![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the most common type of chromosome anomaly?
|
Sporadic trisomies
|
|
|
What is the most common trisomy?
|
Trisomy 16
It is incompatible with life |
|
|
What is the most common chromosomal anomaly compatible with life?
|
Trisomy 21
|
|
|
What are the general characteristics of children with Trisomy 21?
|
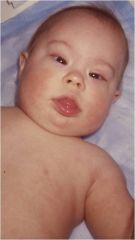
1. Multi-system anomalies
2. Congenital heart defects 3. Hypotonia (floppy) 4. Developmental Impairment 5. Increased risk of leukemia 6. Nuchal thickening 7. Small, C-shaped ears |
|
|
What is the maternal age effect?
|
As mothers age, so do their eggs. This leads to a greater possibility of nondisjunction and thus a child with Trisomy 21.
|
|
|
What are the general characteristics of children with Trisomy 18?
|
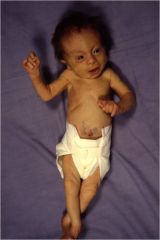
1. Small for gestational age
2. Severe CNS malformations 3. Multi-system anomalies 4. Neurologic Fisting 5. Rocker bottom foot 6 Syndactyly of toes 2 and 3 7. Scissoring of legs 8. Hypogonadism 9. Overwhelming majority die withing first 6 to 12 months |
|
|
What are the general characteristics of children with Trisomy 13?
|
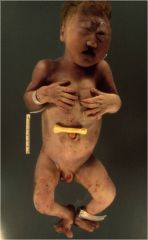
1. Craniofacial anomalies (punched out areas on scalp)
2. Severe brain defects 3. Heart defects 4. Most die withing first few months of life if they weren't spontaneously aborted already |
|
|
What are the general characteristics of children with 4-P Syndrome: Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome?
|
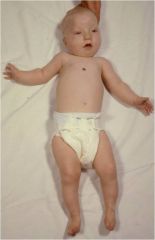
1. Trojan like face
2. Multiple congenital malformations 3. Mod. to severe developmental impairments (microencephaly) 4. Seizures 5. Ambiguous genitalia 6. Coloboma (pupil goes into iris) |
|
|
What are the general characteristics of children with cri-du-chat (5p-)?
|
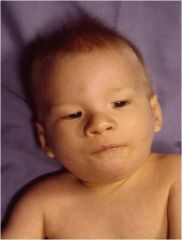
1. Deletion of short arm of chromosome 5
2. Severe developmental retardation (microcephaly) 3. High pitched, "cat-like" cry 4. Simplistic face 5. Aggressive behavioral pattern 6. No interest in self-help activities (potty training etc.) |
|
|
What are the general characteristics of children with Turner Syndrome (Monosomy X)?
|

