![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Element |
Substances that can't be broken into small substances under normal circumstances |
|
|
Protons |
Positively charged sub-atomic particles that makes up the Nucleus with Neutrons |
|
|
Neutrons |
Neutral charged sub-atomic particles that makes up the Nucleus with Protons |
|
|
Electrons |
Negatively Charged sub atomic particles that "orbits" the nucleus |
|
|
Energy Levels |
The "orbit" of the electrons |
|
|
Nucleus |
The center of the atom made of Neutrons and Protons |
|
|
Balanced Atom |
A atom with the same number of protons and electrons |
|
|
Valence Electrons |
amount of electrons on the outer most energy level and make up the properties of the atom |
|
|
Chemical Reaction |
When a new compound is formed |
|
|
Reactants |
Things being used to form a chemical reaction Ex: Na+Cl -> NaCl |
|
|
Product |
The end product of "mixing" the reactants Ex: Na+Cl -> NaCl |
|
|
Yield |
The arrow in chemical equations pointing at the product from the reactants Ex: Na+Cl -> NaCl |
|
|
Subscript |
The small number that is showing how many of the atom there is ()=small number Ex: 2O(2), which means 2 oxygen atoms per compound |
|
|
Co-Efficient |
The number at the front that is showing how many of the compound there is ()=small number Ex: 2O(2), which means there are two O(2) compounds |
|
|
Law of Conservation of Mass and Energy |
The amount of energy and mass in the universe stays constant, and it can't be created or destroyed; Both can change forms |
|
|
Balanced Equation |
Where there is nothing lost or gained on either side of the equation ()=Small Number Ex: 2H+O -> H(2)O |
|
|
Unbalanced Equation |
Where there is something lost or gained on either side of the equation ()=Small Number Ex: H+O -> H(2)O |
|
|
Period |
Horizontal Rows; Determines amount of energy levels |
|
|
Groups |
Vertical Columns; Determines amount of valence electrons |
|
|
APE MAN |
Atomic # = Protons = Electrons (Atomic) Mass - Atomic # = Neutrons |
|
|
Bohr Model |
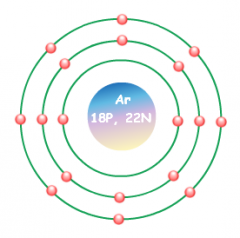
|
|
|
3 types of elements |
Metals, Non-Metals, Metalloids |
|
|
Metals (Name also all 7 Properties) |
(Left Side of the Table) Conducts Electricity, Conducts Heat, Shiny, Malleable, Reacts with Acid, Gives off electrons, Can be magnetic |
|
|
Non-Metals (Name also all 7 Properties) |
(Right Side of the Table + Hydrogen) Insulates Electricity, Insulates Heat, Dull, Brittle, Doesn't react with Acid, Steals electrons, never magnetic |
|
|
Noble Gases (Also Name them all) |
Nonreactive gases on the most right part of the table with 8 valence electrons; Helium, Neon, Argon, Krypton, Xenon, and Radon |
|
|
Metalloid (Name them all) |
(Boron, Silicon, Germanium, Arsenic, Antimony, Tellurium, Polonium, Astatine) On a stair-step line dividing metals and non-metals; properties of metals and non-metals |
|
|
Octet Rule |
Atoms will try everything to become stable with 8 valence electrons |
|
|
Physical Change |
Alters size, shape, or state of matter |
|
|
Chemical Change |
Changes Compound entirely |
|
|
Compound |
When 2 or more elements bond, usually because one is unstable |
|
|
Molecule |
The base unit of a compound Example: ()=Small Number H(2)O= 1 water molecule 2H(2)O= 2 water molecules |
|
|
Diatomic Molecules |
Elements that exist in pairs Ex: () = Small Number O(2) |
|
|
Diatomic Elements (Name them all) |
Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Florine, Chlorine, Iodine, and Bromine |
|
|
Organic Compounds |
Compounds with Hydrogen and Carbon |

