![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
99 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The rusting of iron and the corrosion of other metals costs the US economy nearly how much per year? |
$300 billion per year |
|
|
Rust is also known as what? |
Iron Oxide |
|
|
Whats the other name for an oxidation-reduction reaction? |
Redox reaction |
|
|
What happens in a redox reaction? |
Electrons are transferred from one substance to another. |
|
|
The _________ iron atoms (iron atoms that ______ electrons) bond with the _________ oxygen atoms (oxygen atoms that ______ electrons) to form iron oxide or rust. |
The oxidized iron atoms (iron atoms that lost electrons) bond with the reduced oxygen atoms (oxygen atoms that gained electrons) to form iron oxide or rust. |
|
|
The overall chemical reaction that explains rusting also involves what? Therefore, rust is prevented if iron is what? Rusting also requires what? Rust is accelerated in the presence of what, which is a what? |
Water Kept dry The conduction of electrical charge Salt water, which is a good electrical conductor. |
|
|
The burning of hydrocarbons is a _________ reaction in which hydrocarbons are _________.
|
The burning of hydrocarbons is a redox reaction in which hydrocarbons are oxidized. |
|
|
Respiration is a _______ reaction in which our bodies _________ sugars for energy. |
Respiration is a redox reaction in which our bodies oxidize sugars for energy. |
|
|
T/F Combustion reactions, such as those used for heat or energy production, are actually redox reactions. |
True |
|
|
The burning of coal is what kind of reaction? Oxidation or reduction? C + O2 --> CO2 |
Redox reaction Oxidation |
|
|
The combustion of natural gas is what kind of reaction? Oxidation or reduction? CH4 + 2O2 --> CO2 + 2H2O |
Redox reaction Oxidation |
|
|
The rusting of iron is what kind of reaction? Oxidation or reduction? 4Fe + 3O2 --> 2Fe2O3 |
Redox reaction Oxidation |
|
|
The reaction to form water is what kind of reaction? Oxidation or reduction? 2H2 + O2 --> 2H2O |
Redox reaction Oxidation |
|
|
What is one definition of oxidation? |
The gaining of oxygen. |
|
|
What is one definition of reduction? |
The loss of oxygen. |
|
|
What is this kind of reaction? Oxidation or reduction? CO2 + 2H2O --> CH4 + 2O2 |
Redox reaction Reduction - Carbon loses oxygen and gains hydrogen. |
|
|
What is another definition of oxidation? |
The loss of hydrogen. |
|
|
What is another definition of reduction? |
The gaining of of hydrogen. |
|
|
What is the broadest definition of oxidation? |
The loss of electrons. |
|
|
What is the broadest definition of reduction? |
The gaining of electrons. |
|
|
Based on the idea that oxidation is the loss of electrons and that reduction is the gaining of electrons, we conclude what? |
That reactions that do not include oxygen may also be redox reactions. |
|
|
The most general definitions of oxidation and reduction involve - not the transfer of ________ or ________ - but the transfer of _________. |
The most general definitions of oxidation and reduction involve - not the transfer of oxygen or hydrogen - but the transfer of electrons. |
|
|
Draw an example of a redox reaction containing oxygen using the transfer of electrons. |
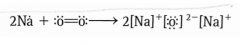
|
|
|
Draw an example of a redox reaction without oxygen using the transfer of electrons. |
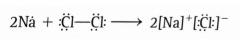
|
|
|
When sodium and chlorine react to form sodium chloride, each sodium atom transfers an electron to a chlorine atom. Therefore sodium is what, while chlorine is what? |
Sodium is oxidized and chlorine is reduced. |
|
|
T/F Oxidation and reduction don't always occur together. |
False, Oxidation and reduction ALWAYS occur together. |
|
|
When ionic bonds form, as in Na2O or NaCl, the transfer of electrons is obvious; the ______ transfers one or more electrons to the ___________. The _______ is oxidized and the __________ is reduced. However, redox reactions need not involve _______ bonding. In ___________ bonding that transfer is only partial, but the same definitions apply. Those atoms that ______ electrons, even if only partially, are oxidized and those that _______ electrons are reduced. |