1. Puffy hands and feet at birth
2. Small stature 3. Nuchal webbing 4. Congenital heart defects 5. Absent or delayed sexual maturity |
|
|
What is mosaicism in regard to monosomy x?
|
1. Not all of your cells are monosomy X (20% of those with Turners)
2. If you have mosaicism there is a possibility of still becoming pregnant |
|
|
What are the general characteristics of children with Klinefelter Syndrome (47, XXY)?
|
1. Small, firm to hard testes
2. Tall stature 3. Increased probability of learning difficulties 4. Infertile 5. Breast enlargement and female fat distribution 6. Low testosterone: elevated LH/FSH 7. 1 in 700-1000 males |
|
|
What does it mean to have contiguous gene syndromes (segmental aneusomy)?
|
Disorders that result from the deletion or duplication of adjacent genes in a specific chromosomal region
|
|
|
What is a well-known contiguous gene syndrome?
|
DiGeorge syndrome
|
|
|
What are the general characteristics of children with a deletion of 22q11.2 (DiGeorge and other contiguous gene syndromes)?
|
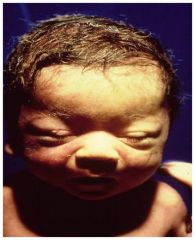
1. Craniofacial anomalies
2. Feeding/failure to thrive 3. Hearing loss 4. Cognitive/developmental delay 5. Mental illness 6. Autism spectrum disorders 7. Cardiac defect 8. Small/absent thymus 9. Endocrine abnormalities |
|
|
What are the general characteristics of children with Williams syndrome?
|
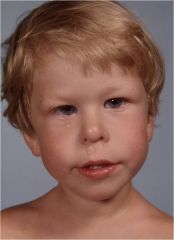
1. Characteristic facies(make sure you pick up the right child at the picnic)
2. Cardiovascular anomalies 3. Infantile hypercalcemia and growth retardation 4. 1 in 10,000 births |
|
|
What are the indications for performing a chromosome analysis?
Possible Test Question |
1. Neonate with multiple congenital anomalies
2. Mental retardation and developmental delay with or without congenital anomalies 3. Down syndrome 4. Family Hx of Down syndrome 5. Recurrent spontaneous abortions 6. Abortus tissue 7. Couple with Hx of infertility 8. Short stature in female with primary amenorrhea 9. Ambiguous genitalia |
|
|
What is the one diagnostic test you always perform if you suspect any chromosome anomaly?
|
Echocardiogram
|
|
|
Who is mitochondrial DNA inherited from?
|
Mother, but "male leakage" is documented
|
|
|
True or False
Mitochondrial DNA sequences are more susceptible to mutation than nuclear DNA. |
True
|
|
|
What is the pattern of mitochondrial inheritance with regard to a pedigree?
|
Affected female has all affected children
(inheritance may resemble Mendelian autosomal dominant) |
|
|
What is the frequency of of mitochondrial disorders?
|
1 in 5,000
|
|
|
What do mitochondrial disorders primarily affect?
|
Nerve and muscle tissue which rely heavily on high levels of energy production
|
|
|
Human triploid fetus characteristics (paternal inheritance vs. maternal inheritance)
|
1. 2 paternal and 1 maternal set of chromosomes have large, cystic placentas and poorly developed fetus.
2. 2 maternal and 1 paternal genome yields a very small placenta but relatively well developed fetus. |
|
|
Characteristics of Prader-Willi Syndrome
|
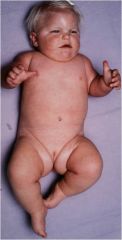
1. Chromosome 15 q11-13
2. Absent paternal gene expression 3.Hypothalmic insufficiency 4. Hypotonia 5. Developmental delay 6 Hyperphagia leading to obesity 7. Mental impairment |
|
|
Characteristics of Angelman Syndrome
|
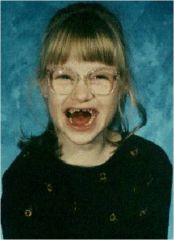
1. Chromosome 15q11-13
2. Absent maternal gene expression 3.Severe developmental delay and mental impairment 4. Inappropriate happy demeanor including frequent laughing, smiling, and excitability 5. Gait ataxia (puppet-like) 6. Seizures |
|
|
Characteristics of Sotos Syndrome
|

1. Related to defect in tumor suppressor genes
2. Big brain; dilated ventricules; extra axial fluid 3. Angular facies 4. Risk of embrynal tumors 5. Assymetric 6. Interesting Gait |
|
|
Characteristics of Beckwith-Weidemann syndrome
|
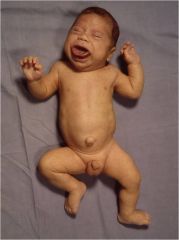
1. Associated with tumor suppressor genes
2. Macroglossia 3. Everything is just bigger 4. High risk of embrynal tumors 5. Cognitively normal 6. Hypoplasia of islet cells and leads to hypoglycemia |
|
|
General Facts about Trinucleotide repeats
|
1. Usually results in down regulation of transcription of associated gene
2. Associated with neurological degeneration 3. Autosomal dominant or X-linked recessive predisposition 4. Common Conditions: Huntington Chorea Fragile X Myotonic dystrophy Spinocerebellar ataxias |
|
|
Characteristics of Fragile X
|

1. X-linked dominant
CGG repeats (>200 has full mutation) 2. Mod-severe in boys; milder in girls 3. Delayed motor and verbal development 4. Autistic features 5. Hypermobility |
|
|
Indications for testing for Fragile X Syndrome
|
1. Male family member who is autistic
2. Male(s) with learning disability 3. Female with learning disability planning to have a child 4. Family member with a serious learning problem and/or mental retardation 5. Family member with developmental delays especially in speech and gross motor skills |
|
|
Characteristics of Incontinentia Pigmentia
|
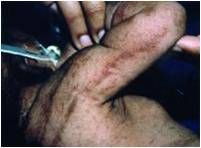
1. Clinical expression related to pattern of X-chromosome inactivation
2. X-linked dominant disorder with lethality in males 3. Germ line mosaicism |
|
|
Characteristics of Cat-eye syndrome
|
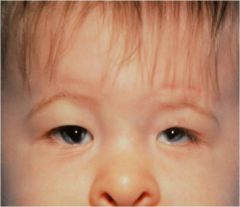
1. Mosaicism for a marker chromosome derived from chromosome 22
2. Partial trisomy 22 |
|
|
Killian-Pallister Syndrome
|
1. Tetrasomy 12p mosaicism
2. Usually identified only in skin fibroblast cultures 3. Blood chromosome analysis is usually normal |

