![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Solid (Shape & Volume) |
Shape: Tightly packed Volume: Fixed |
|
|
|
Liquid (Shape & Volume) |
Shape: close together Volume: shape of container |
|
|
|
Gas (Shape & Volume) |
Shape: free space between particles |
|
|
|
Phase of material that is typically the densest |
Solid |
|
|
|
Phase of material that is most compressible |
Gas |
|
|
|
Ionic Bonds |
Transfer of electrons |
|
|
|
Covalent Bonds |
Sharing of electrons |
|
|
|
IMFs are most important in what phases? |
Solids and Liquids |
|
|
|
IMFs (increase/decrease) with distance? |
Decrease |
|
|
|
Strongest IMFs |
Ion-Dipole |
|
|
|
___ of the ion & ____ of the charge affect how strong the interaction is in Ion-Dipole IMFs |
Size & Magnitude |
|
|
|
Increased ion charge (increases/decreases) the strength of the interaction |
Increases |
|
|
|
Increased ion size (increases/decreases) the strength of the interaction |
Decreases |
|
|
|
Molecules that are (polar/nonpolar) have a permanent dipole moment |
Polar |
|
|
|
What determines the magnitude of the dipole moment and thus the strength of the IMFs? |
Atoms |
|
|
|
Hydrogen Bonding |
H covalently bonded to F, O, and N. |
|
|
|
What leads to highly concentrated partial charges with F, O, N, and H atoms? |
Large difference in electronegativity and the small sizes of F, O, and N |
|
|
|
Which IMFs get stronger with increasing molecular size? |
Dispersion forces |
|
|
|
Cohesion |
Between molecules of the same substance |
|
|
|
Adhesion |
Between different substances |
|
|
|
Viscosity |
Measure of flow |
|
|
|
Phase change of Solid --> Liquid; Energy added or removed? |
Melting; Added |
|
|
|
Phase change of liquid --> gas; energy added or removed? |
Vaporization; Added |
|
|
|
Phase change from gas --> liquid; energy added or removed? |
Condensation; Removed |
|
|
|
Phase change if liquid --> solid; energy added or removed? |
Freezing; removed |
|
|
|
Phase change if solid --> gas; energy added or removed? |
Sublimation; added |
|
|
|
Phase change of gas --> solid; energy added or removed? |
Deposition; Removed |
|
|
|
Increased surface area (increase/decrease) the rate of evaporization? |
Increase |
|
|
|
Increased temperature (increase/decrease) the rate of evaporization? |
Increase |
|
|
|
Why does liquid boil? |
The particles gain enough kinetic energy to completely overcome the attractive forces |
|
|
|
How are gases condensed? |
By decreasing their temperature or increasing the pressure |
|
|
|
The greater the IMFs between molecules the (more/less) energy needed to vaporize? |
More |
|
|
|
The greater the IMFs the (faster/slower) rate of evaporization? |
Slower |
|
|
|
Molecules in the vapor state can (gain/lose) energy though the collisions with other molecules? |
Lose |
|
|
|
The (greater/less) the IMFs, the (greater/less) energy is needed for the vapor molecules to condense? |
Greater; Less |
|
|
|
Volatile |
Liquids that evaporate easily |
|
|
|
Is salt water volatile or nonvolatile? |
Nonvolatile |
Think of the ocean, does it evaporate easily? |
|
|
Equilibrium vapor pressure |
Rate of evaporation = rate of condensation |
|
|
|
At a given temperature is vapor pressure independent or dependent of IMFs? |
Depends on IMFs |
|
|
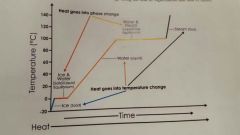
Phase changes |
. |
|
|
|
Clausis-Clapeyron Equation |
ln (P2/P1) = -delta Hvap/ R (1/T2 - 1/T1) |
|
|
|
Solute |
Gets dissolved |
|
|
|
Solvent |
Does the dissolving |
|
|
|
Solution |
Homogeneous mixture |
|
|
|
Endothermic |
+ delta H soln |
|
|
|
Entropy |
Measure of a system's disorder or dispersal of particles throughout a system. Energy tends to disperse throughout the system |
|
|
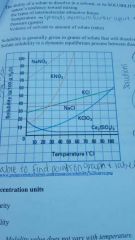
Where is it saturated, unsaturated, and supersaturated? |
Saturated - on the line, Unsaturated - below the line, Supersat - above the line |
|
|
|
Molarity |
Moles solute / L solution |
|
|
|
Molality |
Moles solute / kg solvent |
|
|
|
Henry's Law |
Sgas = (KH)(Pgas) |
|
|
|
Van't hoff factor of NaCl |
2 |
Number of pieces it breaks into |
|
|
Van't Hoff factor of CaCl2 |
3 |
|
|
|
Van't Hoff factor of NH3 |
1 (covalently bonded non metal) |
|
|
|
Van't Hoff of NaOH |
2 |
|
|
|
Van't Hoff of Na3PO4 |
4 |
|
|
|
Van't Hoff of CH3OH |
1 (all covalently bonded) |
|
|
|
Osmotic Pressure Formula |
(pie symbol) = iMRT |
|
|
|
Which intermolecular forces are the weakest? |
Dispersion forces |
|
|
|
What are the only things coligative properties depend on? |
Concentration of solute particles in a solution |
|
|
|
Which concentration unit is temperature dependent? |
Molarity |
|

