![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which elements exist as independent forms in nature? |
Noble gases |
|
|
Van der Waals radius and covalent radius |
Covalent radius is half of the internuclear separation between the nuclei of two single-bonded atoms of the same species (homonuclear). While van der Waals radius is used to define half of the distance between the closest approach of two non-bonded atoms of a given element. |
|
|
Lattice enthalpy |
Lattice enthalpy is a measure of the strength of the forces between the ions in an ionic solid. The greater the lattice enthalpy, the stronger the forces. Those forces are only completely broken when the ions are present as gaseous ions, scattered so far apart that there is negligible attraction between them. |
|
|
Bond enthalpy |
Bond enthalpy (also known as bond energy) is defined as the amount of energy required to break one mole of the stated bond. For example, the bond energy of a O-H single bond is 463 kJ/mol. This means that it requires 463 kJ of energy to break one mole of O-H bonds. |
|
|
Isoelectronic species |

|
|
|
Canonical/resonance structures |
A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical structures). |
|
|
Resonance hybrid |
The net sum of valid resonance structures is defined as a resonance hybrid, which represents the overall delocalization of electrons within the molecule. A molecule that has several resonance structures is more stable than one with fewer. |
|
|
Tautomerism |
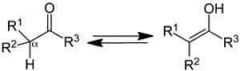
In organic chemistry, keto–enol tautomerism refers to a chemical equilibrium between a keto form (a ketone or an aldehyde) and an enol (an alcohol). The enol and keto forms are said to be tautomers of each other. The interconversion of the two forms involves the movement of an alpha hydrogen and the shifting of bonding electrons; hence, the isomerism qualifies as tautomerism. |
|
|
In which structure canonical or resonance hybrid do actually a molecule exist in nature |
Resonance hybrid |
|
|
Fajans rules for partial covalent character of ionic bonds |
1)The smaller the size of the cation and the larger the size of the anion,the greater the covalent character of an ionic bond 2)the greater the charge on the cation ,the greater the covalent character of ionic bond. 3)For cations of same size and charge, the one with electronic configuration (n-1)d^n ns^0,typical of transition metals is more polarizing than the one with a noble gas configuration,ns2np6,typical of alkali and alkaline earth metal actions. |
|
|
For the prediction of geometrical shapes of molecules with the help of VSEPR theory,it is convenient to divide molecules into categories |
1)molecules in which the central atom has no lone pair 2)molecules in which the central atom has one or more lone pairs. |
|
|
Which are the two theories that are based on quantum mechanical principles? |
Valence bond(VB)Theory Molecular orbital(MO)Theory |
|
|
Give the theories and their developers |
MO--F.hund and RS Mulliken in 1932 VB--Heitler,London,Pauling in 1927 VSEPR--Sidgwick and Powell in 1940 Kossel lewis approach--1916 |
|
|
Schrödinger equation for a system whose energy does not change with time. |
It is written as H¥ =E¥ where H is a mathematical operator called Hamiltonian |
|
|
Atomic orbitals |
The wave function is a mathematical function whose value depends upon the coordinates of the electron in the atom and does not carry any physical meaning.Such wave functions of hydrogen like species with one electron are called atomic orbitals. |
|
|
One-electron systems |
Systems pertaining to one electron species are called one electron systems. |
|
|
On what factors does the energy of orbitals of one electron and multi electron species depend? |
Unlike orbitals of hydrogen or hydrogen like species,whose energies depend only on the quantum number n,the energies of the orbitals in multi-electron atoms depend on quantum numbers n and l. |
|
|
What is the probability of finding an electron at a point |
The probability of finding an electron at a point within an atom is proportional to the square of the orbital wave function |¥|^2 at that point. |¥|^2 is known as probability density and is always positive . |
|
|
Is it possible to get the probable distribution of an electron in an orbital |
Yes |
|
|
What are the types of covalent bonds based on types of overlapping |
Sigma bond(s-s,s-p,p-p) Pi bond |
|
|
On what does the strength of sigma and pi bond depend |
Extent of overlap |
|
|
Hybridization |
hybridization) is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals (with different energies, shapes, etc., than the component atomic orbitals) suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory. |
|
|
Conditions for hybridization |
1)the orbitals present in valence shell of the atom are hybridized 2)the orbitals undergoing hybridization should have almost equal energy 3)Promotion of electron is not essential condition prior to hybridization 4)it is not necessary that only half filled orbitals participate in hybridization.In some cases even filled orbitals of valence shell take part in hybridization. |
|
|
Types of hybridization |
sp(BeCl2) sp2( sp3( |
|
|
Sigma bond |
This type of covalent bond is formed by the end-to-end(head on) overlap of bonding orbitals along the internuclear axis.This is called as head on overlap or axial overlap. |
|
|
Pi bond |
Bonding orbitals overlap in such a way that their axes remain parallel to each other and perpendicular to the internuclear axis. |
|
|
Explain atomic and molecular orbital in MO |

The atomic orbitals of comparable energies and proper symmetry combine to form molecular orbitals |
|
|
Where is the electron density and its consequences in a bonding and anti bonding molecular orbital? |
The electron density in a bonding molecular orbital is located between the nuclei of the bonded atoms because of which the repulsion between the nuclei is very less Most of the electron density is located away from the space between the nuclei in case of antibonding molecular orbital. Infact ,there is a nodal plane(on which the electron density is zero)between the nuclei and hence the repulsion between the nuclei is very high. |
|
|
Conditions for combination of atomic orbitals |
1)The combining atomic orbitals must have the same or nearly the same energy. 2)The combining atomic orbitals must have the same symmetry about the molecular axis. 3)The combining atomic orbitals must overlap to the maximum extent. |
|
|
How does MO account for stability of molecules |
If Nb is the no. of electrons occupying bonding orbitals and Na the no. occupying anti bonding orbitals,then 1)the molecule is stable if Nb is greater than Na 2)the molecule is unstable if Nb is less than Na |
|
|
Do Li2 molecules exist |
Yes...they are diamagnetic and exist in vapour phase |
|
|
When is the magnitude of hydrogen bonds most and least |
Most-solid state Least-liquid state |

