![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
77 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A portion of the lamina located between the superior and inferior articular processes is called the ________. |
Pars interarticularis |
|
|
The superior and inferior vertebral notches join together to form the:
|
Intervertebral Foramina |
|
|
Which radiographic position best demonstrates the Intervertebral foramina? |
Lateral position |
|
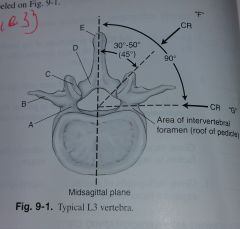
Label A-G |
A. Pedicle B. Transverse processes C. Superior articular process and facet D. Lamina E. Spinous process F. This CR best demonstrates Zygapophyseal Joints G. This CR best demonstrates Intervertebral Foramina |
|
|
Would the degree of angle to demonstrate the Zygapophyseal joints be greater or lesser for the lower lumbar vertebrae compared with the upper? |
50 degree for upper, 30 degree for lower vertebrae to the midsagittal plane. |
|
|
The small foramina found in the sacrum are called: |
Pelvic Sacral Foramina |
|
|
The anterior and superior aspect of the sacrum that forms the posterior wall of the pelvic inlet is called the:__ |
Promontory |
|
|
What is another term for the sacral horns? |
Cornua |
|
|
The sacroiliac joints lies at an oblique angle of ____ degrees to the coronal plane? |
30 Degrees |
|
|
What is the formal term for the tail bone? |
Coccyx |
|
|
What is the name for the superior broad aspect of the coccyx? |
base |
|
|
What classification, mobility type, and movement type is the zygapophyseal joint? |
Synovial, diarthodial, plane |
|
|
What classification, mobility type, and movement type is the intervertebral joint? |
Cartilaginous, ampiarthrodial, none |
|
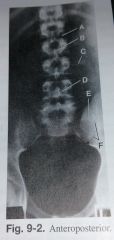
Label A-F |
A. Intervertebral disk space of L1-L2 B. Spinous Process of L2 C. Transverse process of L3 D. Region of lamina (body) of L4 E. Left ala of sacrum F. Left sacroiliac joint |
|
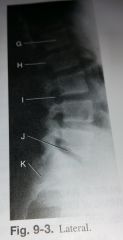
Label G-K |
G. Body of L1 H. Pedicles of L2 I. Intervertebral foramina J. Intervertebral disk space of L5-S1 K. Sacrum |
|
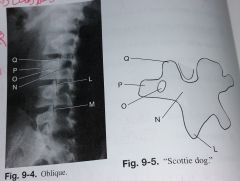
label L-Q |
L. Inferior articular process of L3 M. Zygapophyseal joint of L4-L5 N. Pars Interarticularis (neck) of L3 O. Pedicle of L3 P. Transverse process of L3 (nose) Q. Superior articular process of L3 (ear) |
|
|
What joint or foramina is demonstrated in a LPO? |
Left Zygapophyseal Joint |
|
|
What joint or foramina is demonstrated in a RAO? |
Left Zygapophyseal Joint
|
|
|
What joint or foramina is demonstrated in a Lateral |
Intervertebral Foramina |
|
|
What joint or foramina is demonstrated in a RPO? |
Right zygapophyseal joint |
|
|
What joint or foramina is demonstrated in a LAO? |
Right zygapophyseal joint |
|
|
The degree of obliquity required for an oblique projection at the T12-L1 level is approximately ____ degrees, whereas the L5-S1 level spine requires a(n) _____ degree oblique. Therefore, a(n) _____ degree oblique is performed for general lumbar spine? |
50 degrees, 30 degrees, 45 degrees |
|
|
What vertebral level is the ASIS at? |
S1-S2 |
|
|
What vertebral level is the Xiphoid Process at? |
T9-T10 |
|
|
What vertebral level is the Lower Costal Margin at? |
L2-L3 |
|
|
What vertebral level is the Iliac Crest at? |
L4-L5 |
|
|
What vertebral level is the Symphysis Pubis at? |
Tip of Coccyx |
|
|
T or F: The use of higher kV and lower mAs for L-spine radiography improves radiographic contrast but increases patient dose? |
False |
|
|
T or F: Placing a lead blocker mat behind the patient for lateral lumbar spine positions improves image quality |
True |
|
|
T or F: Gonadal shielding should always be used for male and female patients for studies of the L-Spine, Sarcrum, and coccyx |
False |
|
|
T or F: The AP projection of the L-Spine opens the intervertebral joint spaces better than than the PA projection |
False |
|
|
T or F: The knees and hips should be extended for an AP projection of the L-Spine |
False
|
|
|
T or F: An increased SID of 44-46 inches reduces distortion of spine anatomy? |
True |
|
|
T or F: The lead blocker mat and close collimation must not be used when performing digital imaging of the L-Spine |
False |
|
|
With a 14x17 IR, the CR is centered at the level of the _____ for AP and lateral L-Spine projections |
Iliac Crest |
|
|
