![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe the modern model of the atom.
|
Atoms have a central nucleus with protons and neutrons surrounded by a cloud of moving electrons.
|
|
|
Name the three main types of particles that make up an atom and the charge and location of each.
|
1. protons are positive and in the nucleus
2. neutrons are neutral and in the nucleus 3. electrons are negative and outside the nucleus in the electron cloud |
|
|
Give an explanation of the overall charge on an atom.
|
Atoms are neutral because protons equal electrons - positive charges equal negative charges.
|
|
|
List 5 properties of metals
|
1. luster (shine)
2. malleable 3. ductile 4. good conductors 5. some are attracted by magnets 6. some will oxidize when mixed with oxygen (rust) 7. usually solids |
|
|
List 5 properties of nonmetals.
|
1. dull
2. brittle - not malleable 3. brittle - not ductile 4. not good conductors 5. many are not solids |
|
|
How are radioactive isotopes used to detect and/or treat different medical conditions?
|
1. can be traced through the body to see how it is functioning
2. can kill unhealthy cells |
|
|
The periodic table has how many periods?
The periodic table has how many families? |
7
18 |
|
|
Who was Henri Becquerel? How did he further the study of chemistry?
|
Bequerel discovered was that a piece of mineral which contained uranium could produce it's image on a photographic plate in the absence of light.
He discovered was radioactivity! |
|
|
Who were Marie Curie, and Pierre Curie? How did they further the study of chemistry?
|
They came up with the term "radioactivity" to describe the spontaneous emissions that they studied
discovery of two new radioactive elements which they named polonium and radium |
|
|
Draw an example of each early model of the atom and label with the name of the person credited for that version.
|
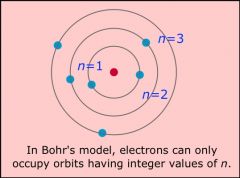
Bohr model
|
|
|
What does the atomic number of an element tell about an atom?
|
atomic number = the number of protons
atomic number = the number of electrons |
|
|
Who was the first person to organize the periodic table of the elements?
|
Mendeleev
|
|
|
How is the modern periodic table arranged?
|
increasing atomic number (number of protons)
in columns with those that have the same electrons in their outside energy level |
|
|
In which group number would I find the Noble Gases?
|
group 18
|
|
|
In which group(s) would I find the transition metals?
|
groups 3-12
|
|
|
In an atom, the number of protons equals the number of what?
|
electrons
|
|
|
Identify the chemical symbols for phosphorous, platinum, potassium, and palladium.
|
phosphorus - P
platinum - Pt potassium - K palladium - Pd |
|
|
Stars exist as what type of matter?
|
plasma
|
|
|
Describe nuclear fusion and how elements are created in stars.
|
atoms squeeze together and combine to form larger atoms - hydrogen fuses to helium
|
|
|
Give one example as to how tracers are used in science and industry.
|
can be followed through a reaction or an industrial process
- can find weak spots in metals or pipes - can detect leaks - can detect small cracks in bridges and buildings |
|
|
What is the element name and chemical symbol for element 112?
|
Cn - Copernicium
|
|
|
The element mercury (Hg) is located in which period?
|
period 6
|
|
|
The element bromine (Br) is located in which family?
|
halogens - group 17
|
|
|
How does the reactivity (chemical property) of metals change as you move across the periodic table?
|
decrease as you move to the right
|
|
|
List the three magnetic elements.
|
iron, nickel, chromium, cobalt
|
|
|
Why are some elements not abbreviated with their English names?
|
based on Latin names
K - kalium (potassium) Na - natrium (sodium) Pb - plumbum (lead) |
|
|
In what state are most of the nonmetals found at room temperature?
|
gas
|
|
|
What properties of metals are the opposite of brittle?
|
malleable and ductile
|
|
|
What property makes certain metalloids useful as “switches” to turn a small electric current on and off?
|
semiconductors - conduct under some conditions but not others - temperature, light...
|
|
|
Why is hydrogen (H) not grouped into a family?
|
actually a non-metal
properties are very different from other elements 90% of universe but less than 1% of Earth's crust, oceans and atmosphere - instead found as water |
|
|
What Greek philosopher first used the word atomos to describe the smallest piece of matter?
|
Democritus
|
|
|
Which element is MORE reactive, sodium (Na) or gold (Au)? Why?
|
Na - has only 1 electron in its outside energy level
|
|
|
What element is the only nonmetal in group 14?
|
C - carbon
|
|
|
What nonmetal is the most abundant element in Earth’s crust? The atmosphere?
|
crust - O - oxygen
atmosphere - N - nitrogen |
|
|
Where on the periodic table are the metalloids found?
|
along stair-step line between metals and non metals
|
|
|
Explain how particle accelerators are used to create new elements.
|
speeds up and crashes particles into one another so they combine forcing more protons into the nucleus
|