When ionic bonds form, as in Na2O or NaCl, the transfer of electrons is obvious; the metal transfers one or more electrons to the nonmetal. The metal is oxidized and the nonmetal is reduced. However, redox reactions need not involve ionic bonding. In covalent bonding that transfer is only partial, but the same definitions apply. Those atoms that lose electrons, even if only partially, are oxidized and those that gain electrons are reduced. |
|
|
What are oxidizing agents? Examples? |
Substances that tend to gain electrons easily. They cause the oxidation of other substances while they are themselves reduced. Oxygen and Chlorine |
|
|
What are reducing agents? Examples? |
Substances that tend to lose electrons easily. They cause the reduction of other substances while they are themselves oxidized. Sodium and Potassium |
|
|
Oxidation is defined by three things. What are they? |
The gain of oxygen The loss of hydrogen The loss of electrons |
|
|
The substance being oxidized is what? |
The reducing agent |
|
|
Reduction is defined by three things. What are they? |
The loss of oxygen The gain of hydrogen The gain of electrons |
|
|
The substance being reduced is what? |
The oxidizing agent |
|
|
Oxidation and reduction must what? |
Occur together. One cannot happen without the other. |
|
|
Identify the elements being oxidized and those being reduced. 2NO + 5H2 --> 2NH3 + 2H2O |
Reduced = Nitrogen Oxidized = Hydrogen |
|
|
Identify the elements being oxidized and those being reduced. 4Li + O2 --> 2Li2O |
Reduced = Oxygen Oxidized = Lithium |
|
|
Identify the elements being oxidized and those being reduced. 2Al + 3Zn^2+ --> 2Al^3+ + 3Zn |
Reduced = Zinc Oxidized = Aluminum |
|
|
Identify the elements being oxidized and those being reduced. 2Fe + 3S --> Fe2S3 |
Reduced = Sulfur Oxidized = Iron |
|
|
Identify the elements being oxidized and those being reduced. CuO + H2 --> Cu + H2O |
Reduced = Copper Oxidized = Hydrogen |
|
|
In a redox reaction the oxidizing agent is itself: a. oxidized b. reduced c. neither |
b. reduced |
|
|
For the following reactions, identify the oxidizing and reducing agents. 2NO2 + 7H2 --> 2NH3 + 4H2O |
Reducing agent = Hydrogen (H2) Oxidizing agent = Nitrogen (NO2) |
|
|
For the following reactions, identify the oxidizing and reducing agents. 2K + Cl2 --> 2KCl |
Reducing agent = Potassium
Oxidizing agent = Chlorine (Cl2) |
|
|
For the following reactions, identify the oxidizing and reducing agents. V2O5 + 2H2 --> V2O3 + 2H2O |
Reducing agent = Hydrogen (H2) Oxidizing agent = Vanadium (V2O5) |
|
|
What is the most common oxidizing agent? |
Oxygen |
|
|
The oxidation of _______-containing materials always produces energy. Our bodies use ________ to oxidize sugars for energy through _____________. |
The oxidation of carbon-containing materials always produces energy. Our bodies use oxygen to oxidize sugars for energy through respiration. |
|
|
Strong oxidizing agents can kill ______________ and are often used as ___________ and _____________. |
Strong oxidizing agents can kill microorganisms and are often used as antiseptics and disinfectants. |
|
|
Antiseptics are what and are used for what? What are three examples of antiseptics? |
Oxidizing agents Are applied to the skin or to minor cuts to prevent infection. Hydrogen Peroxide, Benzoyl Peroxide, Iodine |
|
|
Disinfectants are what and are used for what? What are two examples of disinfectants? |
Oxidizing agents Are used to sterilize and sanitize. Chlorine, bleach (sodium hypochlorite) |
|
|
Oxidizing agents are often used for bleaching fabrics, paper, and food. What are two examples of bleaches? |
Chlorine, Hydrogen Peroxide |
|
|
The simplest and most common reducing agent is what? |
Hydrogen |
|
|
Nitrogen fixation, the reduction of atmospheric nitrogen by the Haber process requires what which is a what? What is created in the process? Draw this process. |
Hydrogen, which is a reducing agent. Ammonia 3H2 + N2 --> 2NH3 |
|
|
Another important reducing agent is what? Also known as what? Which is used for what? |
Elemental Carbon Coke The reduction of metal ores. |
|
|
Photosynthesis and Respiration are what kinds of reactions? |
Redox Reactions |
|
|
What is respiration? |
The oxidation of food for energy. |
|
|
