![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
100 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does "TSCA" stand for?
|
Toxic Substances Control Act (1976)
|
|
|
What does "FIFRA" stand for?
|
Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (1972)
|
|
|
What does "OSHA" stand for?
|
Occupational Safety and Health Act (1970)
|
|
|
What does "CAA" stand for?
|
Clean Air Act (1970)
|
|
|
What does "CWA" stand for?
|
Clean Water Act (1972)
|
|
|
What does "RCRA" stand for?
|
Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (1976)
|
|
|
What does "CERCLA" stand for?
|
Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act (1980)
|
|
|
What does "EPCRA" stand for?
|
Emergency Planning and Community Right to Know Act (1986)
|
|
|
What does "PPA" stand for?
|
Pollution Prevention Act (1990)
|
|
|
What does "PCB" stand for?
|
Polychlorinated biphenyls
|
|
|
Draw an example of a PCB
|
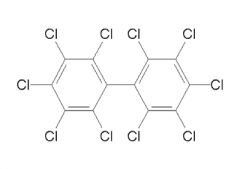
|
|
|
What are HCFC's?
|
Hydro-chloro-fluoro-carbons. Used as refrigerants. Stable, but harm the ozone layer. Not as bad as CFC's. Started to use these after 1996 when CFC's were banned.
|
|
|
Where is the majority of ozone found (which atmospheric layer)?
|
Stratosphere (~90%)
|
|
|
Which is the main type of radiation does ozone filter?
|
UV-b
|
|
|
What's the ODP of an HCFC?
|
Ozone Depletion Potential (combination of the kinds of atoms and their lifetime)
|
|
|
Do Fluorine, Chlorine and/or Bromine deplete ozone?
|
Just Br & Cl, not F, because they can participate in free radical reactions.
|
|
|
Where's the main ozone hole?
|
Over Antarctica.
|
|
|
Draw 1234-yf
|
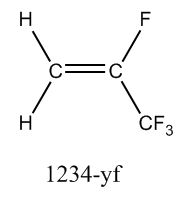
|
|
|
Draw trans-1234-ze
|
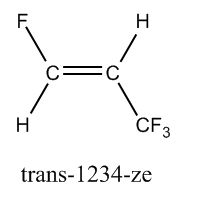
|
|
|
When were CFC's banned?
|
1996.
|
|
|
Describe Lock and Key toxicity as related to PCBs.
|
the shape of the PCB is largely dependent on the arrangement of the chloride groups along the phenyl rings. When they are closer to the bridge, it forms more steric hinderance, which reduces its ability to pervade living tissue, thus lowering its toxicity.
|
|
|
What does TSCA enable the EPA to do?
|
Screen old/new chemicals for unreasonable risks to health/environment in their production or use.
|
|
|
What's a PMN (in regards to chemical manufacturing)?
|
Premanufacture Notification. Sent to the EPA before entering production mode for a chemical, usually a new one.
|
|
|
What's included in a PMN?
|
All pertinent data for a chemical, such as intended use, amounts to manufacture, people exposed, disposal procedure, environmental/health risks, etc.
|
|
|
What statute(s) requires companies to keep a record of chemical exposures/accidents?
|
TSCA (1976), OSHA (1970)
|
|
|
What statute may require companies to test existing chemicals?
|
TSCA (1976).
|
|
|
What statute gives the EPA the power to restrict usage or ban the production of a particular chemical?
|
TSCA (1976).
|
|
|
Are there any limits on the EPA's regulatory control on chemicals?
|
It must use the least burdensome control for a given situation, balancing the risks and economics of it.
|
|
|
Can the EPA inspect anything?
|
Yes. According to TSCA (1976), they can inspect refineries, plants, processing, storage, transporting processes and sites.
|
|
|
What's the intent of the FIFRA?
|
Since pesticides are potentially toxic to plants, animals and the evironment, the FIFRA allows the pesticides to be studied and controlled based on their assessed risks.
|
|
|
What statute requires all pesticides to be registered with the EPA?
|
FIFRA (1972).
|
|
|
What needs to be included in the pesticide registration application to the EPA?
|
Intended crop and insect, and sufficient proof if its effectiveness against the pest.
|
|
|
What are the two levels of pesticide usage control?
|
General and restricted.
|
|
|
What are the requirements for using a restricted pesticide?
