![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
75 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
As [R] increases reaction rate______? |
Reaction rate Increases |
|
|
As Solid reactant surface area Increases reaction rate ______? |
Reaction rate Increases |
|
|
As rate constant k increases reaction rate _____? |
Reaction rate Increases |
|
|
As temperature Increases rate constant k_______? |
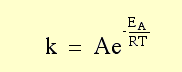
rate constant k Increases by e larger e^x larger # |
|
|
In the presence of a catalyst rate constant k______? |
rate constant k Increases |
|
|
rate = k[R] is for _______ order reaction |
rate = k[R] is for First order reaction |
|
|
ln[R]t = -kt + ln[R]0is for _______ order reaction |
ln[R]t = -kt + ln[R]0 is for First order reaction |
|
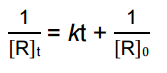
is for _______ order reaction |
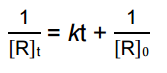
is for Second order reaction |
|
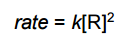
is for _______ order reaction |
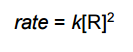
is for Second order reaction |
|
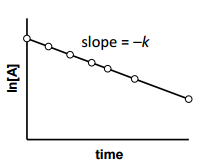
is for _______ order reaction |
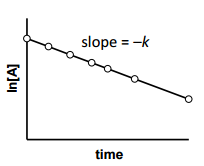
is for First order reaction |
|
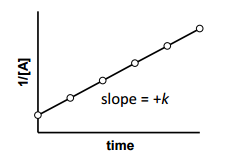
is for _______ order reaction |
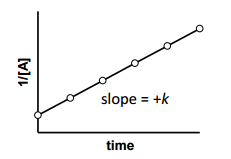
is for Second order reaction |
|
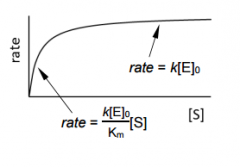
the more substrait you have the affect on rate _______ |
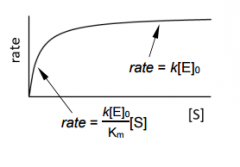
the more substrait you have the affect on rate Decreases. |
|

Q __ K |

Q < K |
|

Q__K |

Q = K |
|

Q __ K |

Q > K |
|
|
Effectively all products: complete reaction K __ 1 |
Effectively all products: complete reaction K >> 1 |
|
|
Product-favoured, some reactant: partial reaction K __ 1
|
Product-favoured, some reactant: partial reaction K > 1 |
|
|
Reactant-favoured, some products: partial reaction K__ 1 |
Reactant-favoured, some products: partial reaction K <1 |
|
|
Effectively all reactants: no reaction K __ 1
|
Effectively all reactants: no reaction K << 1 |
|

Direction of reaction shift ___________? ___________? |

Direction of reaction shift Toward Products Toward Reactants |
|

Effect on K? |

No effect on K |
|

Direction of Reaction Shift _________? _________? |

Direction of Reaction Shift Toward Greater moles of gas Toward lesser moles of gas |
|

Effect on K? |

No effect on K |
|

Direction of Reaction Shift _________? _________? |

Toward absorption of heat Toward Release of heat |
|

Effect on K? |
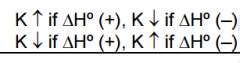
T up T up |
|
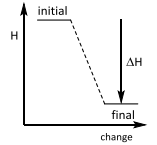
Enthalpy changes This is an ________ reaction? |
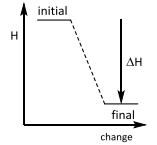
Enthalpy changes This is an Exothermic reaction. |
|
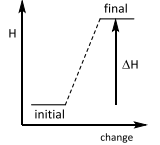
Enthalpy changes
This is an ________ reaction? |
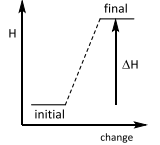
Enthalpy changes This is an Endothermic reaction. |
|
|
Exothermic reactions ________ q |
Exothermic reactions Release q |
|
|
Endothermic reactions _______ q |
Endothermic reactions Absorb q |
|
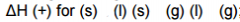
Delta H for phase change: |
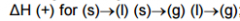
Delta H for phase change: |
|
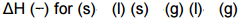
Delta H for phase change: |
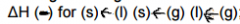
Delta H for phase change: |
|

