![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the definition of Endothermic? |
The system gains heat from its surroundings and the surroundings cool down |
|
|
What is the definition of Specific Heat Capacity |
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1°c |
|
|
What is the definition for Enthalpy? |
The heat gained or lost by a system at constant pressure |
|
|
What is the definition for Exothermic |
The system loses hear to its surroundings and the surroundings heat up |
|
|
What is the definition for Energy? |
A measure of ability to do work or create heat |
|
|
What is the definition of Heat? |
The energy transferred between two objects as a result of a difference in temperature between them |
|
|
What is the definition of Calorimetry? |
The measurement of the heat flow in or out of a system |
|
|
State the law of conservation of energy. |
Energy is neither created or destroyed; the sum total of energy in the universe remains constant |
|
|
What is the q value for an Endothermic Reaction? |
+ |
|
|
What is the ∆H value of an Endothermic Reaction? |
+ |
|
|
What is the q value for an Exothermic Reaction? |
- |
|
|
What is the ∆H value of an Exothermic Reaction? |
- |
|
|
How would you calculate the quantity of Heat flow? |
q=mC∆T |
|
|
How do you find ∆T? |
Final temperature-initial temperature |
|
|
How do you calculate Enthalpy? |
∆H=n•∆Hfus or ∆H=n•∆Hvap |
|
|
Where do you find the value of ∆Hfus or ∆Hvap? |
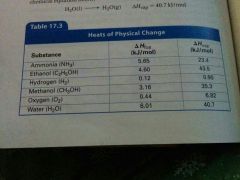
On the table called "Heat of Physical Change" |
|
|
How are the heat values for a system and its surroundings related? |
Equal magnitude, opposite signs |
|
|
How would you figure out how much heat is released when 75.0 g of water reacts with sodium by the following reaction? 2Na(s)+2H2O(l)➡150kJ+H2+2NaOH(aq) |
Turn grams to moles: 75.0gh2o•1mol/18.02g=4.16molh2o Turn moles to kJ: 4.16molh2o•150kJ/2molh2o=312kJ |
|
|
How would you draw a heating curve for bromine heated from 20°c to 900°c and label the portions of the curve that represent ∆Hfusion, ∆Hvaporization, qgas, qliquid, qsolid? Melting point =97.8°. Boiling point=883°c |
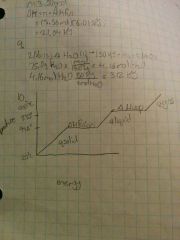
|
|

How do you calculate how much energy is required to heat 20.0g of mercury from -35°c to 500°c |
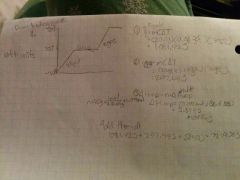
|
|
|
How would you calculate the heat if 0.175 mol of NaOH(s) is dissolved in water? NaOH➡Na+(aq)+OH-(aq) ∆H= -445.1kJ/mol |
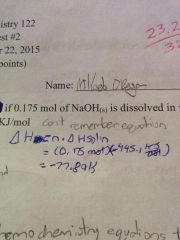
∆H=n•∆Hsol =(0.175mol)(-445.1kJ/mol) =-77.89kJ |
|
|
State Hess' Law |
If you add two or more thermochemistry equations to get a final equation, you can add the heats of the reaction to get a final heat of reaction |
|
|
How do you calculate ∆H for the following equation: C2H4(g)+Cl2(g)➡C2H3Cl(g)+HCl(g) |
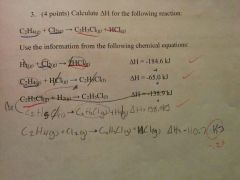
|
|
|
How do you calculate ∆H for reactions using standard heats of formation? |
∆H=∆Hprod-∆Hreact |
|
|
What are four factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction? Explain each what factor does that affects reaction rate. |
Temperature- Increases rate of collisions(more particle movement increase collision and more effective) Catalyst- Lowers activation energy Concentration- more particles causes more collisions Smaller Particles- size makes more particles available to react |
|
|
State "le Châtelier's Principle" |
If a system in dynamic equilibrium is disturbed, it will react to reach a new equilibrium |
|
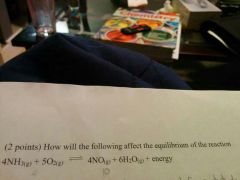
|

