![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
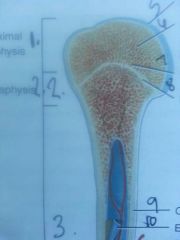
Section 1
|
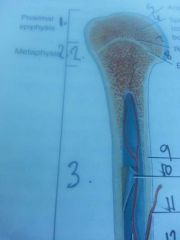
Proximal epiphyses
|
|
|
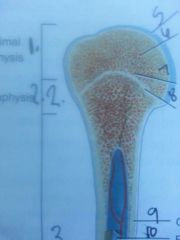
Section 2
|
metaphysis
|
|
|
line 5
|
articular cartilage
|
|
|
line 6
|
spongy bone
|
contains red bone marrow
|
|
line 7
|
red bone marrow
|
|
|
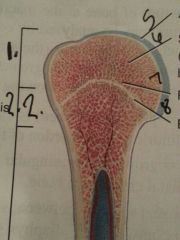
line 8
|
epiphyseal line
|
growth plate
|
|
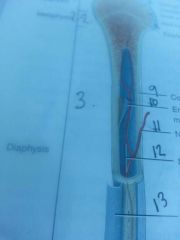
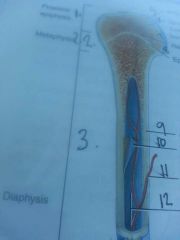
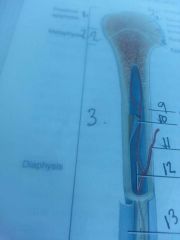
Section 3
|
diaphysis
|
shaft of bone
|
|
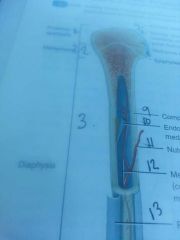
line 9
|
compact bone
|
outer edge of bone
|
|

line 10
|
endosteum
|
lines medullary cavity
|
|
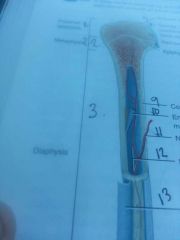
line 11
|
nutrient artery
|
|
|
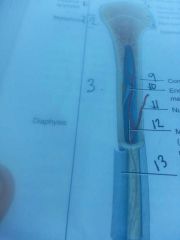
line 13
|
periosteum
|
|
|
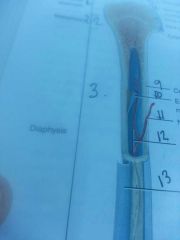
line 12
|
medullary cavity
|
contains yellow bone marrow in adults
|
|
section 2
|
metaphysis
|
|
|
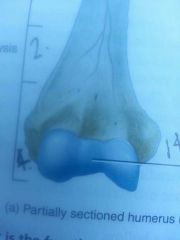
section 4
|
distal* epiphyses
|
|
|
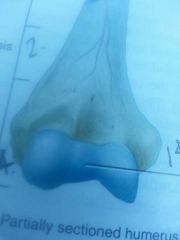
line 14
|
articular cartilage
|
|
|
|
Narrow slit between adjacent parts of bones thru which blood vessels or nerves pass
|
Fissure
|
superior orbital...
|
|
|
Opening thru which blood vessels nerves or ligaments pass
|
Foramen
|
optic...
|
|
|
shallow depression
|
fossa
|
mandibular...
|
|
|
furrow along bone surface that accommodates blood vessel, nerve, or tendon
|
Sulcus
|
intertubercular ... of humerus
|
|
|
tubelike opening
|
meatus
|
external auditory....
|
|
|
larege, round protuberance with a smooth articular surface at end of bone
|
Condyle
|
|
|
|
smooth, flat, slightly concave or convex, articular surface
|
Facet
|
|
|
|
usually rounded, articular projection supported on neck of bone
|
Head
|
|
|
|
prominent ridge or elongated projection
|
crest
|
|
|
|
typically roughened projection above condyle
|
epicondyle
|
|
|
|
long narrow ridge or border (less prominent than crest)
|
linea
|
|
|
|
sharp slender projection
|
spinous process
|
|
|
|
very large projection
|
trochanter
|
|
|
|
variabky sized rounded projections
|
tubercle
|
means knob
|
|
|
variably sized projection that has a rough bumpy surface
|
tuberosity
|
|
|
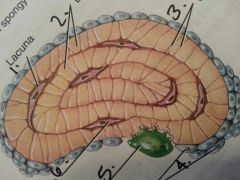
1
|
Lacuna
|
|
|
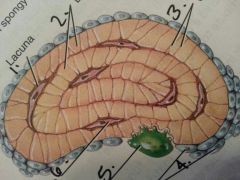
2
|
lamellae:layer?
|
|
|
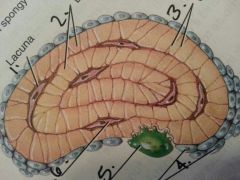
3
|
canaliculi: like a gap junction
|
|
|
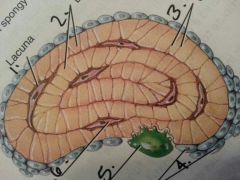
4
|
osteoblasts:build bone
|
|
|
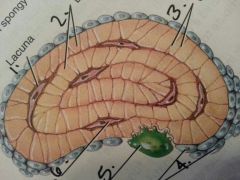
5
|
osteoclasts: breaks down bone
|
|
|
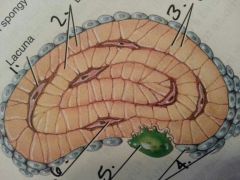
6
|
osteocyte: maintains bone
|
|
|
|
in endochondral formation what is the original pattern for bone made of
|
hyaline cartilage
|
|
|
|
where is bone marrow contained
|
medullary cavity
|
|
|
|
why does a bedridden person lose bone mass
|
there is no mechanical stress on the bone so there is no breaking down and repair
|
|
|
|
The study of bones
|
osteology
|
|
|
|
why is bone considered an organ
|
it is complex and living
|
|
|
|
What makes up the skeletal system
|
bones + cartilage
|
|
|
|
What are 6 functions of bones
|
1. Support
2. Protection 3. Assistance in motion 4. Mineral homeostasis 5. Blood cell production 6. Triglyceride storage |
|
|
|
Classification of bones according to shape
|
1. Long
2. short 3. irregular 4. sesamoid 5. sutural 6. flat |
|
|
|
define long bone
|
length > width
ex. phalanges |
|
|
|
define short bone
|
about equal dimensions
ex. carpal bones |
|
|
|
define flat bones
|
....they're flat
ex. sternum, ribs, cranium, scapula |
|
|
|
define irregular bone
|
bone that doesnt fit in any other category
ex. ear bones |
|
|
|
define sesamoid bone
|
oval shaped like a sesame seed?
ex. patela |
|
|
|
define sutural bone
|
dense irregular CT holding bones?
|
|
|
|
what connects the periosteum to underlying bone
|
perforating (Sharpey's) fibers
|
|
|
|
What makes up articular cartilage
|
hyaline cartilage always
|
|
|
|
define articular cartilage
|
cartilage at contact points between 2+ bones. used for shock absorbing and friction reducing
|
|
|
|
use for periosteum
|
allows for bone growth, nourishment, protection, repair, and serves as an attachment point for ligaments and tendons
|
|
|
|
Tendon attachment points
|
muscle to bone
|
|
|
|
ligament attachment points
|
bone to bone
|
|