Draw the equation for respiration and label the substance that is oxidized, the substance that is reduced, the oxidizing agent, and the reducing agent. |
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy Carbon (Glucose) is oxidized, making it the reduction agent. Oxygen (O2) is reduced, making it the oxidizing agent. |
|
|
Draw the equation for Photosynthesis and label the substance that is oxidized, the substance that is reduced, the oxidizing agent, and the reducing agent. |
6CO2 + 6H20 + Energy --> C6H12O6 + 6O2 Carbon is reduced, making it the oxidizing agent. Water is oxidized, making it the reducing agent. |
|
|
Animals use oxygen to ________ carbon and plants use water to __________ carbon. |
Animals use oxygen to oxidize carbon and plants use water to reduce carbon. |
|
|
What substance is the oxidizing agent in respiration? |
Oxygen |
|
|
Batteries are based on what kind of reactions? |
Redox reactions |
|
|
T/F By physically separating two substances that undergo a redox reaction, the electrons can be forced to travel through an external circuit as an electrical current. |
True |
|
|
If zinc metal is immersed in a solution containing copper ions, a redox reaction occurs. What happens to the zinc? What happens to the copper ions? Write this reaction. |
The zinc loses electrons (oxidation). The copper ions gain electrons (reduction). Zn + Cu^2+ --> Zn^2+ + Cu |
|
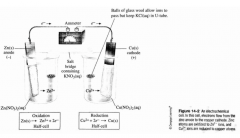
This diagram is an example of what? T/F Batteries can be constructed by this reaction. |
An Electrochemical cell True |
|
|
By physically separating the __________, we have forced the ___________ to flow through a wire, producing an electrical current. The electrode where oxidation occurs is called the ______ of the cell and is marked (___), whereas the electrode where reduction occurs is called the _________ and is marked (___). Electrons always flow from the ______ (___) to the ______ (___). |
By physically separating the reactants, we have forced the electrons to flow through a wire, producing an electrical current. The electrode where oxidation occurs is called the anode of the cell and is marked ( - ), whereas the electrode where reduction occurs is called the cathode and is marked ( + ). Electrons always flow from the anode ( - ) to the cathode ( + ). |
|
|
T/F Batteries have limited lifetimes because the reactants in them deplete. |
True |
|
|
T/F In a rechargeable battery, the recharge cycle uses an external source to force electrons to travel in the opposite direction. The reaction goes in reverse and regenerates the reactants. |
True |
|
|
The battery in an automobile is what kind of battery? |
An acid-lead battery. |
|
|
The anode of a lead-acid battery (car battery) consists of what in what? |
Of porous lead plates in sulfuric acid solution. |
|

Explain why no reaction occurs in part D of the diagram. |

The natural tendency, as you can see from parts a-c, is for Zn to lose electrons to Cu^2+. In part D, copper is present as Cu and Zn^2+. Copper will not lose electrons to Zn^2+ (the opposite of the natural tendency observed in parts a-c). |
|
|
The inexpensive flashlight batteries sold in retail stores use a design called what? |
Called a Leclanche dry cell. |
|
|
T/F The body of Leclanche dry cell batteries is made of zinc, which acts as the anode. The zinc is oxidized. A carbon rod acts as the cathode, but the substance being reduced is MnO2, which is mixed into a moist paste in the interior of the battery. |
True |
|

What is this diagram an example of? |
An inexpensive battery (Leclanche dry cell). |
|
|
The more expensive alkaline batteries use a slightly different reaction that employs a _______, hence the name alkaline, in the oxidation of zinc. Alkaline batteries have a _________ shelf life, a ________ battery life, and are less subject to ____________ than the standard Leclanche cell. |
The more expensive alkaline batteries use a slightly different reaction that employs a base, hence the name alkaline, in the oxidation of zinc. Alkaline batteries have a longer shelf life, a longer battery life, and are less subject to corrosion than the standard Leclanche cell. |
|
|
Fuel cells are batteries with what? |
Continually renewed reactants. |
|
|
In a normal battery, the reactants _________ over time. In a fuel cell, the reactants ______ into the cell as needed to produce electricity, and the products ______ _____. |