|
It must be administered by a certified applicator.
|
|
|
How long does a pesticide registration last?
|
Five years unless renewed and approved.
|
|
|
What statute requires a label with instructions and ingredients to appear on a pesticide?
|
FIFRA (1972).
|
|
|
What is the intent of the OSHA?
|
To ensure a safe working environment for employees/
|
|
|
How many employees must there be before a company is required to be OSHA compliant?
|
10 employees.
|
|
|
Is everyone accountable to OSHA?
|
No, some industry sectors are exempt, like some segments of transportation, mining, nuclear; they have their own safety regulations.
|
|
|
What 3 kinds of exposure does OSHA look at?
|
Short term, long term and carcinogenic exposure.
|
|
|
What statute requires companies to collect hazard data and assemble them in the form of MSDS's?
|
OSHA (1970)
|
|
|
What is a MSDS?
|
Material Safety Data Sheet
|
|
|
What statute requires a company to train its employees on hazardous materials and their proper handling?
|
OSHA (1970)
|
|
|
What statute requires a company to label chemicals with proper handling instructions?
|
OSHA (1970)
|
|
|
In addition to the requirements given by OSHA, what additional documentation should a company have prepared?
|
A written plan called a hazard communcation plan.
|
|
|
OSHA requires companies to keep records of their steps in doing what?
|
Becoming OSHA compliant.
|
|
|
How long must a company keep employee exposure/death records?
|
30 years.
|
|
|
What needs to be done if OSHA issues a citation?
|
It must be posted in a prominently noticeable location for at least 3 days.
|
|
|
What is the intent of the CAA?
|
To control emissions of chemicals into the air by making air quality standards.
|
|
|
What are the two types of air pollution sources?
|
Stationary and mobile.
|
|
|
What kind of air pollution issues does the CAA handle?
|
Hazardous air pollutants, stratospheric ozone depletion, acid rain and car emissions.
|
|
|
What are the NAAQS?
|
National Ambient Air Quality Standards. They define the maximum allowable concentration of specific chemicals in the ambient air.
|
|
|
What kind of chemicals are monitored in the NAAQS?
|
Carbon monoxide, lead, nitrogen dioxide, tropospheric ozone, particulates, sulfur dioxide.
|
|
|
What's an SIP?
|
State Implementation Plan, for achieving the NAAQS (CAA).
|
|
|
What power/responsibility does the CAA give the EPA?
|
To establish the NAAQS, review SIPs to ensure they meet the NAAQS, and take over a state level plan if it's not good enough.
|
|
|
What are the NSPS?
|
New Source Performance Standards. Meant to give tighter control on newer sources of air pollution.
|
|
|
Why NSPS?
|
It's easier to apply more restrictive limits on newer sources than to retrofit many older processes that already produce the older source.
|
|
|
Why are the NSPS national?
|
It's fair, and prevents sneaky companies from setting up or transferring chemicals to states where the pollution standards are less.
|
|
|
What is the New Source Review program?
|
Set up by the CAA, it requires a company to submit data reviewing a new process and/or significant modifications to old processes that affect air quality.
|
|
|
What are HAP's?
|
Hazardous Air Pollutants. More stringent regulations are applied to these.
|
|
|
What qualifies a company to regulations regarding HAP's?
|
If they emit 10 tons/yr of one HAP or 25 tons/yr of a combination of HAP's.
|
|
|
What's the MACT?
|
Maximum Achievable Control Technology
|
|
|
Are there rewards for good behavior with the CAA?
|
Yes. If a company demonstrates that it has reduced its HAP emissions by 99%, it's compliance deadline may be extended by 6 years.
|
|
|
What's the intent of the CWA?
|
To reduce pollutant discharges in waterways.
|
|
|
What are examples of materials classified as waste to CWA?
|
Dredged spoil, solid waste, incinerator residue, sewage, garbage, sewage sludge, munitions, chemical waste, biological materials, radioactive materials, wrecked or discarded equipment, ...
|
|
|
What's the NPDES?
|
National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System. It's a permit program
|
|
|
What are POTW?
|
Publicly Owned Treatment Works. It's a construction program.
|
|
|
What's changed in the funding of the POTW?
|
Used to be funded by federal grants, now by low-interest loans.
|
|
|
What are two types of sources to the NPDES?