Spontaneity? Q __ K ? |

Spontaneity? Q __ K ? Forward Q < K Equilibrium Q = K Reverse Q > K |
|
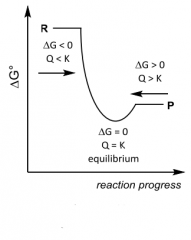
G __ 0, K __ 1 ______favoured |
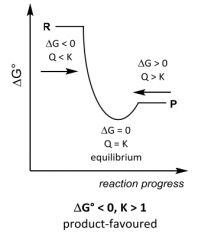
|
|
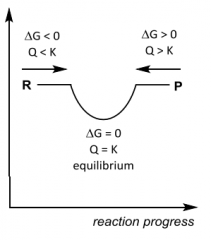
G __ 0, K __ 1 ______favoured |
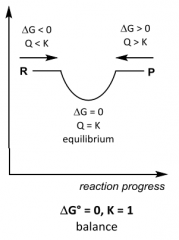
|
|
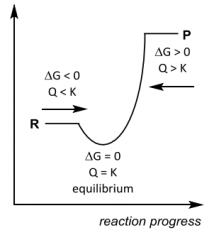
G __ 0, K __ 1 ______favoured |
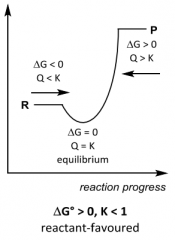
|
|
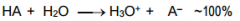
This is a ________ |
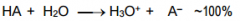
This is a Strong Acid |
|
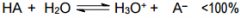
This is a _______ |
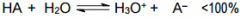
This is a Weak acid |
|
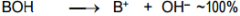
This is a _______ |
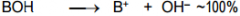
This is a Strong base |
|
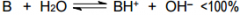
This is a ______ |
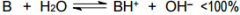
This is a Weak base |
|
|
Bronsted-Lowry Acid: ___________ Bronsted-Lowry Base:___________ |
Bronsted-Lowry Acid:Proton donor Bronsted-Lowry Base:Proton acceptor |
|