Which two structures can be evaluated to determine whether rotation is present on a radiograph of an AP projection of the L-Spine? |
A. SI joints are equidistant from the spine B. Spinous process should be midline to the vertebral column (transverse processes are equal length) |
|
|
How much rotation is required to properly visualize the zygapophyseal joints at the L5S1 level? |
30 degrees |
|
|
Which specific set of zygapophyseal joints is demonstrated with an LAO position? |
Right (upside) |
|
|
The _____, which is the eye of the "Scottie dog", should be near the center of the vertebral body on a correctly obliqued lumbar spine. |
Pedicle |
|
|
Which positioning error has been committed if the pedicle is projected too far posterior with a 45 degree oblique position of the L-spine? |
Excessive rotation |
|
|
Which position or projection of the L-spine series best demonstrates a possible compression fracture? |
Lateral |
|
|
A patient with a wide pelvis and narrow thorax may require a CR angle of ______ degrees _____ for a lateral position of the L-spine? |
5-8 degrees caudad |
|
|
How should the spine of a patient with scoliosis be positioned for a lateral position of the L-Spine? |
With the sag or convexity of the spine closest to the IR |
|
|
Why should the knees and hips be flexed for an AP lumbar spine projection? |
Reduces lumbar curvature which opens up the intervertebral disk space |
|
|
Where is the CR centered fora lateral L5-S1 projection of the L-spine? |
1.5 inches inferior to the iliac crest and 2 inches posterior to ASIS |
|
|
What amount and direction of CR angulation is required for an AP Axial L5-S1 projection on a male patient? |
30 degrees cephalad |
|
|
T or F: A PA or AP projection for a scoliosis series frequently includes one erect and one recumbent position for comparison |
True |
|
|
T or F: The lower margin of the cassette must include the pubic symphysis for a scoliosis series |
False |
|
|
T or F: A PA projection for a scoliosis series produces only about 1/10 the dose to the breasts as compared with the AP projection, even if proper collimation is used |
True |
|
|
Which once of the following techniques or devices produces a more uniform density along the vertebral column for an AP/PA scoliosis projection? a. use of a 14X36 inch cassette b. lower kV C. Higher mAs D. Compensating Filter |
D. Compensating Filter |
|
|
Which side of the spine should be elevated for the second exposure for the AP/PA projection (ferguson method) scoliosis series (by having the patient stand on a block with one foot)? |
The Convex side of the spine |
|
|
During the AP (PA) right and left bending projectiions of the L-spine, the _____ must remain stationary during positioning. |
pelvis |
|
|
Which projections should be taken to evaluate flexibility following spinal fusion surgery? |
Hyperextension and Hyperflexion |
|
|
How much CR angulation is required for an AP projection of the sacrum for a typical male patient? |
15 degrees cephalad |
|
|
If a patient cannot lie on his back for the AP sacrum because it is too painful, what alternate projection scan be taken to achieve a similar view of the sacrum? |
A PA prone with 15 degree caudad CR angle |
|
|
Where is the CR centered for an AP projection of the Coccyx? |
2 inches superior to pubic symphysis |
|
|
T or F: The AP projections of the sacrum and coccyx can be taken as one single projection to decrease gonadal dose. |
False |
|
|
Patients should be asked to empty the urinary bladder before performing which projection(s) of the vertebral column? |
AP Sacrum and Coccyx |
|
|
In addition to good collimation, what should be done to minimize overall "fogging" on a lateral lumbar spine or lateral sacrum and coccyx radiograph? |
Place lead blocker on tabletop behind patient |
|
|
Which sacroiliac (SI) joint is visualized with an RPO position? |
Left |
|
|
How much rotation of the body is required for oblique positions of the SI joints? |
25-30 degrees |
|
|
What type of CR angle is recommended for the AP axial projection of the SI joints on a female patient? a. 20 degrees cephalad b. 30 degrees cephalad c. 30 degrees caudad d. 35 degrees cephalad |
d.35 degrees cephalad |
|
|
Where is the CR centered for an oblique projection of the SI joints? |
1 inch medial from upside |
|
|
