![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
As the ___ of a fixed amount of gas increases at constant ___ , its ___ decreases
|
volume,temperature, pressure
|
|
|
The ___ of a gas increases as the ___ of gas increases at constant ___ and ___.
|
volume, amount, temperature, pressure
|
|
|
Intermolecular forces
|
are attractive forces that exist between molecules
|
|
|
Surface tension
|
is the tendency of liquids to minimize surface area.
Surface tension increases with increasing intermolecular forces |
|
|
Liquids that evaporate easily are
|
volatile
|
|
|
Vaporization
|
is a physical change in which is a substance is converted from its liquid form to its gaseous form.
|
|
|
nitrogen narcosis.
|
too much N2,
Also known as rapture of the deep |
|
|
oxygen toxicity
|
too much O2, a condition called
PO2 > 1.4 atm. |
|
|
hypoxia.
|
Partial pressures of O2—lower than 0.1 atm
Unconsciousness or death |
|
|
heliox
|
What divers that go below 50 m use
mixture of He and O2 contains a lower percentage of O2 than air. |
|
|
vapor pressure
|
The partial pressure of the water vapor
depends only on the temperature Higher the Temp= Higher Pressure |
|
|
Zn metal reacts
with ___ to produce ___. |
HCl(aq), H2(g)
|
|
|
In reactions of gases, the amount of a gas is often given as a ___.
Instead of |
volume,moles
|
|
|
molar volume
|
work at STP.
1 mol = 22.4 L |
|
|
the volume of the
gas is or is not effected by the size of the molecules (under ideal conditions). |
is not
|
|
|
Dalton's Law
|
Ptot=Pa+Pb+Pc+ ...
|
|
|
Ideal Gas Law
|
PV = nRT
|
|
|
Boyle's law
|
V = 1/P
|
|
|
Charles's Law
|
V = T
|
|
|
Avogadro's Law
|
V = n
|
|
|
The value of R
(ideal gas constant) |
= 0.0821 x Lxatm / molxK
|
|
|
the melting points of covalent atomic solids relative to those of other types of solids are?
|
High
|
|
|
the melting points of nonbonding atomic solids relative to those of other types of solids are?
|
Low
|
|
|
the melting points of metallic atomic solids relative to those of other types of solids are?
|
Variable
|
|
|
the melting points of ionic solids relative to those of other types of solids are?
|
High
|
|
|
surface tension ___ with increasing intermolecular forces
|
increases
|
|
|
What is the formula for percent composition?
|
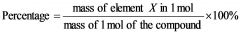
|
|
|
Combustion reactions are a subclass of ...
|
oxidation–reduction reactions.
-Involve the transfer of electrons between atoms |
|
|
Cumbustion Reactions are ...
|
Reactions in which O2 is consumed by combining with another substance
Always release heat and/or other forms of energy. Produce one or more oxygen-containing compounds. |

