![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Draw an electron shell diagram for Magnesium.
|
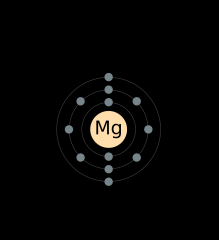
|
|
|
The rule of calculating the max number of electrons in each shell.
|
Electron Capacity = 2n2
The variable n represents the Principal Quantum Number, the number of the energy level in question. Refer to; http://education.jlab.org/qa/electron_number.html |
|
|
Write an Ionic Bonding formula. (Cross over method)
Ca+2 + Cl-1 ---> ? + ? Cr+3 + O-2 ---> ? + ? |
CaCl2
Cr2O3 |
|
|
What are Anions and Cations?
|
Anions are negatively charged ions.
Cations are positively charged ions. |
|
|
Properties of Ionic Compounds.
|
- Hard
- Form crystal lattices not molecules - Good insulators - High melting points/ Boiling Points - Conduct electricity when dissolved in water or as a liquid. - Solids do not conduct electricity |
|
|
Difference between simple ions and compound ions?
|
Simple ions only have one element. Compound ions have two or more elements.
|
|
|
Covalent bonding. Draw an electron dot diagram for Sodium.
|
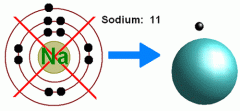
|
|
|
Properties of covalent bonds.
|
Soft-tend to be gases, liquids or soft solids
Poor conductors of heat and electricity. Molecules. Brittle or cleave rather than deform. Non-electrolytes - Do not conduct electricity in water. |
|
|
Name three compounds.
1) 2) 3) |
1) Water - H2O
2) 3) Salt - |
|
|
Define reactants.
|
Reactants are substances combined in order to make a product.
|
|
|
Difference between chemical and physical changes?
|
You can't undo chemical changes, whereas physical changes can be reversed.
|
|
|
Three states of matter.
|
Solid, Liquid and Gas.
|
|
|
Law of Conservation of Mass.
|
The matter can't be created or destroyed during a chemical reaction.
|
|
|
Types of Chemical Reactions - Synthesis reactions.
Sodium + Chloride ---> |
When two substances are combined to form one product.
NaCl |
|
|
Decomposition reactions.
|
In a decomposition reaction a compound is broken into smaller chemical species.
AB ---> A + B |
|
|
Single displacement reactions.
|
A single-displacement reaction, also called single-replacement reaction, is a type of oxidation-reduction chemical reaction when an element or ion moves out of one compound and into another. (One element is replaced by another in a compound.)
A + BX → AX + B |
|
|
Double displacement reactions.
|
In double displacement reactions two ionic compounds switch cations.
The general pattern of a double displacement reaction is: AB + CD ® AD + CB |
|
|
Corrosion reactions.
|
In a corrosion reaction, a material reacts with chemicals in its surroundings and breaks down. For example, when iron reacts with water and air, it "rusts" or "corrodes" to make iron oxide, Fe2O3 (rust).
|
|
|
Methods of transferring heat - Convection
|
Convection is the spread of heat due to the movement of particles in liquids and gasses. Hot particles will rise as they are less dense. Cold particles will fall.
|
|
|
Define Conduction.
|
Conduction is when heat transfer occurs in solids. Heat is transferred with particles coming into contact with each other.
|
|
|
Define Radiation.
|
vcghdcjgchg
|

