![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
tissue
|
collection of similar cels that act together to perform a function
|
|
|
4 main types of tissues
|
-epithelial
-connective -muscle -nervous |
|
|
epitelial tissue
|
covers and lines most of the body but also some parts fiund within the body.
these cells are packed tightly together forming a sheet that has no blood vessels in it |
|
|
shapes of epithelial cells
|
-squamous
-cuboidal -columnar -transitional |
|
|
squamous
|
flat or scalelike
|
|
|
cuboidal
|
cube-shaped
|
|
|
columnar
|
columnlike
|
|
|
transitional
|
stretchy and variably shape
|
|
|
simple
|
cells are arranged in a single layer
|
|
|
stratified
|
cells are arranged in several layers
|
|
|
pseudostratified
|
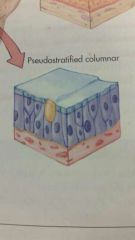
epithelium that looks stratified but isnt
|
|
|
membrane
|
sheetlike structure found throughout the body that perform special functions.
|
|
|
matrix
|
noncellular material in which cells can be embedded
|
|
|
epithelial membrane
|
posses a layer of epithelial tissue and a thin bottom layer of a specialized connective tissue
|
|
|
epithelial membrane divided into 3 sections
|
-cutaneous
-serous -mucous |
|
|
cutaneous
|
aka skin
main organ of the integumentary system makes up 16% of total body weight |
|
|
serous
|
two layered membrane with potential space in between
-parietal -visceral |
|
|
parietal
|
lines the wall of the ventral body cavities
also produces serous fluid, reduces friction between tissues and organs |
|
|
visceral
|
wraps around the organs
also produces the serous fluid, reduces friction between tissues and organs |
|
|
mucous
|
lines openings to the outside of the body,
named this because they contain special cells that produce mucus |
|
|
connective tissue
|
holding things together provides structure and support, storing fluid and nutrients.
|
|
|
connective tissue 4 subcategories
|
-connective tissue proper
-cartilage -bone -blood |
|
|
connective tissue proper
|
delicate webs of loose connective tissue that holds tissues and organs together
|
|
|
cartilage
|
had its cells embedded in tiny holes in a gelatinous matrix
|
|
|
bone
|
hardest if your tissues, cells live in holes called lacunae, the matrix is made of calcium and phosphate thus is very hard
|
|
|
synovial
|
is the membrane type associated with connective tissue
|
|
|
synovial fluid
|
found in the spaces between joints and produces slippery substance, reduces friction
|
|
|
muscle tissue
|
provides the means for movement by and within the body
|
|
|
3 types of muscle tissue
|
-skeletal
-cardiac -smooth |
|
|
skeletal muscle
|
striated, is attached to bones and causes movement by contracting and relaxing
|
|
|
voluntary muscle
|
conscious effort
|
|
|
cardiac muscle
|
found in the walls of the heart
|
|
|
involuntary muscles
|
subconscious movement
|
|
|
smooth muscle
|
forms the walls of hollow organs
|
|
|
nervous tissue
|
acts as arapid messenger service for the body
|
|
|
nervous tissue 2 subcategories
|
-neurons
-neuroglia |
|
|
neurons
|
conductors of information
|
|
|
neuroglia
|
cells function as support cels
|
|
|
dendrites
|
branchlike formations that make up party of the neuron,
they receive sensory information |
|
|
axon
|
trunklike shaped structure,
transports information away from the cell body |
|
|
meninges
|
membranes associated with nervous tissue covering the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
fibroblasts
|
cells that can develop into connective tissue
|
|
|
vital organs
|
organs you can not live without
|
|
|
muscular system.
|
responsible for getting you up and moving.
|
|
|
integumentary system
|
regulates the body temperature, and changes the diameter of blood vessel
|
|
|
nervous system
|
rapid messenger of the body that both receives and sends message for activities to occur
|
|
|
sensations
|
measurements of conditions that occur inside and out the body
|
|
|
3 main function for nervous system
|
sensory, processing and interpreting messages, and motor
|
|
|
4 main part of the nervous system
|
nerve cells, spinal cord and fluid, peripheral nerves, and the brain
|
|
|
endocrine system
|
release chemical substance called hormones, reguate the bodys metabolic process, regulate the fluid and the eletrolyte balances of the body
|
|
|
cardiovascular system
|
main transport system to each cell in the body, substance necessary for life and transported to the cells and waste is transported away from cells.
|
|
|
respiratory system
|
supplies us with fresh oxygen, maintain proper acid-base balance of the blood and aids in eliminating ingested alcohol
|
|
|
lymphatic system
|
responsible for helping to maintain proper fluid balance in our body and protecting it from infection
|
|
|
lymph nodes
|
act as filters to capture unwanted infective agent
|
|
|
immune system
|
produces special infection-fighting whute blood cells
|
|
|
lymphocytes
|
infection-fighting whiteblood cells
|
|
|
digestive system
|
breaks down raw materials mechanically and chemically into a use able substance, then is absorbed and transported to the cells or the waste part of the body
|
|
|
urinary system
|
filtration of the blood and eliminate waste products, regulate number of red blood cells and the acid-base and electrolyte balance of the blood
|
|
|
reproductive system
|
reproduces offspring so we can continue to exist
|
|
|
genitourinary//GU system
|
reproductive and urinary systems combined
|

