![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Gamete |
A reproductive cell |
|
|
Zygote |
The single cell formed from the union of two gametes, a sperm and an ovum. |
|
|
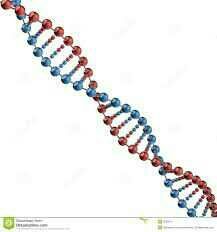
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) |
The chemical composition of the molecules that contain the genes. |
|
|
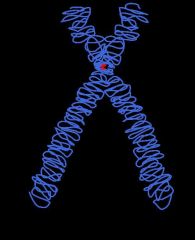
Chromosome |
One of the 46 molecules of DNA (in 23 pairs) that virtually each cell of the human body contains and that, together, contain the genes. |
|
|
Gene |
A small section of a chromosome; the basic unit for the transmission of heredity. |
|
|
Allele |
A variation that makes a gene different in some way from other genes for the same characteristics. |
|
|
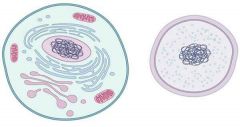
Cell |
|

|
Nucleus |
|
|
Chromosome |
|
|
DNA molecule |
|
|
Epigenetics |
The study of how environmental factors affect genes and genetic expression. |
|
|
Genome |
The full set of genes that are the instructions to make an individual member of a certain species. |
|
|
Genotype |
An organism's entire genetic inheritance, or genetic potential. |
|
|
Homozygous |
Referring to two genes of one pair that are exactly the same in every letter of their code. |
|
|
Heterozygous |
Referring to two genes of one pair that differ in some way. |
|
|
23rd pair |
The chromosome pair that, in humans, determines the sex. |
|
|
XY |
A 23rd chromosome pair that consists of an X-shaped chromosome from the mother and a Y-shaped chromosome from the father. XY zygotes become male. |
|
|
XX |
A 23rd chromosome pair that consists of two X-shaped chromosomes, one each from the mother and the father. XX zygotes become female. |
|
|
How many pairs of chromosomes and how many genes does a person usually have? |
23 pairs of chromosomes (46 in all) 20,000 genes |
|
|
What causes the similarities of all humans? |
All humans have most of the same genes with identical codes. |
|
|
Why do two sisters or two brothers in the same family differ genetically? |
Some alleles from the father differ from the alleles from the mother, their combination produces a zygote unlike either parent. Thus each new person is a product of two parents but unlike either one. |
|
|
Which is more important for a person's daily life, the phenotype or genotype, and why? |
Phenotype because it is the set of observable characteristics of an individual resulting from the interaction of its genotype with the environment |
|
|
What determines whether a baby will be a boy or a girl? |
23rd chromosome pair. |
|
|
Stem cells |
Cells from which any other specialized type of cell can form. |
|
|
Monozygotic (MZ) twins |
Twins who originate from one zygote that splits apart very early in development. (Identical twins) |
|
|
Dizygotic (DZ) twins |
Twins who are formed when two separate ova are fertilized by two separate sperm at roughly the same time. (Fraternal twins) |
|
|
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) |
A general term for the techniques designed to help infertile couples conceive and then sustain a pregnancy. |
|
|
In vitro fertilization (IVF) |
Fertilization that takes place outside a woman's body (as in a glass laboratory dish) |
|
|
Intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) |
An in vitro fertilization technique in which a single sperm cell is injected directly into an ovum. |
|
|
How does differentiation affect stem cells? |
In differentiation, cells specialize, taking different forms and reproducing at various rates depending on where they are located. |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of being a monozygotic twin? |
Advantages: Donate an organ to their twin with no organ rejection |
|
|
What ART measures help a woman who is infertile? |
A woman can take a drug, clomid, to cause ovulation. |
|
|
What ART measures help a man who is infertile? |
The woman can be inseminated with another man's sperm. |
|
|
Phenotype |
The observable characteristics of a person, including appearance, personality, intelligence, and all other traits. |
|
|
Polygenic |
Referring to a trait that is influenced by many genes. |
|
|
Multifactorial |
Referring to a trait that is affected by many factors, both genetic and environmental. |
|
|
Human genome project |
An international effort to map the complete human genetic code |
|
|
Dominant- recessive pattern |
The interaction of a heterozygous pair of alleles in such a way that the phenotype reflects one allele more than the other. |
|
|
Carrier |
A person whose genotype includes a gene that is not expressed in the phenotype. |
|
|
X-linked |
A gene carried on the X chromosome. |
|
|
Copy number variation |
Genes with various repeats or deletions of base pairs. |

