![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
G1 Phase |
L-Asparaginase |
|
|
L-Asparaginase |
Deprives cells of asparagine |
|
|
G2 Phase |
Bleomycin |
|
|
Bleomycin |
Complex undergoes oxidation |
|
|
M Phase |
Paclitaxel Vinblastine |
|
|
Paclitaxel
|
Hyperstabilizes |
|
|
Vinblastine |
Prevent microtubule |
|
|
S/G2 Phase |
Etoposide |
|
|
Etoposide |
Inhibits topoisomerase II |
|
|
Non-specific Cell Cycle |
Alkylating Agents Platinum Complexes Antitumor Antibiotics |
|
|
Platinum Complexes |
Cisplatin |
|
|
Cisplatin |
Cross-link |
|
|
Antitumor Antibiotics |
Dactinomycin Anthracyclins |
|
|
Anthracyclins
|
-Intercalates in DNA -> -Inhibition of -Generates free radicals |
|
|
Dactinomycin |
-Intercalates between -Inhibition of -Generates free radicals |
|
|
Alkylating Agents |
Carmustine Busulfan Cyclophosphamide
Others: Procarbazine Temozolamide Melphalan Mechlorethamine Chlorambucil |
|
|
Carmustine |
Requires bioactivation |
|
|
Busulfan |
Cross-links DNA |
|
|
Cyclophosphamide |
Covalently X-link (interstrand) DNA at guanine N-7. Require bioactivation by liver (CYP450) |
|
|
S Phase |
Cytarabine Methotrexate 6-Mercaptopurine Irinotecan 5-FU Hydroxyurea |
|
|
6-Mercaptopurine |
Purine analog, causing decreased de novo |
|
|
Irinotecan |
Topoisomerase I inhibition -> DNA |
|
|
5-FU |
Pyrimidine analog, activated inhibition -> ↓dTMP -> ↓DNA and |
|
|
Hydroxyurea |
Inhibits ribonucleotide |
|
|
Methotrexate |
Folic acid analog that inhibits
|
|
|
Cytarabine |
Pyrimidine analog, causing |
|
|
Trastuzumab |
Antibody against HER-2 (c-erbB2), a tyrosine kinase receptor |
|
|
Imatinib (Gleevec) |
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor of bcr-abl (Philidelphia chromosome in CML) and c-Kit |
|
|
Rituximab |
Antibody against CD20, found in most B-cell neoplasms |
|
|
Bevacizumab |
Antibody against VEGF, inhibits angiogenesis |
|
|
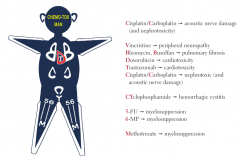
Common Chemotoxicities |
|

