![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Elements |
Substances that cannot be broken down into a simpler substance |
|
|
Properties of metal |
Bright and shiny luster malleable most silver-gray in color most are solid good conductors of heat and electricity
|
|
|
Properties of nonmetal |
Solids, liquid, gases dull luster different colors poor conductors of heat ans electricity |
|
|
Metalloid |
Share some properties with metals and some with non metals. |
|
|
Atom |
Smallest particle of an element that has the properties of that element |
|
|
Element |
Matter made of atoms of only one kind |
|
|
Model |
Used to describe things that cannot be observed directly |
|
|
who invented first atomic model |
Democritus |
|
|
Model of Democritus atom |

|
|
|
Dalton |
formed his model after collecting data about chemical reactions and behavior of gases |
|
|
J.J Thompson |
was credited with discovering electrons |
|
|
J.J. Thompson's model |
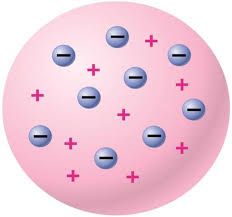
|
|
|
Rutheford thought about the atom |
atom is mostly made of empty space and all of the positive charge of an atom is located in a very small point in its center called the nucles. |
|
|
Rutheford's model |
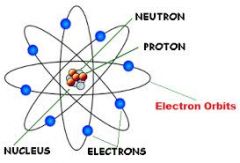
|
|
|
Nucleus |
Center of the atom, has most of the mass of the atom |
|
|
Proton |
Positively charged particle found inside the nucleus |
|
|
Neutron |
Particle with no charge found in the atom's nucleus |
|
|
Atomic number |
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom |
|
|
Mass number |
is the number of neutrons |
|
|
Isotopes |
atoms of any elements with different numbers of neutrons |
|
|
Chemical Symbol |
a notation of 1 or 2 letters that represent an elemt |
|
|
Electrons |
Travel around the nucleus in paths called orbits |
|
|
Bohr Model |
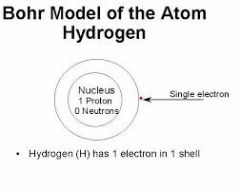
|
|
|
What happens when you add energy? |
Electrons move farther from the nucleus |
|
|
What happens when you give off energy? |
Electrons move closer to the nucleus |
|
|
What are the electron shells and how many electrons can it hold? |
K-2 L-8 M-18 N-32 |
|
|
Dmitri Mendeleev |
Made the first periodic table |
|
|
Henry Moseley |
developed the periodic table that is arranged by atomic number |
|
|
Periods |
Horizontal rows across the periodic tabe |
|
|
Groups |
vertical columns |
|
|
Alkali Metals |
In group 1 and are silvery solids with low densities and low melting points |
|
|
Alkaline Earth Metals |
In group 2 and is denser, harder, and has a higher melting point.
|
|
|
Halogen |
In group 17 contains bromine and means salt former |
|
|
NobleGases |
In group 18 ans rarely combine w/ other elements because they have a full outer shell. |
|
|
Chemical bond |
the force that holds two atoms together |
|
|
Ionic Bonding |
created when a positive and negative ion form a ionic bond |
|
|
Metallic bonding |
bonding with other metals |
|
|
Covalent bond |
Nonmetal atoms share electrons |
|
|
A.) Which electron has less energy? B.) Which electron has more energy?
|
A.) electron closer to the nucleus B.) electron farther from the nucleus |
|
|
Chemical Change |
produces new substances that have different properties from those of the original substances |
|
|
Physical change |
only affect physical properies |
|
|
name the different signs of the chemical reaction |
-change of color -formation of a precipitate -release of heat -absorbing of heat -gas produced
|
|
|
Exothermic reaction |
release of heat |
|
|
Endothermic reaction |
absorbing of heat |
|
|
Reactants |
substance that exist before the reaction begins |
|
|
products |
substance that form as a result of the reaction |
|
|
Law of Conservation of Mass |
the mass of the products must be the same as the mass of the reactants in the chemical reaction and you never create or destroy atoms |
|
|
Radioactive elements |
unstable elements that naturally break down or decay and slowly convert to a more stable non radioactive substance |
|
|
Radioactive decay |
the breaking down of particles from the nucleus and energy in the form of heat and light |
|
|
Radiation |
the release of particles and energy |
|
|
what happens during a radioactive decay |
the element will slowly change into atoms of a more stable non radioactive element |
|
|
Transmutation |
the changing of one element to another through radioactive decay |
|
|
Half life |
the amount of time it takes for half of the atoms of a radioactive element to convert to atoms of a more stable non radioactive element
|
|
|
how many protons and neurons does a alpha particle have |
2 protons and 2 neutrons |
|
|
what happens of a loss of a single alpha particle |
it will change the atomic number by 2 and the mass by 4 |
|
|
what happens when a beta particle is loss |
increases the atomic number by 1 |
|
|
What happens to a loss of a gamma particle |
no change in the mass or atomic number |

