![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The lowest allowable energy state of an atom is called its ____________________. |
ground state |
|
|
Bohr’s model of the atom predicted the ____________________ of the lines in hydrogen’s atomic emission spectrum. |
frequencies |
|
|
According to Bohr’s atomic model, the larger an electron’s orbit, the ____________________ the atom’s energy level. |
higher |
|
|
According to Bohr’s atomic model, the smaller an electron’s orbit, the ____________________ the atom’s energy level. |
lower |
|
|
Bohr proposed that when energy is added to a hydrogen atom, its ____________________ moves to a higher- energy orbit. |
e- |
|
|
According to Bohr’s atomic model, the hydrogen atom emits a photon corresponding to the difference between the ____________________ associated with the two orbits it transitions between. |
energy levels |
|
|
Bohr’s atomic model failed to explain the ____________________ of elements other than hydrogen. |
atomic emission spectrum |
|
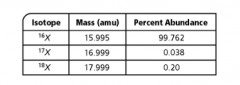
Use the table below to calculate the atomic mass of element X. Then use the periodic table to identify the element. Show all your work. |
AMU 15.9, O |
|
|
The isotope carbon-14 can be used to determine the ages of objects that were once living, such as wood, bones, and fossils. While alive, living things take in all the isotopes of carbon, including carbon-14. Carbon- 14 undergoes radioactive decay continuously. After an organism dies, the carbon-14 in its body continues to decay. However, its body no longer takes in new carbon-14. Thus, by measuring how much carbon-14 a once- living object contains and comparing it with the amount of carbon-14 in a currently living thing, you can determine the age of the object. In terms of subatomic structure, how does carbon-14 differ from carbon-12 and carbon-13? |
Carbon-14 differs from Carbon-12 + Carbon-13 because carbon-14 has 8 n0, |
|
|
How do the Bohr model and the quantum mechanical model of the atom differ in how they describe electrons? |
Bohr - tries to predict e- path, desc. as particles ; Quantum Mech. - cannot predict (Heisenburg's), wave properties |
|
|
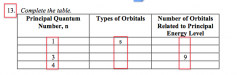
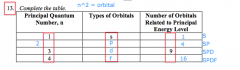
Describe how each pair is related. valence electron, electron-dot structure principal energy levels, energy sublevels |
1. valence e- <-> e- dot structure : v.e-. -- e- in outer shell ; e- dot structure -- a type of shorthand notation that uses 2. Principal E lvls. - periods <-> E lvls. -- increase in E. lvl. --> sublevel inc. |
|
|
Write the orbital diagram and complete electron configuration for each atom. fluorine sodium |
1. [HE]2s^2 2p^5 2. [Ne]3p^1 |
|
|
|
|
|
Identify each atom, and write the Lewis dot structure a. 1s22s22p1 b. [Ar]4s1 |
a. Boron b. Potassium |
|
|
What are the difference between electromagnetic spectrum, atomic emission spectrum, and the continuous spectrum of white light? |
EMF - x + v = all |
|
|
Compare the wave and particle models of light. What phenomena can only be explained by the particle model? |
particle - photoelectric effect |
|
|
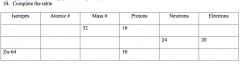
Name the 3 sub-particles that make up an atom. Describe it in terms of location and charges. |
p+ -- nucleus n0 -- nucleus e- -- outside nucleus |
|
|
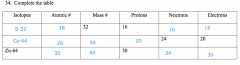
|
|

|

|
|
|
For the following question, do not use the periodic table. |
[He] 2s^2, [Ar] 3s^2, [Kr] 4s^2
|
|
|
For the following questions, do not use the periodic table. [He]2s22p4 |
1. Period 2 ; P block ; 6A |
|
|
Rank the following atoms in order of decreasing radii. Al,Na,P,S As, Ge, Ga |
1. Na, Al, P, S 2. Ga, Ge, As |
|
|
Rank the following atoms in order of decreasing electronegativity. K, Sc, Ca As, Sn, S |
1. Sc, Ca, K 2. S, As, Sn |
|
|
What is ionization energy? |
the minimum amt. of E required to remove an e- |
|
|
What does the electronegativity of an element indicate? |
affinity for e-'s |
|
|
Orange light has a frequency of 4.8 × 1014 s–1. What is the energy of one quantum of orange light? |
3.2 * 10^-19 J |
|
|
Write the alpha decay of Hassium [Hs] which has an atomic mass of 273 and an atomic number of 108. |
... |
|
|
Write the beta decay of Fermium [Fm] which has an atomic mass of 105 and a n atomic number of 100. |
... |
|
|
Write the electron configuration of Zirconium (Zr), the dot structure, and how much VE it contains? |
[Kr]5s^2 4d^2 -- 2 V.e- |
|
|
What is the wavelength of a photon that gives off 5.66 x 10-23 J. |
... |
|
|
A light source has a wavelength of 5.6 nm, what is its energy? |
3.55 * 10^-17 J |
|
|
What is the frequency of a photon that has a wavelength of 789 km? |
380 HZ |

