![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
If a pure substance is not an element, it is a ________ ________. |
chemical compound |
|
|
A _______ ________ is a pure substance composed of atoms of one or more elements combined in fixed ratios. |
chemical compound |
|
|
Some examples of chemical compounds include: |
|
|
|
True or False? Once elements are combined to form compounds, the original, characteristic properties of the elements are replaced by the characteristic properties of the compounds. |
True. Consider the difference between table sugar, a white crystalline substance that is soluble in water, and its constituent elements: carbon, which is usually a black powder and is not water soluble; hydrogen, the lightest gas known; and oxygen, the atmospheric gas needed for respiration. |
|
|
A(n) ____ _________ is something with a uniform and fixed composition at the nanoscopic level. It can be recognized by the unchanging nature of its properties. |
pure substance |
|
|
A(n) _______ is a pure substance composed of only one kind of atom. |
element |
|
|
A(n) ____ is the smallest particle of an element, and different elements have different atoms |
atom |
|
|
______ is anything that has mass and occupies volume. |
matter |
|
|
The four states of matter are ______, _______, _____, and _______. |
solids, liquids, gases, plasma |
|
|
A(n) _____ is matter that retains its shape and volume, regardless of the container in which it is placed. |
solid |
|
|
A(n) ______ is matter that retains its volume, but not its shape. |
liquid |
|
|
A(n) _____ is matter that does not retain its shape or volume. |
gas |
|
|
Samples of matter large enough to be seen, felt, and handled—and thus large enough for ordinary laboratory experiments—are called ___________ samples. |
macroscopic |
|
|
___________ samples are so small that they have to be viewed with the aid of a microscope. |
microscopic |
|
|
The structure of matter that really interests chemists, however, is at the __________ level, i.e., in the range of 0.0000000001 m. |
nanoscopic |
|
|
Most samples of matter as they occur in nature are not pure substances, but ________. |
mixtures |
|
|
A _____________ mixture has a nonuniform composition that is clearly visible and uneven, as in chocolate chip cookies or the different kinds of crystals in many rocks. |
heterogeneous |
|
|
____________ mixtures are uniform in composition and are referred to as solutions. |
homogeneous |
|
|
A homogeneous mixture that may be in the solid, liquid, or gaseous state is called a(n) _________. |
solution |
|
|
Some examples of solutions are: |
|
|
|
When any mixture is separated into its components, the components are said to be ________. |
purified |
|
|
Some examples of elements include: |
|
|
|
Heterogeneous samples of matter are all ________ and can be physically separated into various kinds of homogeneous matter. |
mixtures |
|
|
Homogeneous matter can be either a ____ ________ or a _______. If it is a _______, it is described as a solution and has the same composition throughout. |
pure substance, mixture, mixture |
|
|
If the homogeneous matter is a pure substance, it has a fixed composition and must be either a(n) ________ or a ________. |
element, compound |
|
|
Once elements have combined into compounds, only ________ _________ can separate them. |
chemical reactions |
|
|
About __ of the elements on the periodic table are not found anywhere in nature but have only been produced artificially in laboratories, usually in extremely small quantities. |
18 |
|
|
What are the two distinguishing properties of metals? |
|
|
|
True or False? The familiar nonmetals include all of the elemental gases, and carbon, sulfur, phosphorus, and iodine, which are solids |
True. |
|
|
Seven nonmetals exist under everyday conditions as two-atom molecules, known as ________ __________. |
diatomic molecules (hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, fluorine, iodine, chlorine, bromine) |
|
|
A(n) _______ ________ is a written combination of element symbols that represents the atoms combined in a chemical compound. The symbols represent the elements, and the subscripts indicate the relative numbers of atoms of each kind. |
chemical formula (H2O, is two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom) |
|
|
Sometimes a line or lines are drawn between symbols to indicate which atoms are connected in molecules. Formulas that show the connections in this way are known as _________ formulas, whereas formulas that give just one symbol for each element present are called ________ formulas. |
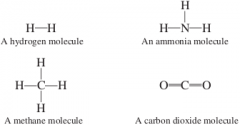
structural, molecular |
|
|
Methane and the many millions of compounds that contain carbon combined with hydrogen—and often also with nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, or sulfur—are known as _______ __________. |
organic compounds |
|
|
Compounds not based on carbon are referred to as _________ __________. |
inorganic compounds |
|
|
Which of the following represent elements and which represent compounds?
