![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Complications of Transmural MI
|
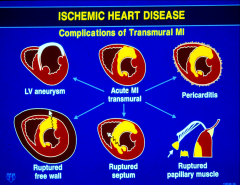
|
|
|
Transmural Infarction size
|
If the area of the transmural infarction is small, the necrotic wall may be dyskinetic, a term meaning “difficulty in moving.”
If the damage to the myocardial tissue is more extensive, the myocardial muscle may become akinetic, meaning “without motion.” |
|
|
Effect of myocardial ischemia, injury and infarction on ECG
|
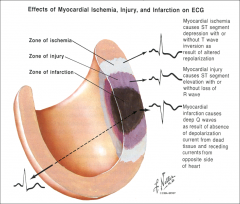
|
|
|
Most common complication after MI
|
Arrhythmias in 80%.
Caused by any condition that affects myocardial sensitivity to nerve impulses (ischemia, electrolyte imbalance, and SNS stimulation) |
|
|
MI complication - papillary rupture and treatment
|
Postero-medial papillary muscle (75%), Antero-lateral papillary muscle (25%), leads to mitral regurgitation
4-7 days after MI Reduce magnitude regurgitation, increase systemic perfusoin and ventricular performance. Use nitroprusside, nitroglycerin, dobutamine, IABP |
|
|
MI --> Pericarditis (timing)
|
Inflammation of pericardium may result in cardiac compression, decreased ventricular filling and emptying --> cardiac failure
2 -3 days after MI |
|
|
Dressler Syndrome
|
As late as 1-8 wks after MI. Treat with aspirin 650 mg every 4-6 hrs. Result of pericardial antigens being exposed and Abs being made against them.
Presentation: Malaise, fever, pericardial discomfort, leukocytosis, elevated ESR and pericardial effusion |
|
|
Complications of MI - ventricular aneurysms
|
Comp of transmular MI leads to hemodynamic compromise (HF, thrombo-embolism and arrhythmias)
Results when infarcted myocardium becomes thin and bulges out |
|
|
Complications of MI - CHF
|
Seen w/in 24 hrs when the pumping power of the heart is diminished
|
|
|
Complication of MI - PE
|
If patient has CHF or stasis
|
|
|
Complications of MI - Cardiogenic Shock
|
When inadequate oxygen and nutrients are supplied to tissue b/c of severe LV failure. Occurs when loss of function of at least 40%
|
|
|
Sudden Cardiac Death
|
Natural unexpected death due to cardiac causes. 300,000 deaths per year in US. Leading cause of death of 20-30 yr old men.
Cause: IHD, Cardiomyopathy, Valvular heart diseases, Tet of Fallot --> Lethal arrhythmias |
|
|
Chronic Ischemic Heart Disease
|
Severe coronary AS with impaired myocardial contractility due to healed MI or ischemic cardiomyopathy and diffuse myocardial fibrosis
|