Anion of ________? |

Anion of Strong acid. Note the pH of solution |
|

Anion of _______? |

Anion of Weak acid. Note the pH of solution |
|

Cation of ________? |

Cation of Strong base. Note the pH of solution |
|
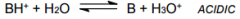
Cation of __________? |
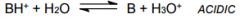
Cation of Weak base. Note the pH of solution |
|
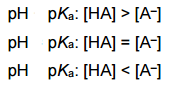
|
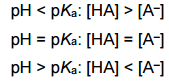
|
|
|
What is Mass Spectrometry? |
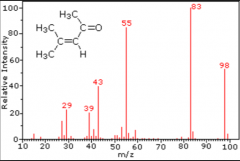
Mass spectrometry measures mass of molecule and molecular fragments |
|
|
What is IR spectroscopy?
|
IR spectroscopy: Different bonds vibrate at different frequencies |
|
|
What is C NMR spectroscopy? |
C NMR spectroscopy one signal per unique carbon environment |
|
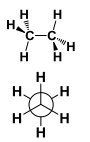
This is a ______ Conformation |
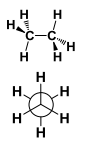
This is a Staggered conformation. |
|
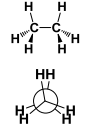
This is a ______ Conformation |
This is a Eclipsed conformation |
|
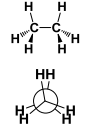
This conformation has a ______ interaction. |
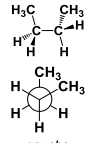
This conformation has a Gauche interaction. |
|
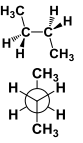
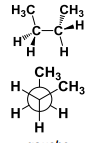
This conformation has atoms arranged in _____ |
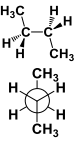
This conformation has atoms arranged in Anti |
|
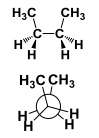
This conformation is considered ________ |
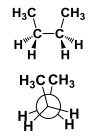
This conformation is considered Fully Eclipsed. |
|
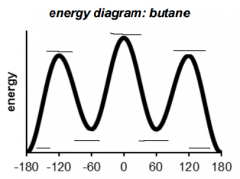
Label diagram |
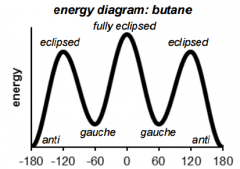
|
|
Label |
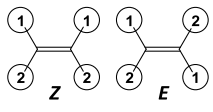
|
|
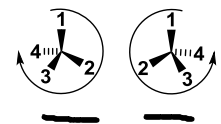
Label |
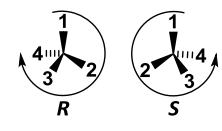
|
|
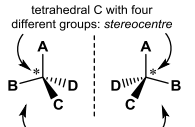
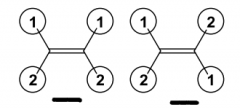
These two molecules are _________ each being considered ______? |
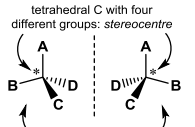
These two molecules are Enantiomers each being considered Chiral? |
|
|
Define Enantiomers. |
Enantiomers: a pair of different mirror image molecules |
|
|
Define Chirality |
Chirality: The property of being non-superimposable on a mirror image. |
|
|
Define Stereocentre |
Stereocentre: Origin of chirality, sp^3 C ( or other tetrahedral atom) with four different groups |
|
|
Define Racemic mixture
|
Racemic mixture: 1:1 mixture of two enantiomers |
|
|
pKa Trends Down column: E-H acidity _____ as E size _____ and E- stabilized |
pKa Trends Down column: E-H acidity Increases as E size Increases and E- stabilized |
|
|
pKa Trends Across row: E-H acidity ____ as Ex ______ and E- stabilized |
pKa Trends Across row: E-H acidity Increases as Ex Increases and E- stabilized |
|
|
pKa Trends similar E-H: resonance in A- = HA acidity _____, A- stablizied |
pKa Trends similar E-H: resonance in A- = HA acidity Increases, A- stablizied |
|
|
pKa Trends Similar E-H / resonance: more high-x atoms = HA acidity _____, A- stabilized |
pKa Trends Similar E-H / resonance: more high-x atoms = HA acidity Increases , A- stabilized |
|
|
Define Nucleophile
|

Nuncleophile |
|
|
Define Electrophile |

Electrophile |
|
|
Define Leaving group |
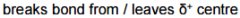
Leaving group |
|
|
Arrow moves |From| Resulting change is
Within a |BP to atom| __________ molecule |
Arrow moves| From |Resulting change is Within a |BP to atom |BP become new molecule LP: Bond order -1 |
|
|
Arrow moves |From |Resulting change is Within a molecule |BP to bond| __________ |
Arrow moves| From |Resulting change is Within a molecule |BP to bond| Old BP becomes new BP: bond changes position |
|
|
Arrow moves |From |Resulting change is Within a molecule| LP to bond| __________ |
Arrow moves | From| Resulting change is Within a molecule |LP to bond| LP becomes new BP: Bond order +1 |
|
|
Arrow moves| From |Resulting change is Between molecules |BP to new atom| ____________ |
Arrow moves| From | Resulting change is Between molecules |BP to new atom| Break old bonds, Form new bonds |
|
|
Arrow moves| From |Resulting change is Between molecules |LP to new atom| _____________ |
Arrow moves| From |Resulting change is Between molecules |LP to new atom |LP becomes new BP: form new bond |
|
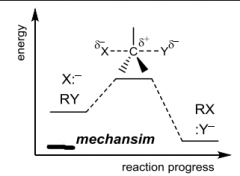
Label |
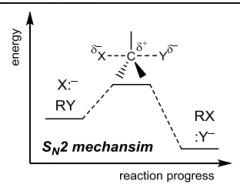
|
|
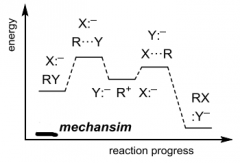
Label |
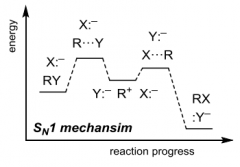
|

