![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is a catalyst
|
it is a substance that lowers the activation energy needed for a reaction to occur by providing an alternative route without being used up in the process. it speeds up the reaction
|
|
|
what is meant by half life
|
it is the time taken for half of the radioactive nuclei to decay
|
|
|
what is entropy
|
it is the measure of the different ways particles in a subtance can be arranged.
|
|
|
what is hess law
|
energy change is the same no matter what route is taken as long as the inital an final conditions are the same
|
|
|
what is the equation for hess law
|
route 1 = route 2 + route 3
|
|
|
what is a mole
|
a mole is 6.02 x 10 (23) particles and is equal to the same amount of particles in 12 grams of carbon 12
|
|
|
what is an emission spectrum
|
previsouly excited elctrons fall down to their ground state whilst emitting energy worth the distance travelled between the shells . the energy relates to frequency in the equation E=hv. the lines are unique to an element
|
|
|
what is clean buring
|
when you have complete combustion taking place where the products are mainly only C02 and H20
|
|
|
what is octane number
|
it is the likelyhood of a substance to auto ignite. A high rating means it will be less likely to auto ignite.
|
|
|
What is the difference between empirical and molecule formula
|
it shows the smallest whole number ratioof atoms in a compound. molecular shows you the actual number of atoms
|
|
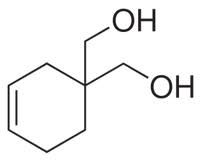
what are the two functional groups
|
alkene (cyclohexane) and an alcohol (0H)
|
|
|
When is the formula Q= MxCxT used and what does each part stand for
|
used to measure enthalpy change (heat water by burning flammable liquid)
q= heat transferred (loss/gain) (J) M=mass C= heat capacity T= the change in temp ( final - initial) |
|
|
Time of flight mass spectrometerflight
|
sample turned into a gas , it is then ionised by high energy electrons as they bombard them knocking off electrons (makes it positive), ions are accelerated by an electric field, they are then deteched at the end . time taken for ion to reach detector depends on size (small=fast)
|
|
|
what is nuclear fusion
|
Nuclear fusion is when two small nuclei combine - high temperture and high pressures (occurs in stars)
|
|
|
how does a hetrogeneous catalyst work
|
molecules arrive at surfaceand bond with catalyst ( ADSORPTION) bonds between reactant weaken/breaks up forming RADICALS. RADICALS join together and form new bonds. new molecule detaches from catalyst(DESORPTION)
|

