![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Proton |
Positively charged sub-atomic particle held within the centre of the atom called the nucleus. |
|
|
Neutron |
A neutrally charged sub-atomic particle held within the centre of the atom called the nucleus. |
|
|
Electron |
A negatively charged sub-atomic particle. Electrons move in regions outside the nucleus. They have energy and this energy will depend on how far away from the nucleus they are likely to be found. |
|
|
Nucleus |
The region within an atom where neutrons and protons are located. It is the centre of the atom. It is extremely dense and makes up the overall mass of the atom. |
|
|
Atom |
All matter is made up of particles called atoms. All atoms are neutral because they have the same number of protons and electrons. |
|
|
Ions |
When atoms lose or gain electrons they form charged particles called ions. Metal atoms will lose electrons and become positive ions. |
|
|
Cations |
Metal atoms that have lost electrons and developed a positive charge. |
|
|
Anions |
Non-metal atoms that have gained electrons and developed a negative charge. |
|
|
Elements |
Pure substances made up of only one type of atom. They cannot be broken down into anything simpler. Each element has its own unique atom. |
|
|
Compounds |
Pure substances made up of two or more different atoms of elements chemically combined. Compounds cannot be broken down by physical processes, but they can be chemically broken down into their individual elements. |
|
|
Mixtures |
Non-pure substances which are a physical combination of substances. These substances may be elements and compounds. Mixtures can be separated by physical processes like filtration, magnetism and distillation. |
|
|
Molecule |
When two or more atoms are chemically combined by sharing electrons. These two or more atoms may be the same or different. The important fact is that they share electrons. |
|
|
Valence electrons |
Electrons in the last energy level of an element. |
|
|
Ionic bond |
When metallic atoms combine with non-metallic atoms. |
|
|
Metallic bond |
When metal atoms combine to form a metallic lattice. |
|
|
Covalent bond |
When non-metallic atoms combine to form either molecules or covalent lattices. |
|
|
Isotopes |
Atoms of the same element, with different amounts of neutrons in the nucleus which gives atoms different masses. |
|
|
What is responsible for the chemical reactivity of an element? |
Electrons |
|
|
What do elements in the same groups on the periodic table share? |
The same number of valence electrons. |
|
|
Atomic number |
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of an element |
|
|
Mass number |
The total number of neutrons and protons in an atom of an element |
|

Where is the atomic number, element symbol and atomic mass? |
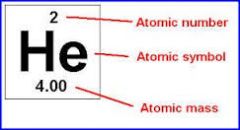
|
|
|
What are the three ways atoms become stable? |
1. Giving electrons to another atom 2. Taking electrons from another atom 3. Sharing electrons with another atom |
|
|
Prefix - one |
Mono |
|
|
Prefix - two |
Di |
|
|
Prefix - three |
Tri |
|
|
Prefix - four |
Tetra |
|
|
Prefix - five |
Penta |
|
|
Prefix - six |
Hexa |
|
|
Prefix - seven |
Hepta |
|
|
Prefix - eight |
octo |
|
|
Prefix - nine |
nona |
|
|
Prefix - ten |
deca |
|
|
When should prefixes be used? |
For chemical equations of covalent compounds |
|
|
What do the roman numerals after transition metals show? |
The charge of the transition metal |
|
|
Combination reaction |
A reaction where two or more reactants combine to form one product. |
|
|
Decomposition reaction |
A reaction where one reactant produces two or more products |
|
|
Combustion reaction |
A reaction where an element or compound reacts with oxygen, often producing energy in the form of heat and light. |
|
|
Double replacement reaction |
A reaction involving an exchange of positive ions between two compounds. They often form a precipitate. |
|
|
Single replacement reaction |
A reaction in which one element replaces another in a compound. The element will only replace the other if it is more reactive. |
|
|
Signs a chemical reaction has taken place |
Change in temperature, change in colour, emission of gas, and a smell or odour. |