|
|

|
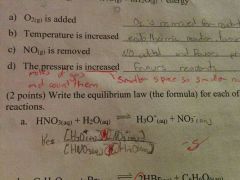
|
|
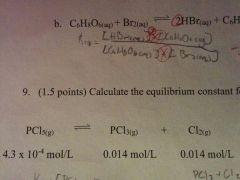
How do you calculate the equilibrium constant for the following raction |
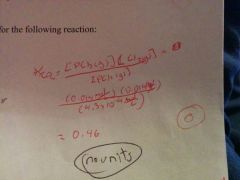
|
|
|
What is the common ion effect? |
Lowering of the solubility of a salt due to the addition of a common ion |
|
|
What is a spontaneous reaction? |
Naturally occurring reaction that favours the products, releases energy |
|
|
What is a non-spontaneous reaction? |
A reaction that doesn't produce significant product at equilibrium |
|
|
What is entropy? |
Measurement of disorder in a system |
|
|
What is an Arrhenius acid? |
Compound that ionize to produce hydrogen ions |
|
|
What is an Arrhenius base? |
Compound that ionize to produce hydroxide ion |
|
|
What is a Bronsted-Lowry acid? |
Hydrogen ion donor |
|
|
What is a Bronsted-Lowry base? |
Hydrogen ion acceptor |
|
|
What is a Lewis acid? |
Accepts a pair of electrons during a reaction |
|
|
What is a Lewis base? |
Donates a pair of electrons during a reaction |
|
|
How to get pH from [H+] |
pH=-log[H+] |
|
|
[H+] to [OH-] |
[OH-]=kW/[H+] |
|
|
[OH-] to [H+] |
[H+]=kW/[OH-] |
|
|
[OH-] to pOH |
pOH=-log[OH-] |
|
|
pH to pOH |
pOH=14-pH |
|
|
pH to [H+] |
[H+]=10^-pH |
|
|
What is a Hydroxide ion? |
Water molecule that loses a hydrogen ion |
|
|
What is a polyprotic substance? |
Have the ability to lose or gain more than one proton |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
Maintains a nearly constant pH when diluted or when a strong acid or base is added |
|
|
What are strong acids |
100% dissociation when dissolved in water |
|
|
What is a Hydronium ion? |
Water molecule that gains a hydrogen ion |
|
|
What are weak acids? |
Less than 100% dissociation when dissolved in water |
|
|
What is the pH scale? |
A way to express the hydrogen ion concentration |
|
|
List two properties of acids and two properties of bases |
Acids- sour taste, conducts electricity, and neutralise bases Base- bitter taste, conducts electricity, neutralise acids, and feels slippery |
|
|
What is an amphiprotic substance? |
A substance that can be a Bronsted-Lowry acid or a Bronsted-Lowry base depending on the situation |
|
|
Which way will the 50% be eating? |
The acid or base higher on the chart |
|
|
What is a neutralisation reaction? |
When a reaction between an acid and base produce water and a salt |
|
|
What a sketch of a base with an acid looks like |

|
|
|
What a sketch of a curve of an acid with a base |
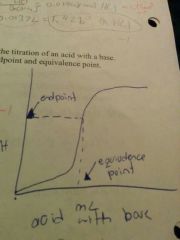
|
|
|
How do indicators work? |
A substance that is one colour when it gains a proton and another when it loses a proton |
|
|
What is the equation for Ka? |
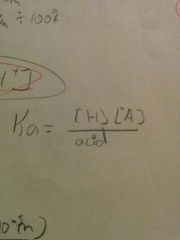
|
|
|
What concentration would you use to find concentration or volume? |
C1V1=C2V2 |
|
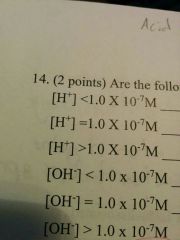
|
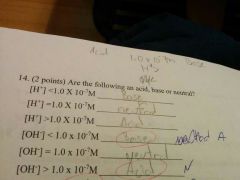
|
|
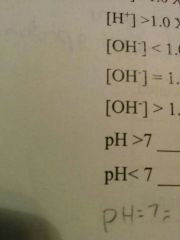
|
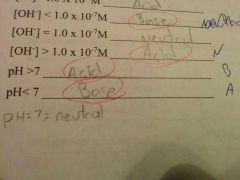
|

