![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How do temperature, pressure and concentration affect Kc? |
Temperature - dependant on exothermic/endothermic reaction. Kc increases with temperature if reaction is endothermic. Pressure and Concentration - Le Chatilier's principle reduces changes in pressure and concentration so Kc is unaffected. |
|
|
How do conjugate acid-base pairs work? |
An acid loses a proton to form its conjugate base. The base accepts the proton to form its conjugate acid. |
|
|
Define Ka |
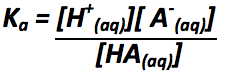
|
|
|
Define Rate of Reaction |
– Change of concentration of a reactant of product per unit time. |
|
|
Define half-life |
The time taken for the concentration of a reactant to reduce by half |
|
|
What is the rate determining step |
The slowest step in the reaction mechanism of a multi-step reaction |
|
|
How do you find pKa? |
-log(Ka) |
|
|
What is a buffer solution? |
A system thatminimises pH changes on addition of smallamounts of an acid or a base. |
|
|
How do you find the[H+] value of a buffer solution? |
Kacidoversalt |
|
|
Define Lattice Enthalpy |
The enthalpy change that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of ionic compounds from its gaseous ions under standard conditions. |
|
|
Standard Enthalpy of formation |
One mole of a compound formed from its constituent elements in their standard states. |
|
|
Standard enthalpy of atomisation |
One mole of gaseous atoms formed from its element in standard states. |
|
|
First ionisation energy |
Energy needed to form 1 mole of gaseous 1+ atoms through the removal of 1 mole of electrons from an atom in its gaseous state. |
|
|
First electron affinity |
Energy needed to form 1 mole of gaseous 1- atoms through the addition of 1 mole of electrons from an atom in its gaseous state |
|
|
Standard enthalpy change of solution |
Enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is completely dissolved in water under standard conditions. |
|
|
Standard Enthalpy change of hydration |
Enthalpy change when one mole of isolated gaseous ions is dissolved in water forming one mole of aqueous ions under standard conditions. |
|
|
What affects enthalpy and how so? |
Charge - Greater charges have a stronger attractive force so there is less ionic radius so the lattice enthalpy is more negative and more exothermic. Ionic radius- greater ionic radius means less attraction so lattice enthalpy is greater and less exothermic. |
|
|
What is entropy |
A measure of the‘disorder’ of a system. The system becomes energetically more stable when itbecomes more disordered. |
|
|
How do you find entropy and what does its value mean? |

|
|
|
How can we find if a reaction is feasible? |
∆G = ∆H - T∆S the more negative ∆G, the more feasible the reaction. |
|
|
Write the equation and observations for precipitate reaction of Cu2+ |
Cu2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) ---> Cu(OH)2 (s) pale blue solution ---> blue precipitate. |
|
|
Write the equation and observations for precipitate reaction of Co2+ |
Co2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) ---> Co(OH)2 (s) Pink Solution ---> Blue precipitate (Beige in presence of air) |
|
|
Write the equation and observations for precipitate reaction of Fe2+ |
Fe2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) ---> Fe(OH)2 (s) Pale green solution ---> Green precipitate (rusts in presence of air) |
|
|
Write the equation and observations for precipitate reaction of Fe3+ |
Fe3+(aq) + 3OH-(aq) ---> Fe(OH)3 (s) Pale yellow solution ---> Rusty brown solution |
|
|
What is a ligand? |
A molecule or ion that can donate a pair of electrons with the transition metal ion to forma coordinate bond. |
|
|
What is cis-platin and how is it used in cancer treatment? |
Cis-platin is the cis complex of [PtCl2(NH3)2] Cis-platin binds to the DNA of thecancerous cells preventing them from reproducing. This leads to thedeath of the cancer containing cells. |
|
|
Give an example of ligand substitution where the coordination number and shape do not change, with observations. Why do these properties not change? |
[Co(H2O)6]2+ + 6NH3 <==> [Co(NH3)6]2+ + 6H2O octahedral pink octahedral pale brown The ligands are similar size so easily substitute without changing. |
|
|
Give an example of ligand substitution where the coordination number and shape change, with observations. Why do these properties change? |
[Co(H2O)6]2+ + 4Cl- <==> [CoCl4]2- + 6H2O(l) octahedral pink tetrahedral blue [Cu(H2O)6]2+ + 4Cl- <==> [CuCl4]2- + 6H2O(l) octahedral pale blue tetrahedral yellow The ligands are different sizes e.g: H2O Cl- |
|
|
Give an example of partial ligand substitution, with observations. |
octahedral pale blue elongated octahedral deep blue [Cu(H2O)6]2+ + 4NH3 <=> [Cu(NH3)(H2O)2]2+ + 4H2O |

