![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
92 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Weight |
A measure of gravitational attraction for an object |
|
|
Independent variables |
The variable you plan to change |
|
|
Matter |
Anything that has mass and takes up space |
|
|
Observation |
The act of gaining information |
|
|
Qualitative data |
Descriptive non numerical information |
|
|
Hypothesis |
A tentative explanation |
|
|
Substance |
Matter with a definite and uniform composition |
|
|
Conclusion |
A judgement based on observed information |
|
|
Theory |
An explanation of natural behavior |
|
|
Scientific law |
A description of natural behavior a relationship supported by many observations |
|
|
Quantitative |
Numerical information |
|
|
Pure research |
Research for the sake of gaining knowledge alone |
|
|
Experiments |
Controlled observation for testing a hypothesis |
|
|
Control |
A standard for comparison |
|
|
Mass |
A measure of the amount of matter in an object |
|
|
Model |
A visual verbal or mathematical explanation of experimental data |
|
|
Scientific method |
An organization approach to finding the solution for a problem |
|
|
Systematic approach |
A systematic approach used in the study of science |
|
|
Dependent variable |
The variable that changes as the result of your planned changes |
|
|
Synthetic |
Man made |
|
|
Technology |
The application of science to the solution of everyday needs |
|
|
Applied research |
Research for the sake of solving everyday problems |
|
|
Scientific notation |
A method of expressing numbers in the form of 2.3 X 10^8 |
|
|
Significant figures |
All the known digits in a measurement plus one estimated digit |
|
|
Density |
Mass per unit volume |
|
|
Experiment |
A set of controlled observation used to test hypothesis |
|
|
Independent variable |
The variable that changed during an experiment |
|
|
Base unit |
A defined unit based on an object or event in the natural world |
|
|
Error |
The difference between an experimental value and the accepted value |
|
|
Graph |
A visual display of data |
|
|
Accuracy |
How close a measurement is to the accepted value |
|
|
Mass |
A measure of the amount of matter |
|
|
Percision |
How close a group of measurements are to each other |
|
|
Derived unit |
A unit defined by the combination of base units |
|
|
Liter |
A derived unit used for measuring liquid volumes |
|
|
Percent error |
Measure of error as a percent of the accepted value |
|
|
Quantitative data |
Numerical information |
|
|
Chromatography |
A separation technique based on how one materials travels across the surface of another material |
|
|
Liquid |
State of matter with a definite volume and takes the shape of the container |
|
|
Homogeneous mixture |
A mixture with uniform characteristics |
|
|
Phase change |
The transition of matter from one state to another |
|
|
Element |
A pure substance that cannot be broken down by chemical or physical process |
|
|
Solid |
A state of matter that has a definite shape and a definite volume |
|
|
Physical change |
A change that does not change the identity of the substance |
|
|
Intensive property |
A property not dependent upon the amount of the material |
|
|
Proportion |
A numerical relation of one part to another part or to the whole |
|
|
Chemical change |
A change in which one or more new substance are formed |
|
|
Physical property |
A characteristic of a material that does not involve changing the identity of the material |
|
|
Distillation |
A separation technique based on differences in boiling points |
|
|
heterogeneous mixture |
A mixture that does not have uniform composition |
|
|
Solution |
A homogeneous mixture |
|
|
Compound |
A chemical combination of two or more elements |
|
|
Solute |
The part of a solution that is dissolved |
|
|
Mixture |
A physical combination of two or more substances |
|
|
Observation |
Information gathering about a phenomena |
|
|
Crystallization |
A separation technique that produces solid particles from a solution |
|
|
Chemical property |
A characteristic describing how a substance will react to form new substances |
|
|
Substance |
Matter with a definite composition |
|
|
Percent by mass |
The ratio of the mass of an element to the mass of a compound expressed as a percent |
|
|
Extensive property |
A physical property depending upon the amount of the material |
|
|
Solvent |
The part of a solution that does the dissolving |
|
|
Vapor |
The gas or form of a substance normally a liquid or a solid at room temperature |
|
|
State of matter |
The physical form in which all matter naturally exists |
|
|
Filtration |
A separation technique that uses a porous barrier to separate solids from liquids |
|
|
Sublimation |
Changing from a solid to a gas directly |
|
|
Gas |
State of matter with no definite shape and no definite volume |
|
|
Density |
Mass per unit volume |
|
|
Atom |
The smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element |
|
|
Alpha particle |
A helium nucleus |
|
|
Atomic mass unit |
1/12 the mass of one atom carbon-12 |
|
|
Cathode ray |
A stream of charged particles |
|
|
Gamma ray |
A very high energy from a radioactive decay |
|
|
Beta particle |
An electron originating from the nucleus |
|
|
Proton |
A positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom |
|
|
Nucleus |
The positively charged end center of an atom |
|
|
Neutron |
A neutral particle in the nucleus of an atom |
|
|
Periodic table |
A table that organizes all known element into a great of horizontal and vertical columns |
|
|
Element |
A pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by physical or chemical means |
|
|
Atomic number |
The number indicating the number of protons in an atom and the identity of the element |
|
|
Isotope |
One or more atoms containing the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons |
|
|
Electron |
A negatively charged particle that is part of all forms of matter |
|
|
Model |
A visual verbal and mathematical explanation of data collected from many experiments |
|
|
Mass number |
A number representing the number of protons and neutrons in an atom |
|
|
Theory |
An explanation supported by many experiments |
|
|
The density of 6 grams of a material that has a volume of 7 |
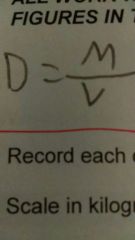
Use the formula D=M/V |
|
|
What are the six things that needs to be on a graph |

Measurement of X measurement of Y used correct rounded off numbers for both and the title which is y versus X |
|
|
Complete the matter mixture pure substance chart |
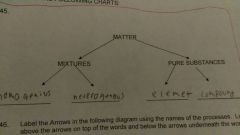
For mixture homogeneous and heterogeneous for pure substance element and compound |
|
|
Finish the solid liquid gas charge |

|
|
|
Finish the neutron electron proton Chart |
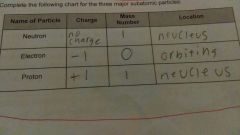
Neutron has no charge has the mass number of 1 and location is in the nucleus electron have the charge of -1 mass number is 0 location is orbiting proton has the charge of +1 mass number 1 location nucleus |
|
|
Finish the symbol - atomic number and mass number chart |
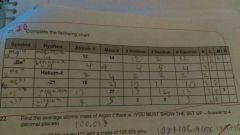
Put the symbol in the middle put a Tomic number at the bottom but mass number at the top - you write the whole element down then put mass number on the bottom atomic number you get it from the Periodic Chart mass number you get from adding number of protons and neutrons number of protons and electrons is the atomic number and neutrons you get from subtracting mass number and protons |
|
|
Electron configuration notation what is the notation for 16 |

|
|
|
Electron dot symbol |
Whatever group it is in is how many dots it has |

