![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a tangent? |
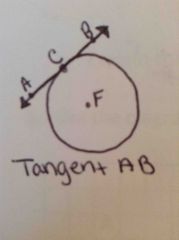
A line in the plane of the circle that intersects the circle at exactly one point |
|
|
What is the point of tangency |
The point where the tangent intersects the circle |
|
|
What is a secant? |
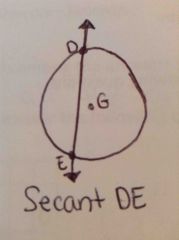
A line in the plane of the circle that intersects the circle at two points |
|
|
What are tangent circles? |
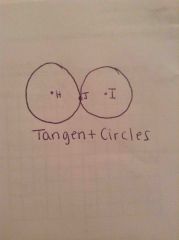
Two circles that intersect at one point. |
|
|
What are cocentric circles? |
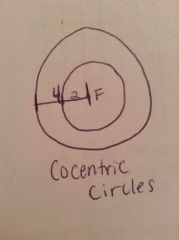
Circle that share a common center |
|
|
What is a common tangent? |
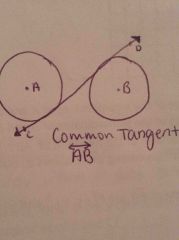
A tangent line or segment that intersects two coplanar circles |
|
|
What is a radius? |
A line segment connecting the center of a circle to any point on the outside of the circle |
|
|
What is a diameter? |
A line connecting two points outside the circle and goes through the center of the circle |
|
|
What is a chord? |
A line segment connecting any two points on a circle |
|
|
Tangent Line to a Circle Theorem (10.1) |
A line is tangent to a circle if and only if it is perpendicular to a radius |
|
|
External Tangent Congruent Theorem(10.2) |
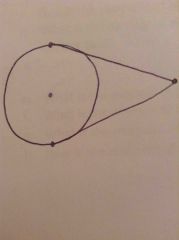
If two tangent segments to a circle share a common endpoint outside the circle, then the two circles are congruent |
|
|
What is an arc? |
Part of a circle equal to the degrees of the central angle it corresponds |
|
|
What is a major arc? Minor? Semi circle? |
A major arc is greater the 180 degrees. A minor is less then 180. A semi circle is 180(is a diameter) |
|
|
Arc addition postulate |
The measure of a arc formed by two adjacent arcs is the sum of the measures of the two arcs |
|
|
What is the formula for find arc length? |
(Measure arc/360)x2pixr |
|
|
Congruent Circles Theorem (10.3) |
Two circles are congruent if and only if they have the same radius |
|
|
Congruent Central Angles Theorem (10.4) |
In the same circle, or in congruent circles, two minor arcs congruent if and only if their corresponding angles are congruent |
|
|
Similar Circles Theorem(10.5) |
All circles are similar |
|
|
Congruent Corresponding Chords (10.6) |
In the same circle, or in congruent circles, two minor arcs are congruent if and only if their corresponding chords are congruent |
|
|
Perpendicular Chord Bisector Theorem(10.7) |
If the diameter of the circle is perpendicular to a chord, then the diameter bisects the chord and its arc |
|
|
Perpendicular Chord Bisector Converse (10.8) |
If a chord of a circle is a perpendicular Bisector of another chord, then the first chord is a diameter |
|
|
Equidistant chords Theorem(10.9) |
In the same circle, or congruent circles, 2 chords are congruent if and only if they are equidistant from the center |
|
|
What is an inscribed angle? |
A angle whose vertex is on the circle and whose sides are chords of the circle |
|
|
Measure of an Inscribed angle theorem (10.10) |
The measure of an inscribed angles is 1/2 the measure of its intercept arc |
|
|
Measure of an Inscribed angle theorem (10.10) |
The measure of an inscribed angles is 1/2 the measure of its intercept arc |
|
|
Inscribed angles of a circle (10.11) |
If two inscribed angles of of a circle intercept the same arc, the. The angles are comgruent |
|
|
Inscribed right triangle theorem(10.12) |
If a right triangle is inscribed in a circle, then the hypotenuse is the diameter of the circle |
|
|
Inscribed Quadrilateral Theorem(10.13) |
A quadrilateral can be inscribed in a circle of and only if it's opposite angles are supplementary |