|
Point sources and non-point sources. Point sources are pollutant sources that can be "pin-pointed" to a certain location/responsible party, like a refinery. Non-point sources could be like agricultural fertilizer runoff.
|
|
|
What are the two types of point sources?
|
Municipal and industrial.
|
|
|
What does the NPDES require of its permit holders?
|
To monitor discharges, collect data and keep record of pollutants. Must submit reports to the CWA regularly. CWA can review records and/or inspect effluent samples for compliance.
|
|
|
Some industrial point sources do not need NPDES permits. Why?
|
For the waste that eventually makes its way to POTW, it will be treated there, so NPDES does not enforce registration. However, the company may need to obtain local and state permits, and comply with EPA regulations.
|
|
|
What's BACT?
|
Best Achievable Control Technology.
|
|
|
What's the deal with oil/hazardous material discharge into navigable waterways?
|
it's prohibited and if it happens, the company must immediately contact the Nation Coast Guard, or responsible parties can be jailed for 5 years.
|
|
|
What's the intent of RCRA?
|
To manage waste disposal to land areas (landfills, etc) and underground storage.
|
|
|
Does RCRA deal with non-hazardous materials?
|
Yes.
|
|
|
What are the HSWA?
|
Hazardous & Solid Waste Amendments. These add more regulatory provisions for hazardous waste disposal sites primarily, as well as underground storage sites.
|
|
|
What statue uses the "cradle-to-grave" approach to regulating hazardous materials?
|
RCRA (1976). It means you are the responsible party from the formation of hazardous materials until they are properly disposed of. Your liability cannot be lost or transferred.
|
|
|
What characterizes a substance as hazardous waste?
|
Ignitibility, Corrosivity, Reactivity, Toxicity, or if the EPA says so.
|
|
|
What substances are exempted from the being classified as hazardous waste?
|
Household waste, agricultural waste (that goes into fertilizer), waste from working with ores/minerals like coal.
|
|
|
What is a "generator" as defined by the EPA under RCRA?
|
A facility that causes the generation of a waste that is listed as hazardous waste.
|
|
|
How long does a waste generator have to register with the EPA?
|
90 days from the initial generation of waste.
|
|
|
What is a UHWM?
|
Uniform Hazardous Waste Manifest. This must accompany the waste at all times.
|
|
|
What are "transporters" defined by the EPA under RCRA?
|
Persons that transport hazardous waste by air, rail, highway, or water from point of generation to the final destination of treatment, storage or disposal.
|
|
|
What are TSDF's?
|
Treatment, Storage and Disposal Facilities.
|
|
|
What event initiated the CERCLA?
|
Love Canal.
|
|
|
What's the intent of the CERCLA?
|
To identify and clean up hazardous waste sites and put the liability on potentially responsible parties.
|
|
|
What's the NPL?
|
National Priority List for the CERCLA.
|
|
|
What's the Superfund?
|
It's the Hazardous Substance Trust Fund, with money to help clean up sites that no responsible party can be found, or they have no money.
|
|
|
What's SARA?
|
Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act.
|
|
|
What are PRP's?
|
Potentially Responsible Party
|
|
|
What "liability is strict, joint and several" mean?
|
Liability can be imposed on you regardless of fault or negligence. You are responsible for the other parties' actions, but the costs is indivisible, meaning you can pay for the whole thing.
|
|
|
What does the EPA have to prove to say you're a PRP?
|
Only a connection from the hazardous waste to the records/activities of the party.
|
|
|
What are the two goals of the EPCRA?
|
1. Have the states create local emergency plans and units
2. Have the EPA compile a list of toxic releases |
|
|
What's the TRI?
|
Toxic Release Inventory
|
|
|
How long does a company need to keep it's TRI?
|
For three years.
|
|
|
What are the energy usage #'s for coal, petroleum, natural gas, nuclear, and renewables?
|
Coal: 22%
Petroleum: 39% Natural Gas: 23% Nuclear: 8% Renewables: 8% |
|
|
How many gallons are in a barrel of oil?
|
42 gallons.
|
|
|
What is the sustainability of various energy sources?
|
Coal: 230-1500 years
Petroleum: 50-100 years Natural Gas: 60-200 years Nuclear: 14,000 years (fast breeder) |
|
|
What's the IPCC?
|
International Panel on Climate Change
|

