![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a hydroxy acid?
|
An acid with both a carboxylic acid and an OH functional group.
|
|
|
What is an example of a hydroxy acid and what is it used for?
|
Glycolic acid is used in chemical skin peels.
|
|
|
Show hydrogen bonding between 2 propanoic acid molecules
|
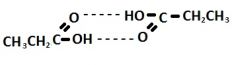
|
|
|
How to carboxylic acids compare to other functional groups in terms of polarity?
|
Carboxylic acids are more polar than hydrocarbons, ketones, aldehydes, and alcohols.
|
|
|
How do carboxylic acids compare to other functional groups in terms of boiling point and water solubility?
|
Strong molecular hydrogen bonding gives carboxylic acids higher boiling points than other functional groups. Carboxylic acid can hydrogen bond making it very soluble in water.
|
|
|
Name this compound: CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2COOH
|
Heptanoic acid
|
|
|
Name this compound: CH3CH2CH(CH3)COOH
|
2-Methylbutanoic acid
|
|
|
Name this compound: CH3CH(CH3)CH2COOH
|
3-Methylbutanoic acid
|
|
|
What are the reactants involved in an esterification reaction? What are the products generated in this reaction?
|
Reactants: an Alcohol and an Acid
Products: an Ester and Water |
|
|
What is an analgesic?
|
Pain reducer
|
|
|
What is an Atipyretic?
|
Fever reducer
|
|
|
What is an anti-inflammatory?
|
Inflammation reducer
|
|
|
What is nitroglycerin used for?
|
As a vasodilator to treat heart disease.
|
|
|
Primary, Secondary, or Tertiary?
CH3CH2NHCH3 |
SECONDARY
|
|
|
Primary, Secondary, or Tertiary?
CH3CH2CH2CH2NH2 |
PRIMARY
|
|
|
How do amines compare to other functional groups in terms of boiling point?
|
Amines have higher boiling points than alkanes but lower than alcohols and carboxylic acids.
|
|
|
What is a central nervous stimulant?
|
Any substance that stimulates the central nervous system.
|
|
|
Give an example of a CNS stimulant.
|
Epinephrine
|
|
|
What is a neurotransmitter?
|
Chemical messengers between nerve cells
|
|
|
Give an example of a neurotransmitter.
|
Aceylcholine
|
|
|
Are amides basic?
|
No, they are neutral because the OH of the carboxylic acid has been replaced with an amino group.
|
|
|
What are 2 commonly used amides and what are thier general uses?
|
Acetaminophen is a pain reliever
Nylon is used in clothing |
|
|
What are the 4 general groups of biochemical substances?
|
Proteins
Lipids Carbohydrates Nucleic Acids |
|
|
Define Carbohydrate.
|
A polyhydroxy aldehyde, a polyhydroxy ketone, or a compound that yields these upon hydrolysis
|
|
|
What functional group is present in all carbohydrates?
|
OH
|
|
|
Name and describe 2 important functions of carbohydrates
|
Carbohydrate oxidation provides energy
Carbohydrates for part of the structural framework of DNA and RNA molecules |
|
|
Define monosaccharide
|
a carbohydrate with a single polyhydroxy aldehyde or ketone unit
|
|
|
Define ogilosaccharide
|
2-10 monosaccharides bonded together
|
|
|
Define Disaccharide
|
2 monosaccharides bonded together
|
|
|
Define Polysaccharide
|
many monosaccharides bonded together
|
|
|
Chemical name for:
Fruit Sugar |
Fructose
|
|
|
Chemical name for: Blood Sugar
|
Glucose
|
|
|
Chemical name for:
Grape sugar |
Glucose
|
|
|
Chemical name for:
Brain Sugar |
Galactose
|
|
|
Chemical name for:
Table Sugar |
Sucrose
|
|
|
What is a chiral molecule?
|
A chiral molecule is one whose mirror images is not superimposable
|
|
|
What is a chiral center?
|
A chiral center is an atom with 4 different groups bonded to it
|
|
|
What is an enantiomer?
|
Enantiomers are stereoisomers whos molecules are nonsuperimposable mirror images of eachother.
|
|
|
What is a diastereomer?
|
Diastereomers are stereoisomers whose molecules are not mirror images of eachother
|
|
|
What is an optically active compound?
|
An optically active compound is a sample which contains an excess of one enantiomer
|
|
|
How do you tell if a structure is a D- or L- isomer?
|
if the OH on the chiral center is on the left it is L- if its on the right it is D-
|
|
|
What properties differ between D- and L- isomers?
|
Solubility in chiral solvents
effect on plane polarized light |
|
|
What type of reaction is responsible for the formation of the cyclic Haworth projection form of monosaccharides?
|
Intramolecular hemiacetal reaction
|
|
|
Benedicts and Tollens tests are used to test for what kind of sugars?
|
Reducing sugars
|
|
|
What disease is associated with glucose in the urine?
|
Diabetes
|
|
|
What test is typically used for glucose in the urine?
|
Benedicts reagent
|
|
|
What is the linkage between monosaccharides in a disaccharide called
|
Glycosidic linkage
|
|
|
What is Galactosemia?
|
A deficiency of one or more enzymes needed to convert galactose to glucose..
|
|
|
Give an example of a storage polysaccharide in plants and animals.
|
Plants: Starch
Animals: Glycogen |
|
|
Name the 2 components of starch.
|
Amylose and Amylopectin
|
|
|
Which component of starch is branched and which is linear?
|
Amylopectin is branched and Amylose is linear.
|
|
|
define homopolysaccharide and heteropolysaccharide
|
Homopolysaccharides contain only one type of monosaccharide
Heteropolysaccharides contain more than one type of monosaccharide |
|
|
Give an example of a structural polysaccharide in animals and plants.
|
Animals: Chitin
Plants: Cellulose |
|
|
What structural polysaccharide is the major component of dietary fiber?
|
Cellulose
|
|
|
What is the difference between dietary simple and complex carbohydrates?
|
Simple is usually sweet and complex is not.
|
|
|
What is a lipid
|
An organic compound found in living organisms that is insoluble in water, but soluble in nonpolar organic solvents
|
|
|
describe 2 fuctions of lipids
|
Energy storage
membrane formation |
|
|
What is a fatty acid?
|
A fatty acid is a naturally occuring monocarboxyilic acid that makes up part of a complex lipid molecule that is usually 4 to 26 carbons long.
|
|
|
What is an Omega 3 fatty acid?
|
A fatty acid with the double bond 3 carbons away from the methyl end of the fatty acid
|
|
|
What is an omega 6 fatty acid?
|
A fatty acid with the double bond 6 carbons away from the methyl end
|
|
|
What effects water solubility of fatty acids?
|
Water solubility decreases as carbon chain length increases
|
|
|
What effects melting points of fatty acids
|
melting point increases with chain length but decreases with the number of double bonds
|
|
|
Which has a higher melting point?
18:0 or 18:1 |
18:0
|
|
|
Which has a higher melting point?
14:0 or 16:0 |
16:0
|
|
|
Which is more water soluble?
12:0 or 20:0 |
12:0
|
|
|
What are the 4 structural subunits that contribute to the structer of a triacylglycerol
|
Glycerol and 3 fatty acids
|
|
|
what is an essential fatty acid
|
An essential fatty aid is a fatty acid required in the human diet.
|
|
|
give an example of an essential fatty acid.
|
Linoleic Acid
|
|
|
What are essential fatty acids used for in the body
|
Cell membrane structure and as starting materials for longer chain fatty acids.
|
|
|
How is soap made?
|
Animal fat is heated with a strong base to produce 3 fatty acids and one glycerol molecule
|

