![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Circulatory Pathway Through Heart |
Superior and Inferior Vena Cava -> Right Atrium -> Right Ventricle -> Pulmonary Arteries -> Lungs -> Pulmonary Veins -> Left Atrium -> Left Ventricle -> Aorta -> Body |
|
|
Circulatory Pathway Through Heart |
Three Portal Systems: Blood travels through an extra capillary bed before returning to the heart. - Liver (hepatic), kidney, and brain (hypophyseal). |
|
|
Fetal Circulation |
Foramen Ovale: Connects right and left atria. Ductus Arteriosus: Connects pulmonary artery to aorta. Along with foramen ovale, shunts blood away from lungs. Ductus Venosus: Connects umbilical vein to inferior vena cava, connecting umbilical circulation to central circulation. |
|
|
Blood Components |
Plasma: Aqueous mixture of nutrients, wastes, hormones, blood proteins, gases, and salts. |
|
|
Blood Components |
Erythrocytes (red blood cells): Carry oxygen - Hemoglobin: four subunits carry O2 and CO2. Iron controls binding and releasing. - Oxygen-hemoglobin Dissociation |
|
|
Blood Components |
Leukocytes (white blood cells): Function in immunity. |
|
|
Blood Components |
Platelets: Clotting - Platelets release thromboplastin, which (along with cofactors calcium and vitamin K) converts inactive prothrombin to active thrombin - Thrombin converts fibrinogen into fibrin, which surrounds blood cells to form the clot. |
|
|
Blood Typing |
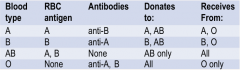
|
|
|
Blood Typing |
- Antigens are located on the surface of red blood cells. - Blood cells with Rh factor are Rh+; these individuals produce no anti-Rh antibody. Rh- blood cells lack the antigen; these individuals produce an antibody if exposed. |

