, Windows 8 pro enterprise, Requires two NTFS disk partions |
|
|
|
Drive wiping And overwriting |
If donating wipe, delete the hard drive partition and recreate them. |
|
|
|
Overwrites |
Utility that some drive manufacturers have that rewrites hard drives. The hard drive with all 1s or all 0s to prevent data remnants from being recovered |
|
|
|
Disk caches |
An easy way to speed up a hard drive. Puts data into RAM where it can be retrieved much faster than If the data is Still on the hard drive. |
|

