![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
exists when the solubility reaction is in equilibrium. No additional solute can be dissolved; the solution is "at capacity" |
saturated solution |
|
|
when all the solid material dissolves; more could dissolve if it was present |
unsaturated solution |
|
|
an unstable condition in which there is more dissolved solute than the solution can theoretically hold |
supersaturated solution |
|
|
Formedat high temperatures where the solubility of the solid is higher, and thenallowed tocoolslowly |
supersaturated solution |
|
|
agitation = |
stirring |
|
|
Generally,a slight agitation in supersaturated solution causes the excess dissolved solute to crystallize leaving a ___ ___ |
saturated solution |
|
|
solubility curves showsthe solubilities ofmany compounds as a function of ____ |
temperature |
|
|
lines of saturation |
solubility |
|
|
Pointson a line represent a ___ solution of that solute |
saturated |
|
|
Areas below the line represents ___ solutions |
unsaturated |
|
|
Areas above the line represent ___ solutions |
supersaturated |
|
|
waysto express how much solute is dissolved in a solvent |
qualitative & quantitative |
|
|
dilute, concentrated |
qualitative |
|
|
Molarity, molality, % by volume |
quantitative |
|
|
a little solute dissolved in thesolvent |
dilute |
|
|
a lot of solute dissolved in thesolvent |
concentrated |
|
|
used to determine concentration |
molarity |
|
|
dilute & concentrated are ___ ___ |
relative terms |
|
|
(M - most common) moles of solute/liters of solute |
molarity |
|
|
(m - Usedfor Bp andFpcalculations) moles of solute/kilograms of solute |
molality |
|
|
IN MOLARITY PROBLEMS - Convert,if necessary, mass to ___ - Convert, if necessary, volume to ___ |
moles; liters
|
|
|
Whena solution is diluted, ___ is added to lower its concentration |
solvent |
|
|
refersto the more concentrated solution |
stock solution |
|
|
Whenwater is added to a stock solution, its concentration ___ |
lowers |
|
|
moles BEFORE = moles AFTER |
M1V1 = M2V2 |
|
|
partiallydissociates. Most solute particles stay intact and only a few dissociate intoions |
weak electrolyte |
|
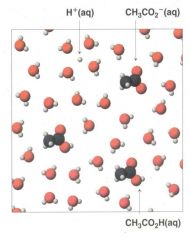
Acetic Acid, an example of...... |
weak electrolyte
|
|
|
isa solute that does not dissociate into ions. The solute particles stay intact |
nonelectrolyte |
|
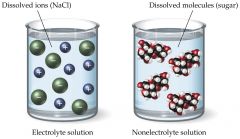
An example is sugar. Most covalentsolutes are non-electrolytes |
nonelectrolyte |
|
|
solute exists as molecules only (dissolving - nonconductor!!) |
non electrolyte |
|
|
solute exists as ions & molecules(dissolving some dissociation - some what conductor) |
weak electrolyte |
|
|
solute exists as ions only - (dissociation - conductor) |
electrolyte |
|
|
example of gas & gas solvent |
air |
|
|
example of gas & liquid solvent |
Carbonated drinks |
|
|
example of solid & solid solvent |
alloys (Fe & C |
|
|
solute then solvent.............or solvent then solute? (in a cup) |
solute then solvent |
|
|
2 ways to increase the solubility of a gas |
decreased temp & increased pressure |
|
|
what type of relationship do gases have in a graph |
inverse |