In a normal battery, the reactants deplete over time. In a fuel cell, the reactants flow into the cell as needed to produce electricity, and the products flow out. |
|
|
What are the steps involved in electricity production from combustion reactions? What are the steps involved in electricity production from electrochemical reactions? Which reaction has higher efficiency? What are the efficiencies of both? |
Chemical energy to heat energy. Heat energy to mechanical energy. Mechanical energy to electrical energy. Chemical energy to electrical energy. Electrochemical reactions are more efficient. Fuel cells = 50-80% Coal power plants = 40% |
|
|
A common fuel cell is the... |
... hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell. |
|
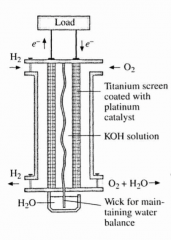
This diagram is an example of what? |
A hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell. |
|
|
What is the most promising type of fuel cell called? |
Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell |
|
|
What does MCFC stand for? |
Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell |
|
|
Depending on how much secondary heat is recaptured and reused, what is the electrical generation efficiency of MCFCs? |
54-85% |
|
|
Why are MCFCs attractive? Why are they not attractive? |
The small space they occupy. Their dependance on methane. |
|
|
The rusting of iron is what kind of reaction? |
A redox reaction. |
|
|
Draw the half reaction for the rusting of iron, the oxidation part. |
2Fe --> 2Fe^2+ + 4e- |
|
|
Draw the half reaction for the rusting of iron, the reduction part. |
O2 + 2H2O + 4e- --> 4OH- |
|
|
Draw the overall reaction for the oxidation of iron. |
2Fe + O2 + 2H2O --> 2Fe(OH)2 2Fe(OH)2 than reacts via several steps to form iron oxide (Fe2O3). |
|
|
______ is an important component in the reaction of the oxidation of iron. |
Water is an important component in the reaction of the oxidation of iron. |
|
|
T/F Unlike iron, which has structural integrity, iron oxide is crumbly. It is a powder that flakes from the metal, exposing new metal, which is susceptible to further rusting. If the conditions are right, entire pieces of iron will rust away. |
True |
|
|
One-fifth of the iron produced in the United States goes to what? |
To replace rusted iron. |
|
|
What are the three ways to prevent rusting of iron? Which way is the simplest? |
-Cover the iron with paint. -Attach a more active metal to the iron, which will oxidize in the place of iron. -Mix or coat iron with a metal whose oxide is structurally stable. Galvanization is an example of this. Using paint to cover iron. |
|
|
Antioxidants include... |
... fat-soluble vitamin E, water-soluble vitamin C, and beta carotene. |
|
|
Antioxidants are ________ agents, which means they promote __________ and retard _________. |
Antioxidants are reducing agents, which means they promote reduction and retard oxidation. |
|
|
What is an example of using an antioxidant to retard oxidation? |
An apple will turn brown over time as the oxygen in the air oxidizes it. However, a vitamin C solution spread on the surface of the apple prevents oxidation, and the apple remains fresh. |
|
|
What are free radicals? What do free radicals do? |
Atoms or molecules with unpaired electrons. They are extremely reactive and will scavenge electrons from biological molecules, oxidizing them. The oxidized biomolecules can no longer serve their function, and disease can develop. |
|
|
Free radicals can also do what? |
They can also attack other molecules within the cell such as DNA. |
|
|
What are the best sources of anioxidants? |
Fruits and vegetables. |
|
|
Antioxidants work by ______________ free radicals and preventing the __________ of biological molecules in much the same way that magnesium metal prevents iron from rusting. |
Antioxidants work by deactivating free radicals and preventing the oxidation of biological molecules in much the same way that magnesium metal prevents iron from rusting. |
|
|
LEO says GER = |
= Loss of electrons is oxidation. Gain of electrons is reduction. |
|
|
What is Fe2O3? |
Iron oxide |
|
|
Show the equation for how we reduce Iron oxide back to iron. |
Fe2O3 + 3CO --> 2Fe + 3CO2 |

