![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
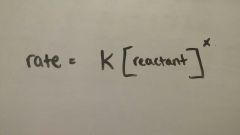
|
Rate Law |
|
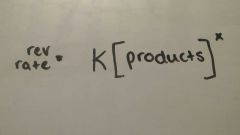
|
Reverse rate |
|
|
K >>>>> 1 |

Product Favored |
|
|
K <<<<<< 1 |
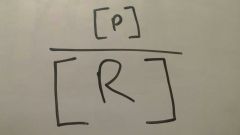
Reactant favored |
|

|
Pressure constant |
|
|
Hess' Law |
Each step of a single reaction has its own K |
|
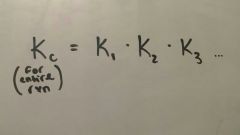
|
Hess' Law |
|

|
Hess' Law |
|

|
ICE Chart ****WATCH FOR MOLAR MASSES**** |
|
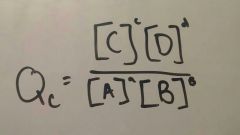
|
Reaction Quotient For a rxn NOT at EQ |
|
|
Q > K |
Reverse rxn favored R > P |
|
|
Q < K |
Forward reaction favored R < P |
|
|
Q = K |
Reaction is at equillibrium |
|
|
Heterogeneous Equillibrium |
Rs or Ps are in more than one phase |
|
|
SOLIDS and LIQUIDS are NOT in Kc |
Their concentrations don't matter |
|
|
Haber Process |
Produces amonia (NH4) Iron catalyst @high temp and pressure |
|
|
LeChatlier: Change in [CONCENTRATION] |
Rxn shifts to consume excess |
|
|
LeChatlier: Change in pressure (volume) |
Rxn shifts to reduce the mols of gas |
|
|
LeChatlier: Change in temp |
increase T = decrease Kp |
|
|
Catalyst |
Increase both fwd and rev rxns |
|
|
Arrhenius Acid |
Increases [H+] |
|
|
Arrhenius Base |
Substance that increases [OH-] |
|
|
BronLowry Acid |
Proton donor |
|
|
BronLowry Base |
Proton acceptor |
|
|
Lewis Acid |
Electron pair acceptor |
|
|
Lewis Base |
Electron pair donor ***same as BronLowry*** |
|
|
Amphiprotic |
Can be acid or base H2O |
|
|
Conjugates |
CONJ ARE WEAK IF STRONG ACID/BASE |
|
|
HCl |
SA |
|
|
HBr |
SA |
|
|
HI |
SA |
|
|
HNO3 |
SA |
|
|
HClO3 |
SA |
|
|
HClO4 |
SA |
|
|
H2SO4 |
SA |
|
|
STRONG Bases |
NaOH KOH Ca(OH)2 Sr(OH)2 Ba(OH)2 |
|
|
Kw = [H+] * [OH-] |
1*10^-14 |
|

|
Percent ionization |
|
|
Ka and Kb |
Big Ka means ACIDIC Big Kb means BASIC |
|
|
If Kc in seperate steps are >10^3 apart, IGNORE 2ND K |
Polyprotic acids |
|
|
Cation rxn w H2O |
Acidic |
|
|
Anion rxn w H2O |
Basic |
|
|
Increasing acid strength |
Increase polarity Weaker H-X bond Increased stability of conjugate bond |
|
|
Binary acids |
Members of a group |
|
|
Binary trends |
Bond strength. Dec as go down table Acid strength. Inc as go up and R Acidity. Inc w electronegativity |
|
|
Oxyacids |
Y-O-H O inc electronegativity |
|
|
Carboxylic |
Resonance STABALIZES base and increases acidity |
|
|
Reverse rxn |
1/K |
|
|
2x (rxn) |
K^2 |

