![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Whole Blood |
Measures both the liquid and cellular component |
|
|
Serum |
Liquid part that remains after clotting and centrifugation |
|
|
Plasma |
Liquid part of unclotted blood |
|
|
Accuracy |
W/out error, close to true value |
|
|
Precision |
Closeness of repeated results, expressed as the SD |
|
|
Sensitivity |
Smallest amount of a concentration that can be measured directly |
|
|
Specificity |
method ability to measure only the analyte in question |
|
|
Analyte/solute |
Substance being measured |
|
|
Solvent |
liquid that the solute is located in |
|
|
Which led to the automation we have today ____ & _____? |
Ph meter & colorimeter |
|
|
Advantages of automation |
TAT shorter & small amount of sample needed |
|
|
F= |
(C x 1.8) + 32 |
|
|
C= |
(F - 32) x 5/9 |
|
|
K= |
C + 273 |
|
|
Standard Reference Material (SRM): |
Developed for chemistry, have a verified SD & is called the calibrator
|
|
|
Grade II Water: |
For reagent/control preparation |
|
|
Grade III Water: |
For cleaning |
|
|
Volumetric flask: |
Used to bring a reagent to final volume |
|
|
Erlenmeyer Flask: |
Used in reagent preparation |
|
|
Graduated cylinder: |
Measure volume of liquid |
|
|
Pipette TC: |
To contain, has certain volume but does not dispense exact volume |
|
|
Pipette TD: |
To deliver, will dispense the stated volume |
|
|
Serological pipette: |
(Blow out pipette) Has # markings to the end of the tip |
|
|
Mohr pipette: |
(Self-draining) Doesn't have number markings on the tip |
|
|
Micropipette: |
(Blow out pipette) Dispenses 1 volume |
|
|
Volumetric Flask: |
(Self-draining) Holds 1 volume of liquids, used for preparing reagent |
|
|
Most critical step: |
Patient ID |
|
|
Order of draw for venipuncture: |
Cultures, blue, yellow/red sst, green, lavender, gray |
|
|
Anticoagulant present: Light blue: Green: Lavender: Gray: |
Light blue: Na Citrate Green: NA/Li/NH3Heparin Lavender: EDTA Gray: K+ oxalate |
|
|
Trough: |
30 minutes before the dose is given, should be low measurement |
|
|
Peak: |
30-60 min. AFTER a 30 min. infusion. Should be higher measurement than trough |
|
|
CSF tubes: Tube 1: Tube 2: Tube 3: |
Tube 1: Chemistry Tube 2: Microbiology Tube 3: Hematology |
|
|
Body fluids: Pericardial: Synovial fluid: Peritoneal: Pleural: |
Pericardial: Heart Synovial fluid: Joint Peritoneal: Abdominal fluid Pleural: fluid from lungs |
|
|
MUST have _______ & ________ |
number value & unit |
|
|
1,000 ug = 1,000,000 ug= |
1 mg 1g |
|
|
Mean: |
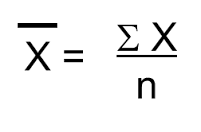
|
|
|
Standard Deviation: |
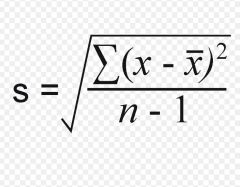
Indicator of how close values in a set are distributed |
|
|
Variance: |
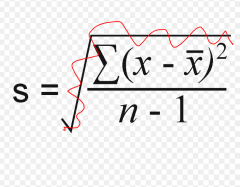
Defined as the square of the SD |
|
|
Quality assurance |
All actions taken by the lab to ensure that the services provided will satisfy the needs of the patient |
|
|
Quality control |
Alaboratories system for recognizing and minimizing analytical errors |
|
|
Random error: > > * > |
>Due to chance >Possibilities: *Pipetting error, Mixing error, Temperature fluctuation >Repeat testing |
|
|
Systematic error: |
>Data move in 1 direction or another >Rise or fall from established data >Possibilities: *Improper calibration, deterioration, instrument drift >Still out recalibrate, New controls |
|
|
Three types of standards Primary: Standard Reference Materials (SRM): Secondary Standard: |
>Primary: High purity, exact known [ ], expensive and hard to make >Standard Reference Materials (SRM): developed for Chemistry, have a verified SD (standard deviation) >Secondary Standard: Lower purity |
|
|
Water I: |
>Purist >Used when analysis is critical and needs no/few impurities |
|
|
Amniotic Fluid: |
>protect w/ light > Use dark tubes |