|
The chemical symbols in (1) and (4) represent compounds—the second letter in an element symbol is never a capital letter; (2) and (3) represent the elements cobalt and silver; and (5) represents the element chlorine, which exists as diatomic molecules. |
|
|
A ________ ________ is a process in which one or more pure substances are transformed into one or more different pure substances. |
chemical reaction |
|
|
A representation of a chemical reaction by the formulas of reactants and products is called a _______ _________. |
chemical equation |
|
|
A chemical equation in which the total number of atoms of each kind is the same in reactants and products is known as a __________ chemical equation. |
balanced |
|
|
A(n) ________ is a substance that undergoes chemical change. |
reactant |
|
|
A(n) _______ is a substance produced as a result of chemical change. |
product |
|
|
A property that can be observed without changing the identity of a substance is known as a(n) ________ _______. |
physical property (boiling point, melting point, color, odor, volume, density) |
|
|
The measurement of mass per unit of volume is called ________. |
density (d = m/v) |
|
|
Processes that result in changes of identity of a substance are known as ________ ________. |
chemical changes |
|
|
A(n) ________ ________ is observable in chemical reactions and changes in the identity of one or more reactants. |
chemical property (reactivity, flammability, oxidation states, chemical stability) |
|
|
A(n) ________ ________ produces a new arrangement of atoms. The number and kinds of atoms in the reactants and products remain the same, but the reactants and products are different substances that can be recognized by their different properties. |
chemical reaction |
|
|
Some physical changes and almost all chemical reactions are accompanied by changes in ______. |
energy |
|
|
_____ is the ability to cause change or, in the formal terms of physics, to do work. |
energy |
|
|
Energy in storage, waiting to be used, is __________ ______. |
potential energy |
|
|
Energy in use, rather than in storage, is _______ ______, the energy associated with motion. |
kinetic energy |
|
|
The word _________ describes information that is numerical. |
quantitative |
|
|
The word __________ describes information that is not numerical. |
qualitative |
|
|
Converting a quantity expressed in one set of units to another is known as _____ _________. |
unit conversion |
|
|
An _______ a way of expressing one quantity using two different units |
equality (12 eggs = 1 dozen eggs) |
|
|
A(n) __________ ______ is a ratio in which the numerator refers to the same quantity as the denominator. |
conversion factor |
|
|
Would it be possible for two pure substances to have exactly the same set of properties? Give reasons for your answer. |
No, they would be the same substance. |
|
|
Nitroglycerine, the chemical compound that led to Alfred Nobel’s fortune, is also used for the treatment of heart conditions. What does this illustrate about the versatility of many chemical compounds? Are the risks and benefits associated with the use of nitroglycerin as an explosive the same as for using it to treat angina, a heart condition? |
This fact illustrates that one chemical can have many different uses depending on its quantity. The benefits of using a small amount of nitroglycerin in treating angina outweigh the risks, while when used in larger quantities, the risks can be reversed, such as when it is used as an explosive. |
|
|
Chemical changes can be both useful and destructive to humanity’s purposes. Cite a few examples of each kind of change from your own experience. Also give evidence from observation that each is indeed a chemical change and not a physical change. |
One example is the combustion of gasoline to propel vehicles. This reaction is a chemical change because the liquid gasoline is converted to heat and gases. Another constructive example is the burning of coal to heat water into steam, which is then used to turn a turbine and produce electricity. The combustion of coal results in a flame and in other gases. The above two examples are examples of chemical changes because the products have a different chemical formula than reactants; another way to look at this reaction is that it is not reversible. On the other hand, a destructive reaction is the use of ammonia nitrate to construct bombs for devastation. This compound is a solid but, when mixed with the correct reactants, will produce a flame and a rapid expansion of gases that makes the explosion. The products formed in this reaction are definitely different than the starting materials. |
|
|
What is the state (solid, liquid, gas) in which each of the following elements is commonly encountered?
|
|
|
|
True or False? An element is the smallest part of a compound that may still be identified as the compound. |
False, a molecule is the smallest part of a compound. |
|
|
True or False? An atom is the smallest part of a compound that may still be identified as the compound. |
False, a molecule is the smallest part of a compound. |
|
|
You have a mixture of sand and salt . How would you separate these two substances? When you have them as separate substances, how can you prove which is which? |
A mixture of sand and salt can be separated by adding water to the mixture. The salt will dissolve in the water while the sand will not and will settle to the bottom. Filtration of the solution will result in the capture of sand on the filter paper while the dissolved salt will pass through the funnel (filtrate). The sand can be identified because it is not soluble in water and can be recovered by filtering. The salt can be recovered from the filtrate by evaporating the water. |
|
|
Atrazine is a selective herbicide that has the molecular formula . This compound is used for season-long weed control in corn, sorghum, and certain other crops. What elements are present in atrazine? |
Atrazine, C8H14N5Cl , contains the elements carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and chlorine. |
|
|
Which of the following statements is true of a balanced chemical equation?
|
The identity of the atoms in the reactants has to be the same as the products. The number of atoms on each side of the equation must also be equal. |
|
|
Given the following sentence, write a chemical equation using chemical symbols that convey the same information: “One nitrogen molecule reacts with three hydrogen molecules to produce two ammonia molecules, each containing one nitrogen and three hydrogen atoms.” |
N2 + 3 H2 -> 2 NH3 |
|
|
Name four kinds of energy. |
|
|
|
Prove that each of the following equations in question is balanced.
|
|

