![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Inertia |
The property of mass to resist a change of position or motion |
|
|
Density |
The relationship of mass to a unit volume |
|
|
Density (formula) |
D=m/V |
|
|
Mass |
The quantity of matter and has a unit of weight assigned to it |
|
|
Matter |
Anything that has mass and occupies space |
|
|
Gram |
Unit of mass |
|
|
Volume |
Measured in cubic centimeters (cm^3) or milliliters (mL) |
|
|
Properties of a liquid |
Has a definite volume and takes the shape of the container |
|
|
Properties of a solid |
Has a definite size and shape |
|
|
Properties of a gas |
Has neither a definite shape or volume |
|
|
Element |
Made up of only one kind of atom |
|
|
How many different kinds of atoms are there? |
109 |
|
|
Building blocks of elements |
Atoms |
|
|
Compound |
Two or more kinds of atoms joined together in definite grouping or definite proportion by mass and are made up of two or more kinds of atoms |
|
|
Molecule |
The smallest natural occurring unit of a compound |
|
|
Distinct substances |
Can be elements which are made up of one kind of atom and all parts are the same throughout. Or compounds in which the composition is definite all parts react the same properties of the compound are distinct and different from the properties of the individual elements that are combined in its makeup |
|
|
Mixtures |
Composition is indefinite and generally heterogenious. Properties of the constituents are retained. Parts of the mixture react differently to change conditions |
|
|
Physical properties |
Properties that can be observed with our senses |
|
|
Chemical properties |
Properties that can be observed with no regard to whether or not a substance changes chemically, often as a result of reacting with other substances. |
|
|
Physical change |
Alters the physical properties of matter but the composition remains constant |
|
|
Chemical changes |
Changes in the composition and structure of a substance. They are always accompanied by energy changes |
|
|
Exothermic reaction |
When energy is given off usually in the form of heat or light or both. The energy released in the formation of a new structure exceeds the chemical energy in the original substance. |
|
|
Endothermic reaction |
The new structure needs to absorb more energy than is available from the reactants |
|
|
Law of conservation of matter |
Matter can neither be created nor destroyed but only change from one form to another |
|
|
Energy |
The capacity to do work |
|
|
Work |
When a force is applied over distance |
|
|
Joules |
A measurement of work and energy. |
|
|
Potential energy |
Stored energy due to overcoming forces in nature. Example a boulder on the side of a mountain. |
|
|
Kinetic energy |
Energy of motion |
|
|
Products |
The products are the substances that are formed during the chemical change. They are the things that are present at the end. By convention, the chemical symbols for the products are written on the right hand side of the chemical reaction equation. |
|
|
Reactants |
Reactants and Products The reactants are the substances that are present before the chemical change takes place. They are the things that are present at the starting point. By convention, the chemical symbols for the reactants are written on the left hand side of the chemical reaction equation. reaction equation. reaction equation. reaction equation. reaction equation. |
|
|
Law of conservation of energy |
Energy is neither gained or lost during physical or chemical changes |
|
|
Law of conservation of mass and energy |
Mass and energy are interchangeable under special sconditions. E=mc^2. |
|
|
Scientific method |
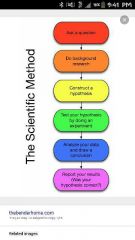
1. Observation and data collection, hypothesis, expirament, generate theories |
|
|
Base unit of mass |
Kilogram |
|
|
Base unit of length |
Meter |
|
|
Base unit of time |
Seconds |
|
|
Base unit of electric current |
Ampere |
|
|
Base unit of temperature |
Kelvin |
|
|
Measurement of amount of substance |
Mole |
|
|
Measurement of luminous intensity |
Candela |

