![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
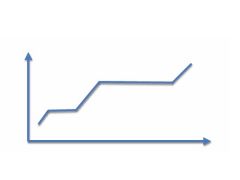
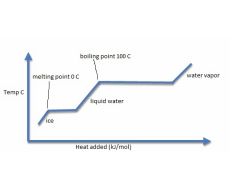
Label the following: ice, liquid water, vapor water, melting point and temp, boiling point and temp, each axis,
|
|
|
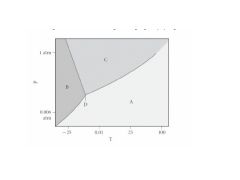
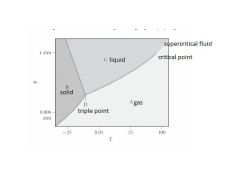
Where are the 3 phases?
Where is the supercritical liquid? Where are the triple and critical points? |
|
|
|
Are polar molecules hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
|
hydrophilic
|
|
|
Are non-polar molecules hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
|
hydrophobic
|
|
|
What kind of substances are detergents?
|
amphipathic
|
|
|
The rate of evaporation in a closed container is ____ the rate of condensation.
|
equal to
|
|
|
While a pure liquid is boiling, the temperature is _____.
|
constant
|
|
|
Is evaporation endothermic or exothermic?
|
endothermic
|
|
|
Is condensation endothermic or exothermic?
|
exothermic
|
|
|
The solid to gas change of state is called ____. Is it exothermic or endothermic?
|
sublimation
endothermic |
|
|
The solid to liquid change of state is called ____ or ____. Is it exothermic or endothermic?
|
melting/fusion
endothermic |
|
|
The liquid to solid change of state is called ____. Is it exothermic or endothermic?
|
freezing
exothermic |
|
|
The liquid to gas state of change is called ____. Is it exothermic or endothermic?
|
vaporization
endothermic |
|
|
The gas to liquid state of change is called ____. Is it exothermic or endothermic?
|
condensation
exothermic |
|
|
Which substance has the highest boiling point and why?
CH3CH2CH2CH2OH OR CH3CH2OCH2CH3 |
CH3CH2CH2CH2OH because of the H-bond
|
|
|
What is the best way to tell in a C H O chain, which one has the highest boiling point?
|
whichever has the higher imf's
OH in it will have higher imf's whichever is biggest will also have higher imf's |
|
|
Place the following in order of increasing imf's.
1. CH4 2. CH3CH2CH3 3. CH3CH3 |
1<3<2
|
|
|
Dispersion forces are also called ____.
|
London forces
|
|
|
The bigger the London forces the ____ the molar mass.
|
larger
|
|
|
The smaller the dispersion forces the ____ the molar mass.
|
smaller
|
|
|
Liquids have a ____ density than gases.
|
higher
|
|
|
Compared to liquids, gases have a ___ strength of imf's.
|
weaker
|
|
|
What are the four types of bonding? Put them in order of weakest to strongest.
|
Dispersion
Dipole-dipole H-bond Ion-dipole |
|
|
What kind of bond force is present in mixtures of ionic compounds and polar compounds?
|
Ion-dipole
|
|
|
Polar liquids are miscible/not miscible with nonpolar liquids.
|
not miscible
|
|
|
Compared to liquids, solids have a ___ strength of imf's.
|
stronger
|
|
|
Polar liquids are miscible/not miscible with polar liquids.
|
miscible
|
|
|
What are immiscible liquids?
|
liquids that don't mix
|
|
|
If one molecule is round and another is oval shaped and they have the same molecular weight, which one has stronger dispersion forces, and why?
|
the oval because it has more surface contact between the molecules
|
|
|
The molar volume of water vapor is ____ than that of liquid water.
|
larger
|
|
|
The molar volume of liquid water is ____ than that of water vapor.
|
smaller
|
|
|
With detergents, H2O bonds to the ____ end and oil bonds to the ____ end.
|
hydrophilic
hydrophobic |
|
|
The higher the temperature, the ____ the rate of evaporation.
|
faster
|
|
|
Liquids that evaporate easily are known as ____ liquids. List a few examples.
|
volatile
gasoline, fingernail polish remover |
|
|
Liquids that do not evaporate easily are known as ____ liquids. List an example.
|
non-volatile
oil |
|
|
The weaker the imf's, the ____ the rate of evaporation.
|
faster
|
|
|
Name the molecular geometries with 2 e- regions, and the degrees.
|
Linear
180 |
|
|
Name the molecular geometries with 3 e- regions, and the degrees.
|
trigonal planar
bent 120 |
|
|
Name the molecular geometries with 4 e- regions, and the degrees.
|
tetrahedral
trigonal pyramidal bent 109.5 |
|
|
Name the molecular geometries with 5 e- regions, and the degrees.
|
trigonal bipyramidal
see saw t shaped linear 90 and 120 |
|
|
Name the molecular geometries with 6 e- regions, and the degrees.
|
octahedral
square pyramidal square planar 90 |
|
|
imf's influence what three different properties?
|
surface tension
viscosity capillary action |
|
|
What is surface tension?
|
the tendancy of liquids to minimize their surface area
|
|
|
The stronger the surface tension would mean the imf's are ____.
|
stronger
|
|
|
What is viscosity?
|
the resistance of a liquid to flow
|
|
|
What three things does viscosity depend on?
|
imf's
size and shape of molecules temperature |
|
|
The stronger the imf's the ____ viscous something is.
|
more
|
|
|
____ and ____ molecules are more viscous.
|
larger and longer
|
|
|
____ and ____ molecules are less viscous.
|
smaller and shorter
|
|
|
The higher the temp the ____ viscous something is. Why?
|
less
more energy available to overcome imf's |
|
|
In capillary action, cohesive force is ...
|
attractive imf's between the liquid molecules
|
|
|
In capillary action, adhesive force is ...
|
attractive imf's that occur between the liquid and the wall of the tube
|
|
|
Cohesive < Adhesive
|
capillary action
|
|
|
Cohesive > Adhesive
|
no capillary action
|
|
|
Intramolecular forces hold ____ together and are ____ than intermolecular forces.
|
atoms
stronger |
|
|
Intermolecular forces hold ____ together and are ____ than intramolecular forces.
|
molecules
weaker |
|
|
The rate of vaporization ____ with the increasing surface area.
|
increases
|
|
|
The rate of vaporization ____ with the decreasing surface area.
|
decreases
|
|
|
The gas to solid state of change is called ____. Is it exothermic or endothermic?
|
deposition
exothermic |

