![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
kenetic molecular theory of gases
|

|

|
|
|
properties of gas
|

|
|
|
|
1 atm
|
760 mmHg
|
|
|
|
Boyle's Law
|

The law states that the volume of a sample of gas changes inversely with the pressure of the gas as long as there is change in the temp. or amount of gas.
|
|
|
|
Charles's Law
|

The volume of a gas is directly related to the temp. when there is no change in pressure or amount of gas.
|
|
|
|
Gay - Lussac's Law
|

The pressure of a gas is directly related to its Kelvin temp.
|
|
|
|
The combined gas law
|

|
|
|
|
gas laws
|
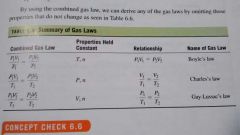
|
|
|
|
Avogadro's Law
|

|
|
|
|
STP
|
standard temperature and standard pressure:
standard temp: EXACTLY 0°C. (273K) standard pressure: EXACTLY 1atm (760 mmHg). |
|
|
|
Molar Volume
|

At STP, one mole of ANY gas occupies a volume of 22.4 L.
|
|
|
|
Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures
|

the total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressure of the gases in the mixture.
|
|
|
|
solution
|
A homogeneous mixture in which one substance called the solute is uniformly dispersed in another substance called the solvent.
|
|
|
|
solutes and solvents
|
* may be solid, liquid or gases.*
|
|
|
|
electrolytes
|
solutes can be classified by their ability to conduct an electrical current.
|
|
|
|
nonelectrolyte
|
dissolve as molecules, not as ions.
|
|
|
|
strong electrolytes
|
(NaCl)
* 100% dissociation of the solute into ions. |
|
|
|
weak electrolyzed
|
a compound that dissolves in water mostly as molecules.
|
|
|
|
unsaturated solution
|
A solute readily dissolves when added to the solvent, the solution does not contain the maximum amount of solute.
|
|
|
|
saturated solution
|
A solution that contains all the solute that can dissolve.
|
|
|
|
mass percent (m/m)
|

|
|
|
|
volume percent (v/v)
|

|
|
|
|
mass/volume percent (m/v)
|

|
|
|
|
molarity (M)
|

|
|
|
|
osmosis
|
water molecules mine through a semipermeable membrane from the solution with lower concentration to solute into a solution with the higher solute concentration.
|
|
|
|
isotonic, hypotonic and hypertonic
|

|
|
|
|
dialysis
|
A semipermeable membrane permits small solute molecules and ions as well as solvent water molecules to pass through.
|
|
|
|
Bronsted Lowry Acid
|
donates a proton. (H+)
|
|
|
|
Bronsted Lowry Base
|
Accepts a proton. (H+).
|
|
|
|
Arrhenius vs. Bronsted Lowry
|

|
|
|
|
Strong Acid
|

|
|
|
|
Strong Base
|

|
|
|
|
pH scale
|

|
|

