![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
These are molecules obtained from living cells that are insoluble in water, but soluble in nonpolar substances
|
Lipids
|
|
|
A long chain carboxylic aced; those in animal fats and vegetable oils often have 12 -22 carbon atoms
|
Fatty acids
|
|
|
Waxes are simple__________
|
Esters
|
|
|
What type of configuration is around the bond of a Natural unsaturated fatty acids?
|
CIS configuration
|
|
|
Explain the bonds of a polyunsaturated fatty acid.
|
more than on double bond
|
|
|
Saturated Fatty Acids 12 - 18 Carbons and MP's increases from 44 - 70c
|
LuMPS
L-Lauric M-Myristic P-Palmitie S-Stearic |
|
|
Unsaturated Fatty Acids 18 Carbons then 20, double bonds increase from 1-4 and MP's decreases from 13 to -50c
|
OLLA
O- Oleic L-Linoliec L-Linolenic A-Arachidonic |
|
|
What are the functions of lipids in the body?
|
Cell membrane
storage of energy Hormones & vitamins |
|
|
Movement of substances across a cell membrane using energy
|
active transport
|
|
|
Movement of a substance across a cell membrane without the use of energy, from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration
|
Passive Transport
|
|
|
Passive transport by the random diffusion through the cell.
|
Simple Diffusion
|
|
|
Passive transport across a cell membrane with the assistance of a protein that changes shape.
|
Facilitated Diffusion
|
|
|
Give some examples of Simple diffusion
|
Lipid soluble and small hydrophilic molecules
hydrophobic through the bilayer Hydrophilic through protein pores |
|
|
Give an example of facilitated diffusion
|
Glucose
down a concentration gradient, but much faster than simple diffusion |
|
|
Explain Active transport
|
energy from ATP is use to change the shape of an integral protein (Na/K) pump.
|
|
|
What is the (Na/K pump)
|
simultaneously bringing two K+ ions into the cell and moving 3 Na+ ions out of the cell
|
|
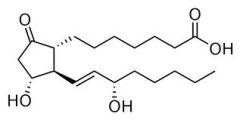
name this
|
Prostaglandin
can lower blood pressure,influence platetlet aggregation during blood clotting,and responsible for pain in swelling |
|
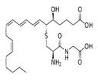
Name this
|
Leukotriene
triggers asthmatic response, severe allergic rxns and inflammation |
|
|
A mixture of triacyglycerols that is solid because it contains a high proportion of SATURATED FATTY ACIDS
|
Fats
|
|
|
A mixture of triacylgyceros that is liquid because it contians a high proportion of UNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS
|
Oils
|
|
|
A mixture of of esters of LONG CHAINS CARBOXYLIC ACIIDS W/ LONG CHAIN ALCOHOLS
|
Waxes
|
|
|
A lipid that has an ester link between PHOSPHORIC ACID & AN ALCOHOL
|
Phospholipids
|
|
|
A lipid derived from the AMINO ALCOHOL SPINGOSINE
|
Shingolipids
|
|
|
A lipid with a FATTY ACID bonded to the 2nd C-NH2 and a SUGAR bonded to the 1st C-NH2 group of sphingosine
|
Glycolipids
|
|
|
What are the Nonsaponifiable lipids
|
Steroids
Eicosanoids |
|
|
Saturated fatty acids have what types of bonds?
|
single bonds (no double bonds)
|
|
|
What is base hydrolysis of fat called
|
saponification
|
|
|
What does soaponification produce from fats
|
salts and long chain Fatty Acids
|
|
|
Proteins extended completely through the membrane
|
Integral Proteins
|
|
|
Proteins adhere temporarily to the membrane and to one face of bilayer
|
Peripheral Proteins
|
|
|
Where are the hydrophobic groups located in the structures of cell membranes?
|
Inside the cell
|
|
|
Where are the hydrophilic groups are on the outside because of it contact w/aqueous fluids?
|
Outside of the cell
|
|
|
Made of phosphobilayer studded w/proteins
|
Plasma membrane
|

