![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define effector? |
Muscles or glands that put messages into effect. |
|
|
What is the endocrine system? |
All the endocrine glands of the body. It is coordinated by the pituitary gland which responds to information from the hypothalamus to bring about change. Made up of: pituitary, thyroid, pancreas, adrenal, ovaries and testes. |
|
|
Describe the relationship between hormones and endocrine glands. |
Hormones are produced by endocrine glands which are scattered throughout the body. |
|
|
Define hormones. |
Chemical substances that act as messengers in the body. |
|
|
Define pituitary gland. |
The endocrine gland that controls the activities of other endocrine glands; it is often called the 'master gland'. |
|
|
What is the role of the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland in controlling the body? |
The hypothalamus constantly checks the internal environment of the body. If conditions change it secretes hormones that act on the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland responds by either secreting other hormones or reducing less of the hormones. Through its action on the pituitary gland, the hypothalamus controls important aspects of the body e.g. temperature, rate of metabolism. |
|
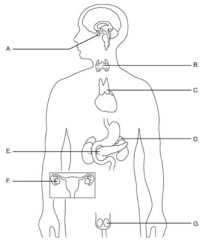
Label the diagram. |
◘ A – Pituitary gland ◘ B– Thyroid gland (throat) ◘ C – Thymus ◘ D– Adrenal glands (above pancreas) ◘ E– Pancreas ◘ F– Ovaries ◘ G– Testes |
|
|
Describe the function of the thyroid gland. |
Thyroid hormones, called thyroxine, increase metabolism rate in cells throughout the body. They control how quickly cells useenergy and make proteins. |
|
|
Describe the function of the pancreas. |
Makes insulin and glycogen which regulate the level of sugar in the blood. |
|
|
Describe the function of the adrenal glands. |
Produces: ◘ adrenaline (epinephrine) which speeds up the heart rate and prepares the body intense activity (i.e. fight-or-flight). ◘ cortisol, which helps the body deal with stress. ◘ aldosterone, which helps regulate the balance of minerals in the body. |
|
|
Describe the function of the ovaries. |
Produce female sex hormones (oestrogen and progesterone) which control body changes at puberty and during the menstrual cycle. |
|
|
Describe the function of the testes. |
Produce male sex hormones (testosterone) which control body changes at puberty and also sperm production. |
|
|
Why are endocrine glands referred to as 'ductless' glands? |
Because endocrine glands release their hormones directly into the bloodstream. |
|
|
How do hormones work? |
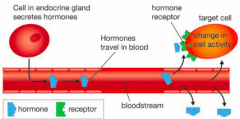
Hormones are produced in small amounts and travel through the blood to act on particular cells in the body known as target cells. Different hormones have different chemical structures therefore their shape varies. Within cells are receptors. A hormone is only active in cells that have receptors that fit the shape of the hormone. |
|
|
Define homeostasis. |
The process of maintaining a constant internal environment. |
|
|
What is negative feedback? |
A response to a stimulus that returnsthe internal environment of the body to homeostasis. |
|
|
Define metabolism. |
All the chemical reactions occurring in the cells throughout the body i.e. digestion, growth, respiration. |
|
|
How does the body control temperature using hormonal control of temperature? |
The hypothalamus acts on the pituitary gland to control body temperature through the thyroid gland. stimulus (fall in body temperature)→receptor (thermo skin receptors & hypothalamus)→pituitary release TSH→thyroid release more thyroxine→metabolism increases→more heat is generated→(negative feedback) body temperature rise. |
|
|
How does the body control a decrease in temperature using nervous control of temperature. |
SHIVERING Hypothalamus detects a fall in body temperature and sends nerve impulses to muscle groups→muscles shake, activity of muscle cells increase which produces heat→negative feedback (body temperature rise). REDUCE OF BLOOD FLOW TO SKIN Sympathetic nervous system narrows blood vessels close to the skin to reduce blood flow and heat flow to skin. Therefore vital organs remain warm. |
|
|
How does the body control an increase in temperature using nervous control of temperature. |
SWEATING Hypothalamus detects rise in body temperature→nerve messages sent to sweat glands and blood vessels→blood vessels close to skin dilate so that more blood carrying heat can reach the surface→heat from body causes sweat produced by glands to evaporate→body temperature cools. |
|
|
Explainwhy the nervous system and endocrine systems are different in terms of response time and how they transmit messages. |
The endocrine system takes longer to respond and react to stimuli as producing hormones to bring about change takes time. The endocrine system transmits messages via hormones whereas the nervous system transmits messages via neurotransmitters (nerve impulses). |
|
|
How does insulin control blood glucose? |
When a rise in blood glucose is detected by receptors in the pancreas, insulin is released. It reduces blood glucose by: ◘ increasing absorption of glucose by cells ◘ causing the liver tostore the excess glucose as glycogen. |
|
|
How does glucagon control blood glucose? |
When a decrease in blood glucose is detected by receptors in the pancreas, glucagon is released. It increases blood glucose by causing the liver to breakdown glycogen backinto glucose. |
|
|
What happens when you are stressed? |
Sympathetic nervous system messages the adrenal glands to produce adrenalin which causes: - increased heart rate - bloods vessels to contract - air passages to dilate This reaction of the body to adrenalin (which increases respiration) makes you more alert and prepares your body to act 'fight or flight' in the stressful/frightening situation. |