A radiograph of an AP projection of the lumbar spine reveals that the spinous processes are not midline to the vertebral column and distortion of the vertebral bodies is present. Which specific positioning error is present on this radiograph? |
Rotation of the spine |
|
|
A radiograph of an LPO projection of the lumbar spine reveals that the downside pedicles and zygapophyseal joints are projected over the anterior portion of the vertebral bodies. Which specific positioning error is present on this radiograph? |
insufficient rotation of the spine |
|
|
A radiograph of a lateral projection of a female lumbar spine reveals that the mid- to lower intervertebral joint spaces are not open. The technologist supported the midsection of the spine with sponges to straighten the spine. What else can be done to open the joint spaces during the repeat exposure? |
If the patient has a wide pelvis the CR can be angled 5-8 degrees with caudad |
|
|
A radiograph of a lateral L5-S1 projection reveals that the joint space is not open. The technologist did support the middle aspect of the spine with a sponge. What else can the technologist do to open up the joint space during the repeat exposure? |
Place additional support beneath spine or use a 5-8 degree caudad angle |
|
|
A radiograph of an AP axial projection of the coccyx reveals that the distal tip is superimposed over the symphysis pubis. What must the technologist do to eliminate this problem during the repeat exposure? |
An increase in CR angle is required to separate the coccyx from the pubic symphysis. |
|
|
A radiograph of an oblique position of the lumbar spine reveals that the downside pedicle and zygapophyseal joint are posterior in relation to the vertebral body. What modification of the position must be made during the repeat exposure to produce a more diagnostic image? |
Decrease rotation of the body and spine |
|
|
A patient comes to the radiology department for a follow-up study for a compression fracture of L3. The radiologist requests that collimated projections be taken of L3. Which specific projections are centering would provide a quality study of L3 and the intervertebral joint spaces. |
AP or PA and collimated lateral projections would provide the best view of the L3 region, CR 2inches above the the iliac crest |
|
|
A young female patient comes to the radiology department for a scoliosis series. She has had repeated radiation exposure over a period of time and is understandably concerned about the radiation. What 3 things can the technologist do to minimize the dose delivered to the patient's breasts? |
1. use high kV technique 2. Perform PA rather than AP 3. Use breast shield |
|
|
A patient with an injury to the coccyx enters the emergency room. When attempting the AP projection, the patient complains that it is too uncomfortable to lie on his back. He is unable to stand. What other options are available to complete this study? |
Perform a PA rather than an AP projection and reverse the direction of the CR from caudad to cephalad. |
|
|
A patient with a clinical history of spondyloisthesis at the L5-S1 level comes to the radiology department. Which specific lumbar spine position is most diagnostic in demonstrating the extent of this condition? |
Lateral L5-S1 position would demonstrate the degree of forward displacement |
|
|
A positioning series for SI joints is performed on a patient. the resultant radiographs do not demonstrate the inferior portion of the joints. What can be done during the repeat exposure to demonstrate this aspect of the SI joints? |
The CR should be angled 15-20 degrees cephalad |
|
|
A patient comes to the radiology department for a lumbar spine series. He has a clinical history of advanced spondylolysis. Which specific projection(s) of the lumbar spine series will best demonstrate this condition? |
AP/PA and lateral of L-spine are helpful but posterior/anterior projections best demonstrates signs of spondylolysis |
|
|
A patient comes to the radiology department for a lumbar spine study following spinal fusion surgery. Her surgeon wants a study to assess mobility of the spine at the fusion site. Which radiographic positions provide this information? |
Hyperflexion and hyperextension laterals |
|
|
A patient comes to the radiology department for a lumbar spine series. She has a clinical history of severe kyphosis. How should the lumbar spine series be modified for this patient? |
Routine projections done erect |

