![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Deduce compound X from H nMR spectrum and explain |
The area of the peaks are at ratio - - have proton ration - in each environment NMR Give 3 peaks 3 different chemical environments in - |
|
|
Suggest one absorption in wavenumbers |
- cm^-1 |
|
|
Suggest the m/z value and species detected ib mass spectrum |
Species: C3H6O+ Dont forget the plus M/z: DB |
|
|
Identify a stationary phase commonly used in thin layer chromatography |
Silicon dioxide SiO2 Alumininum oxide Al2O3 |
|
|
Standard entalphy change of combustion |
The entalphy change when 1 mole of substance is completely burnt at s.c. |
|
|
Std entalphy if neutralization |
E.C when 1 mol of water molecules are formed when acid reacts with an alkali at s.c |
|
|
Standard E.C of formation |

The EC when 1 mole of substance is formed from its elemenys at its std state at s.c. |
|
|
Standard entalphy if solution |
The EC when 1 mole of solute is dissolved in access solvent to form a solution of infinite dilution at s.c. |
|
|
Ave bond entalphy |
The 'average' EC when 1 mole of covalent bond of a gaseous molecule is broken under s.c. |
|
|
Standard states |
100 kPa / 1atm 298 K |
|
|
During equilibrium |

Amount of product and reactant constant Amount of product and reactant is NOT the SAME |
|
|
Pressure on equilibroum question Temperature effect |
Favor less moles of gas to minimize effect of disturbance. Compare #of moles
T : +needs to take in heat to minimize effect of disturbance Careful with 'decreasing the T' |
|
|
Caralyst in equilibrium |
Increase rate of for and backw reaction At same proportion So equilibrium no shift and Kc same Reduces Ea Rate if reaction increase Equlibrium reached faster |
|
|
Describe how formation of IR spectrum can be used to identify bonds of molecule |
Each bond absorb specific freq of IR radiation Bonds absorb radiation that has same freq as their natural freq of vibration Parts of IR spectrum allow identify bonds Note: peak of IR spectrum - how much f of IR is absorbed by molecule |
|
|
How H NMR can distinguish between compounds |
Compare ratio and number of peak Peak ratio tells number of hydrogen in the same environment |
|
|
Percentage yield |
Exp / theoretival * 100 |
|
|
What happens at molecular level when bond absorbs IR radiation |
bend or stretch of bond (vibrate) Changee in polarity |
|
|
Fragments of mass spectrum |
Dont forget + !! |
|
|
Note: MRI is NMR application
State 1 example of MRI over Xray with reference to electromagmetic spectrum Outline how MRI used to scan human body |
NMR use radiowave and is much safer than x-rays MRI is a proton H NMR Hydrogen is present in water in our body Different H detected. Different organ have different water concentration. Magnetic field and radiowaves used. Images of body produced |
|
|
Uses of analytical techniques to determine molecule structure |
IR spectroscopy - identify bonds in molecule Mass spectrometry - relative atomic and molecular mass. Identify fragments / arrangement of atoms NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) - environment of Hydrogen |
|
|
NMR (hydrogen) measure relative to reference standard |
TMS Doesnt interfere; volatile, unreactive |
|
|
Collision theory a) List 3 characteristics of reactant particles that affect rate of reaction |
Reaction occurs only when particles are in correct geometry Above activation E
a) frequency of collision KE of particles Collision geometry -maxwellbolltzmann. T increase Curve flatter. #of particles vs KE |
|
|
Activation E |
Minimum E for a reaction to occur Caralyst lowers the Ea and speeds up rate of reaction by providing an alternative pathways for reacrion to occur |
|
|
Exothermic |
Neutalization Combustion Bond making (change phase) |
|
|
Difference between strong acid & weak acid |
Strong acid completely dissociates into ions Weak acid partially dissociates ibto its ions When dissolved in water |
|
|
Mosts stable allotrope of carbon |
Graphite |
|
|
Increasing rate if reaction what is same |
The number of product is same |
|
|
Define rate of reaction |
The change in concentration of "products/reactants" over the change in time of a chemical reaction |
|
|
Concentration time graph |
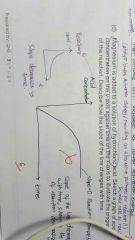
Reactant conc vs. Time Decreases
Product conc vs. Tume Increases Slope decrease showing frequency of collision decreases / rate of reaction decrease as more particles used to form products |
|
|
Affecting rate of reaction |
Concentration tells amount of particles (Volume doesnt affect since conc remains the same)
Powder surface area. Catalyst reduce Ea by give alternative patheay for reaction
T gives kE of particles. To overcome Ea. More frequency of collision
Affect "Frequency of collision" |
|
|
Suggest why result from hes law a d bond entalphy is different |
Bond entalphy is based on "average value" (aberage bond entalphy) Hess law is specific for compound |
|
|
Electronegativity |
An atom's ability to attract a bonding pair of electron |
|
|
Why noble gas not assigned electronegativity values |
It have full valance shell. Its stable. (Cannot attract bonding pair of e-) |
|
|
Explain why MP decrease down group 1 Increase down group 7 |
Group 1: Atomic radius increases Nuclear Attraction between metal ions and delocalized e- decreases VDW increase With increasing # of e & size of electronclouds |
|
|
Experiments to test Strong and weak acid
a) adding magnesium carbonate |
"Solution if equal concentration tested" Strong - Conductivity higher Add carbonate (faster CO3 production) Add reactive metal (faster H2 production)
Similarity: both form bubbles /effervescence Difference: strong acid more vigorous |
|
|
Strongest oxidizing agent (based on reactivity) |
Least reactive Oxidizing agent - reduces - gain e Note: more reactive lose more e (voltaiv) |
|
|
Features of homologous series |
Same functional group (Successive member) differ by CH2 "Similar" chemical properties Same general formula Gadation In physocal properties |
|
|
Outline why solid magnesium chloride doesnt conduct electricity |
Ions are not free to move when solid (Freely moving charged ion) |
|
|
Wjy aluminum is used instead of iron |
Aluminium doesnt corrode Aluminum more duxtile and malleable |
|
|
Dynamic equilibrium |
Rate of forward = rate of backw reactions Concentrations of all products "and" reactants remain constant |
|
|
Affect of removing material on equilibrium |
Equilibrium shift to the _ To keep the Kc constant |
|
|
Explain why lower T is not used in haber Explain why higher pressure is not used |
Temperature low: Slower rate/ Uneconomic Pressure higher: High cost for building plant/ Maintaining plant |
|
|
Lewis base |
Electron pair donor |
|
|
Weak bronsted lowry base |
Proton acceptor And partially dissociated |
|
|
Why its a polar molecule (2) |
_ bond is polar (a more electronegative than b) - assymetric deistribution of "e- cloud" |
|
|
Why BP higher for methanol than chloromethane. |
Methamol have H-bond Stronger dopole2 in methanol (C-OH more polar than C-Cl) |
|
|
Metallic bond Covalent bond Ionic bond |
Metal: Electrostatic attraction between a lattice of positively charged nuclei of a metal and the delocalized e Covalent: EA between a a pair of "shared" e- wnd the positively charged nuclei Ionic: EA between electrical charges of a cation and anion. As a result of transfer of e- |
|
|
Kc |
Large - "almost goes to completion." Mixture contain mostly products. Low - mixture contains mostly reactants. "Reaction hardly proccess" |

