![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List the reactions using alkanes |
Combustion Free radical substitution - with halogens, hydrogen halides |
|
|
Do alkenes perform addition, substitution or elimination reactions? |
Addition reactions |
|
|
What are the conditions for the reaction of an alkene with hydrogen? What type of reaction is this and what products are there ? |
Conditions- nickel catalyst, reactants are usually a gas, pressure is 423k Electrophilic addition Product is an alkane |
|
|
How can you turn an alkene into an saturated molecule? |
Electrophillic addition: Hydrogenation -nickel catalyst, 423k Halogenation- at rm temp Addition of a hydrogen halide ( 2 possible products which are structural isomers of each other) Addition polymerisation high pressure, lots of alkenes |
|
|
How can you turn an alkene into an alcohol? |
Addition reaction: Hydration- add steam with a phosphoric acid catalyst There are two possible products ( these are structural isomers of each other ) |
|
|
How can you turn an alkane into a haloalkane? |
Free radical substitution with a halogen or halogen halide |
|
|
Describe/ draw the mechanism for the reaction between ethene and hydrogen bromide: |
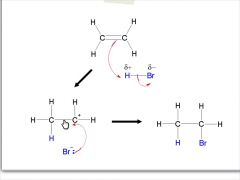
|
|
|
How can you turn an alkene into a polymer ? |
Addition reaction : Heat lots of alkenes at high pressure Double bond breaks, they form long chains of repeat units |
|
|
What type of fission is involved in the electrophillic addition of alkenes? |
Heterolytic fission of either a halogen or halogen halide ( where the halogen takes both the shared electrons when the covalent bond breaks) |
|
|
What type of reaction does a haloalkane do? |
Nuclearphilic substitution reaction |
|
|
list examples of nucleophiles and state what type of reaction they are used in |
_ OH H2O NH3 Nuclearphilic substutution with haloalkanes |
|
|
How do you make an alcohol from a haloalkane? |
Nuclearphilic Substitution - add H2O or a _ OH ion |
|
|
What is the one molecule that all of the alcohol reactions use? |
H2SO4 catalyst |
|
|
What are the reactions with alcohols? |
Substitution of a sodium halide with a sulphuric acid catalyst to form a haloalkane Concebtrated sulphuric acid to form an alkene Oxidation with oxidising agent K2Cr2O7 and sulphuric acid catalyst ( written as K2Cr2O7/ H2SO4 ) is heated Elimination dehydration heated under reflux with an acid catalyst |
|
|
describe the oxidation of a primary alcohol |
K2Cr2O7 will turn solution from orange to green If distilled during gentle heating, an aldehyde is formed If heated in reflux a carboxylic acid is formed |
|
|
Describe the oxidation of a secondary alcohol |
K2Cr2O7 will turn solution from orange to green
If heated in reflux a ketone is formed |
|
|
Oxidation of a tertiary alcohol |
No oxidation |
|
|
why does K2Cr2O7 change from orange to green when reduced? |
Dichromate (VI) ion solution turns to a chromium (III) ion solution |
|
|
Describe/draw the mechanism reaction for hydrolysis of chloro-ethane |
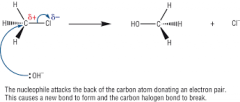
|
|
|
How can you make a haloalkane?
|
Free radical substitution of an alkane with a halogen or hydrogen halide electrophilic addition with a halogen or halogen halide Substitution of a sodium halide with sulphuric acid catalyst to an alcohol |
|
|
Homolytic fission |
When a covalent bond is broken ( by UV light normally) and each atom takes one electron from the covalent bond each to form free radicals |

